5.3.3 Quiz – Exploiting Wired and Wireless Networks Answers
1. Which NetBIOS service is used for connection-oriented communication?
- NetBIOS-NS
- NetBIOS-DGM
- NetBIOS-SSN
- LLMNR
Explanation: NetBIOS provides three different services:
NetBIOS Name Service (NetBIOS-NS) for name registration and resolution
Datagram Service (NetBIOS-DGM) for connectionless communication
Session Service (NetBIOS-SSN) for connection-oriented communication
2. Match the port type and number with the respective NetBIOS protocol service.
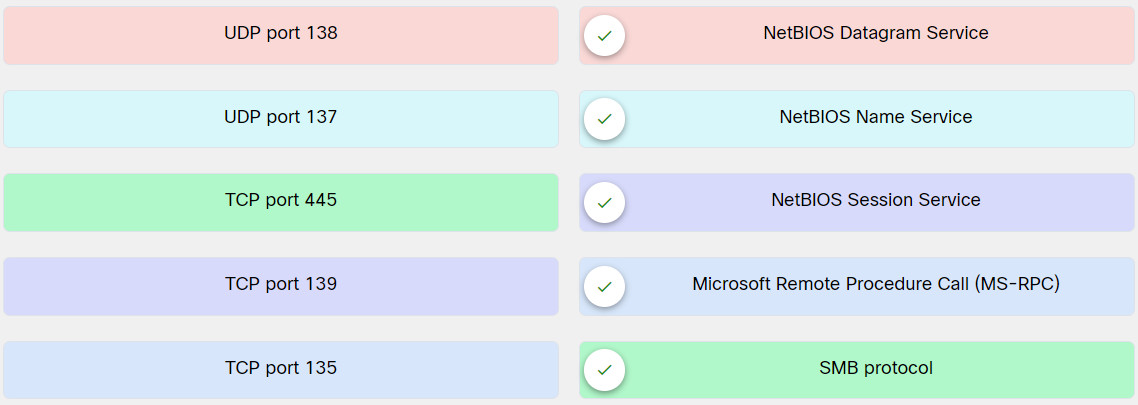
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
UDP port 138: NetBIOS Datagram Service
UDP port 137: NetBIOS Name Service
TCP port 445: SMB protocol
TCP port 139: NetBIOS Session Service
TCP port 135: Microsoft Remote Procedure Call (MS-RPC)
3. What two features are present on DNS servers using BIND 9.5.0 and higher that help mitigate DNS cache poisoning attacks? (Choose two.)
- randomization of ports
- provision of cryptographically secure DNS transaction identifiers
- exclusion of any trust relationships between DNS servers
- secure DNS data authentication
- prevention of any recursive DNS queries
Explanation: DNS servers using BIND 9.5.0 and higher provide features that help prevent DNS cache poisoning attacks. These features include the randomization of ports and provision of cryptographically secure DNS transaction identifiers. Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC), a technology developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), provides secure DNS data authentication and protects against DNS cache poisoning.
4. What UDP port number is used by SNMP protocol?
Explanation: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a protocol that many individuals and organizations use to manage network devices. SNMP uses UDP port 161.
5. Which is a characteristic of a DNS poisoning attack?
- The DNS server forward lookup zone is cleared.
- The DNS server reverse lookup zone is cleared.
- The DNS resolver cache is manipulated.
- The DNS server IP address is changed.
Explanation: DNS cache poisoning involves the manipulation of the DNS resolver cache through the injection of corrupted DNS data. This is done to force the DNS server to send the wrong IP address to the victim and redirect the victim to the attacker system.
6. Which Kali Linux tool or script can gather information on devices configured for SNMP?
- snmp-check
- nslookup
- snmp-brute.nse
- snmp-netstat.nse
Explanation: The Kali Linux snmp-check tool can perform an SNMP walk to gather information on devices configured for SNMP.
