9.5.3 Quiz – Reporting and Communication Answers
1. Which industry-standard method has created a catalog of known vulnerabilities that provides a score indicating the severity of a vulnerability?
- CVSS
- CVE
- OWASP WSTG
- NIST SP 800-115
Explanation: Vulnerability scanners rely heavily on catalogs of known vulnerabilities. The two catalogs of known vulnerabilities that a cybersecurity analyst should be familiar with are the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which provides a score from 0 to 10 that indicates the severity of a vulnerability, and Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), which is a list of publicly known vulnerabilities, each assigned an ID number, description, and reference. OWASP WSTG is a comprehensive guide focused on web application testing. NIST SP 800-115 is a document to provide organizations with guidelines on planning and conducting information security testing.
2. Which vulnerability catalog creates a list of publicly known vulnerabilities, each assigned an ID number, description, and reference?
- CVE
- CVSS
- OWASP WSTG
- NIST SP 800-115
Explanation: Vulnerability scanners rely heavily on catalogs of known vulnerabilities. The two catalogs of known vulnerabilities that a cybersecurity analyst should be familiar with are Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), which is a list of publicly known vulnerabilities, each assigned an ID number, description, and reference, and Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which provides a score from 0 to 10 that indicates the severity of a vulnerability. OWASP WSTG is a comprehensive guide focused on web application testing. NIST SP 800-115 is a document to provide organizations with guidelines on planning and conducting information security testing.
3. Match the CVSS metric group with the respective information.

Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Environmental metric group |
includes modified base metrics, confidentiality, integrity, and availability requirements |
| Base metric group |
includes exploitability metrics and impact metrics |
| Temporal metric group |
includes exploit code maturity, remediation level, and report confidence |
4. Which three items are included in the base metric group used by CVSS? (Choose three.)
- attack complexity
- integrity impact
- modified base metrics
- user interaction
- availability requirements
- remediation level
Explanation: CVSS uses three metric groups in determining scores. The Base metric group includes exploitability metrics (for example, attack vector, attack complexity, privileges required, user interaction) and impact metrics (confidentiality impact, integrity impact, availability impact).
5. Which item is included in the environmental metric group used by CVSS?
- privileges required
- confidentiality requirements
- report confidence
- availability impact
Explanation: CVSS uses three metric groups in determining scores. The Environmental metric group includes modified base metrics, confidentiality, integrity, and availability requirements.
6. Which item is included in the temporal metric group used by CVSS?
- exploit code maturity
- integrity impact
- modified base metrics
- attack vector
Explanation: CVSS uses three metric groups in determining scores. The Temporal metric group includes exploit code maturity, remediation level, and report confidence.
7. Which tool can ingest the results from many penetration testing tools a cybersecurity analyst uses and help this professional produce reports in formats such as CSV, HTML, and PDF?
- Dradis
- Mimikatz
- Nessus
- PowerSploit
Explanation: Dradis is a handy little tool that can ingest the results from many of the penetration testing tools a cybersecurity analyst uses and help this professional produce reports in formats such as CSV, HTML, and PDF.
8. Match the description to the respective control category.
- Key rotation: Technical control
- Input sanitization: Technical control
- Secure software development life cycle: Administrative control
- Role-based access control: Administrative control
- Time-of-day restrictions: Operational control
- Job rotation: Operational control
- Video surveillance: Physical control
- Biometric controls: Physical control
9. Which two items are examples of technical controls that can be recommended as mitigations and remediation of the vulnerabilities found during a pen test? (Choose two.)
- multifactor authentication
- certificate management
- RBAC
- mandatory vacations
- access control vestibule
Explanation: During a penetration testing engagement, the cybersecurity analyst should analyze the findings and recommend the appropriate remediation within the report, including technical, administrative, operational, and physical controls. Technical controls make use of technology to reduce vulnerabilities. Technical controls include system hardening, user input sanitization and query parameterization, multifactor authentication, process-level remediation, patch management, key rotation, certificate management, secrets management solution, and network segmentation.
10. A recent pen-test results in a cybersecurity analyst report, including information on process-level remediation, patch management, and secrets management solutions. Which control category is represented by this example?
- technical
- administrative
- operational
- physical
Explanation: During a penetration testing engagement, the cybersecurity analyst should analyze the findings and recommend the appropriate remediation within the report, including technical, administrative, operational, and physical controls. Technical controls make use of technology to reduce vulnerabilities. Technical controls include system hardening, user input sanitization and query parameterization, multifactor authentication, process-level remediation, patch management, key rotation, certificate management, secrets management solution, and network segmentation.
11. Which document provides several cheat sheets and detailed guidance on preventing vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and command injection?
Explanation: The use of input validation (sanitizing user input) best practices is recommended to mitigate and prevent vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting, cross-site request forgery, SQL injection, command injection, XML external entities, and other vulnerabilities. OWASP provides several cheat sheets and detailed guidance on preventing these vulnerabilities.
12. A cybersecurity analyst report should contain minimum password requirements and policies and procedures. These are examples that are included in which control category?
- technical
- administrative
- operational
- physical
Explanation: During a penetration testing engagement, the cybersecurity analyst should analyze the findings and recommend the appropriate remediation within the report, including technical, administrative, operational, and physical controls. Administrative controls are policies, rules, or training designed and implemented to reduce risk and improve safety. Examples of administrative controls are role-based access control (RBAC), secure software development life cycle, minimum password requirements, and policies and procedures.
13. Which control category includes information on mandatory vacations and user training in the cybersecurity analyst report?
- technical
- administrative
- operational
- physical
Explanation: During a penetration testing engagement, the cybersecurity analyst should analyze the findings and recommend the appropriate remediation within the report, including technical, administrative, operational, and physical controls. Operational controls focus on day-to-day operations and strategies. Operational controls include job rotation, time-of-day restrictions, mandatory vacations, and user training.
14. When creating a cybersecurity analyst report, which control category includes information concerning the access control vestibule?
- technical
- administrative
- operational
- physical
Explanation: During a penetration testing engagement, the cybersecurity analyst should analyze the findings and recommend the appropriate remediation within the report, including technical, administrative, operational, and physical controls. Physical controls use security measures to prevent or deter unauthorized access to sensitive locations or material. Physical controls include access control vestibule, biometric controls, and video surveillance.
15. Match the term to the respective description.