7. Match the SMTP command with the respective description.
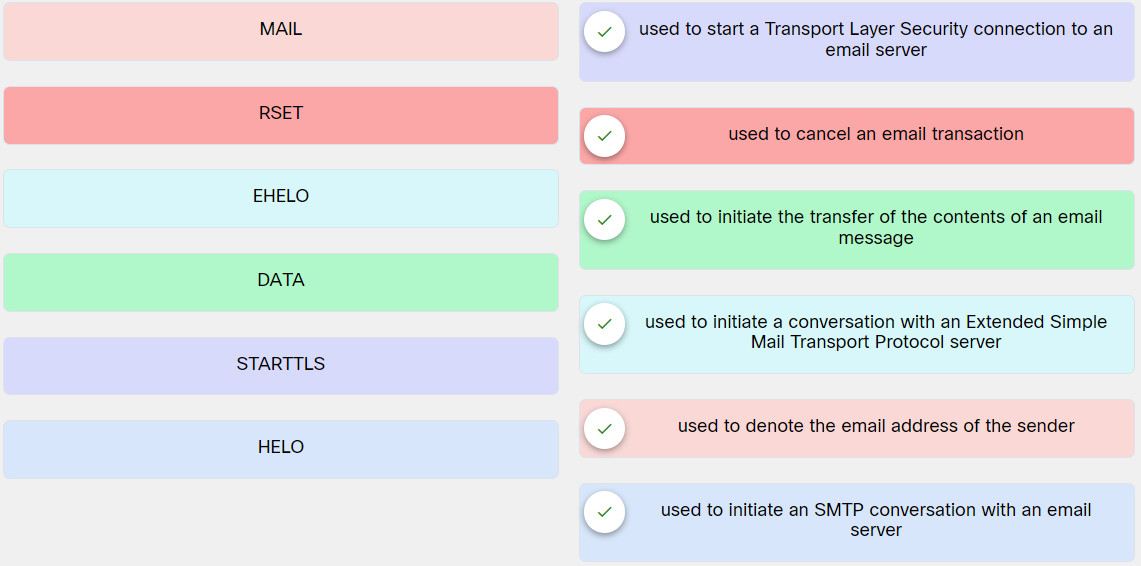
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
MAIL: Used to denote the email address of the sender
RSET: Used to cancel an email transaction
EHELO: Used to initiate a conversation with an Extended Simple Mail Transport Protocol server
DATA: Used to initiate the transfer of the contents of an email message
STARTTLS: Used to start a Transport Layer Security connection to an email server
HELO: Used to initiate an SMTP conversation with an email server
8. Which two best practices would help mitigate FTP server abuse and attacks? (Choose two.)
- limit anonymous logins to a select group of people
- edit the hosts file to limit the number of authorized DNS servers
- use encryption at rest
- consolidate all back-end databases on the FTP server
- require re-authentication of inactive sessions
Explanation: The following are several additional best practices for mitigating FTP server abuse and attacks:
– Use strong passwords and multifactor authentication. A best practice is to use good credential management and strong passwords. When possible, use two-factor authentication for any critical service or server.
– Implement file and folder security, making sure that users have access to only the files they are entitled to access.
– Use encryption at rest—encrypt all files stored in the FTP server.
– Lock down administration accounts. You should restrict administrator privileges to a limited number of users and require them to use multifactor authentication. In addition, do not use common administrator usernames such as root or admin.
– Keep the FTPS or SFTP server software up-to-date.
– Use the U.S. government FIPS 140-2 validated encryption ciphers for general guidance on what encryption algorithms to use.
– Keep any back-end databases on a different server than the FTP server.
– Require re-authentication of inactive sessions.
– Disable anonymous logins.
9. Which is a characteristic of the pass-the-hash attack?
- capture of a password hash (as opposed to the password characters) and using the same hashed value for authentication and lateral access to other networked systems
- reverse engineering of the captured hash password and using the unencrypted password for authentication and lateral access to other networked systems
- compromise of a SAM file and extraction of the password characters to use for authentication and lateral access to other networked systems
- capture of the Windows password before the Kerberos hashing function and use of the unencrypted password for authentication and lateral access to other networked systems
Explanation: The Windows operating system does not know the actual password because it stores only a hash of the password in the SAM database. Since Windows password hashes cannot be reversed, an attacker can just use a password hash collected from a compromised system and then use the same hash to log in to another client or server system.
10. What is a Kerberoasting attack?
- It is an attempt to steal the hash value of a user credential and use it to create a new user session on the same network.
- It attempts to manipulate Kerberos tickets based on available hashes by compromising a vulnerable system and obtaining the local user credentials and password hashes.
- It is a post-exploitation attempt that is used to extract service account credential hashes from Active Directory for offline cracking.
- It attempts to manipulate data being transferred by performing data corruption or modification.
Explanation: Kerberoasting is a post-exploitation activity that an attacker uses to extract service account credential hashes from Active Directory for offline cracking.
11. Match the attack type with the respective description.

Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Reflected DOS |
This attack uses spoofed packets that appear to be from the victim. Then the sources become unwitting participants in the attack by sending the response traffic back to the intended victim. |
| DNS Amplification |
This an attack in which the attacker exploits vulnerabilities in target servers to initially turn small queries into much larger payloads, which are used to bring down the servers of the victim. |
| Direct DOS |
This occurs when the source of the attack generates the packets, regardless of protocol, application, and so on, that are sent directly to the victim of the attack. |
| DDOS |
This attack uses botnets that can be manipulated from a command and control (CnC, or C2) system. |
12. Match the attack type with the respective description.

Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Route Manipulation attacks |
typically a BGP hijacking attack by configuring or compromising an edge router to announce prefixes that have not been assigned to the organization |
| Downgrade attacks |
the attacker forces a system to favor a weak encryption protocol or hashing algorithm that may be susceptible to other vulnerabilities |
| DHCP Starvation attack |
an attacker floods a server with bogus DISCOVER packets until the server exhausts the supply of IP addresses |
| VLAN Hopping attack |
an attacker bypass any layer 2 restrictions built to divide hosts |
| MAC address spoofing attack |
an attacker spoofs the physical address of the NIC device to match the address of another on a network in order to gain unauthorized access or launch a Man-in-the-Middle attack |
13. Which tool can be used to perform a Disassociation attack?
- Airmon-ng
- nmap
- POODLE
- EMPIRE
Explanation: Airmon-ng (part of the Aircrack-ng suite) can perform wireless reconnaissance and disassociation attacks. The Aircrack-ng suite of tools can be downloaded from https://www.aircrack-ng.org.
14. Which is a characteristic of a Bluesnarfing attack?
- An attack that is launched using common social engineering attacks, such as phishing attacks, can be performed by impersonating a wireless AP or a captive portal to convince a user to enter the user credentials.
- An attack that can be performed using Bluetooth with vulnerable devices in range. It is commonly performed as spam over Bluetooth connections using the OBEX protocol.
- An attack that can be performed using Bluetooth with vulnerable devices in range. This attack actually steals information from the device of the victim.
- An attack involves modifying BLE messages between systems that would lead them to believe that they are communicating with legitimate systems.
Explanation: An attack that can be performed using Bluetooth with vulnerable devices in range.This attack actually steals information from the victim’s device. It can also be used to obtain a device’s International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number.
15. Which Wi-Fi protocol is most vulnerable to a brute-force attack during a Wi-Fi network deployment?
- WPA2-EAP
- WPS
- WPA3
- WPA2-TKIP
Explanation: Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a protocol that simplifies the deployment of wireless. Most implementations do not care if millions of PIN combinations are incorrectly attempted in a row, which means these devices are most susceptible to brute-force attacks.
16. What does the MFP feature in the 802.11w standard do to protect against wireless attacks?
- It uses a PNL to maintain a list of trusted or preferred wireless networks.
- It uses a captive portal for all wireless associations.
- It inserts the 802.1q tag to protect the wireless frame.
- It helps defend against deauthentication attacks.
Explanation: The 802.11w standard defines the Management Frame Protection (MFP) feature. MFP protects wireless devices against spoofed management frames from other devices that might otherwise deauthenticate a valid user session.
17. What is a DNS resolver cache on a Windows system?
- It is a database of all WINS records.
- It is a static database entry of all forward and reverse lookup zones.
- It is a temporary database that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
- It is a collective database of all Domain Name Service records of static and cached entries.
Explanation: A DNS resolver cache is a temporary database maintained by Windows that contains records of all the recent visits and attempted visits to websites and other internet domains.
18. Match the TCP port number with the respective email protocol that uses it.
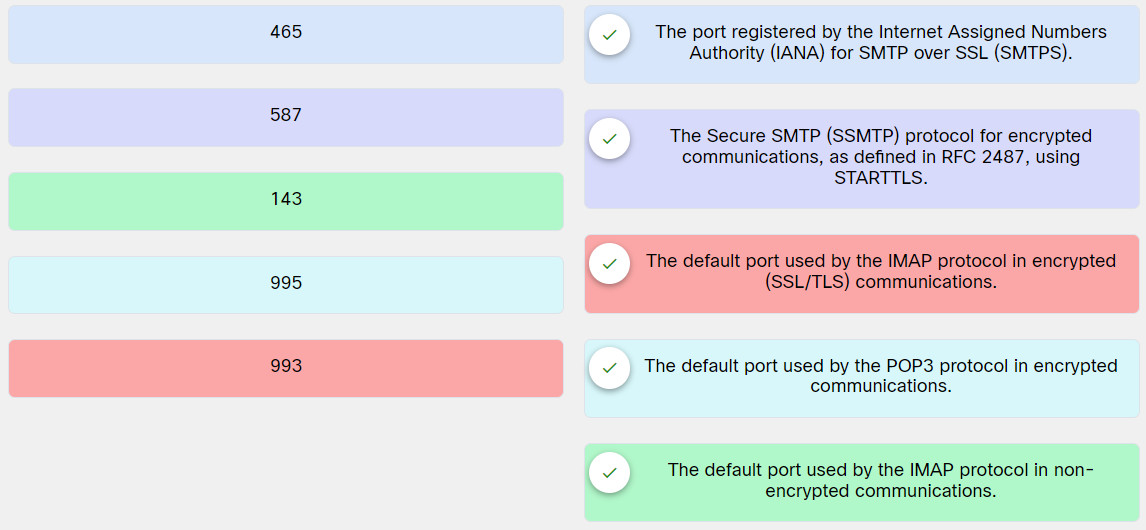
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
465: The port registered by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for SMTP over SSL (SMTPS).
587: The Secure SMTP (SSMTP) protocol for encrypted communications, as defined in RFC 2487, using STARTTLS.
143: The default port used by the IMAP protocol in non-encrypted communications.
995: The default port used by the POP3 protocol in encrypted communications.
993: The default port used by the IMAP protocol in encrypted (SSL/TLS) communications.
19. Which is the default TCP port used in SMTP for non-encrypted communications?
Explanation: The following TCP ports are used in most common email protocols:
TCP port 25: The default port used in SMTP for non-encrypted communications.
TCP port 465: The port registered by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for SMTP over SSL (SMTPS).
TCP port 587: The Secure SMTP (SSMTP) protocol for encrypted communications, as defined in RFC 2487, using STARTTLS.
TCP port 110: The default port used by the POP3 protocol in non-encrypted communications.
TCP port 995: The default port used by the POP3 protocol in encrypted communications.
TCP port 143: The default port used by the IMAP protocol in non-encrypted communications.
TCP port 993: The default port used by the IMAP protocol in encrypted (SSL/TLS) communications.
20. What is a characteristic of a Kerberos silver ticket attack?
- It uses forged service tickets for a given service on a particular server.
- It mimics the authentication hash on a particular server.
- It acts as the LDAP directory for authentication on a target server.
- It coverts the hashed value to the unencrypted value for an authentication attack on a particular server.
Explanation: The Kerberos silver ticket attack uses forged service tickets for a given service on a particular server.
21. Which attack is a post-exploitation activity that an attacker uses to extract service account credential hashes from Active Directory for offline cracking?
- MITM
- On-Path attack
- MAC spoofing
- Kerberoasting
Explanation: Kerberoasting is a post-exploitation activity used by an attacker to extract service account credential hashes from Active Directory for offline cracking. It is a pervasive attack that exploits a combination of weak encryption implementations and improper password practices.
22. Which four items are needed by an attacker to create a silver ticket for a Kerberos silver ticket attack? (Choose four.)
- hash value
- system account
- SID
- FQDN
- target service
- DNS forward lookup zone
- DNS resolver cache
- DNS reverse lookup zone
Explanation: To create a silver ticket, you need the system account (ending in $), the security identifier (SID) for the domain, the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), and the given service (for example, CIFS, HOST).
23. Which kind of attack is an IP spoofing attack?
- On-path
- DDoS
- Pass-the-Hash
- Evil-Twin
Explanation: The On-path attack intercepts communications between two systems. The attacker splits the original TCP connection into 2 new connections, one between the client and the attacker and the other between the attacker and the server. This often uses IP spoofing to trick a victim into connecting to the attack.
24. What is a common mitigation practice for ARP cache poisoning attacks on switches to prevent spoofing of Layer 2 addresses?
- DHCP snooping
- DNSSEC
- DAI
- BIND 9.5
Explanation: A common mitigation for ARP cache poisoning attacks is to use Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Inspection (DAI) on switches to prevent spoofing of the Layer 2 addresses.
25. An attacker is launching a reflected DDoS attack in which the response traffic is made up of packets that are much larger than those that the attacker initially sent. Which type of attack is this?
- downgrade
- amplification
- on-path
- DNS cache poisoning
Explanation: An amplification attack is a form of reflected DoS attack in which the response traffic (sent by the unwitting participant) is made up of packets much larger than those initially sent by the attacker (spoofing the victim). The result is that the victim machine gets flooded by large packets for which it never actually issued queries, causing a denial of services.





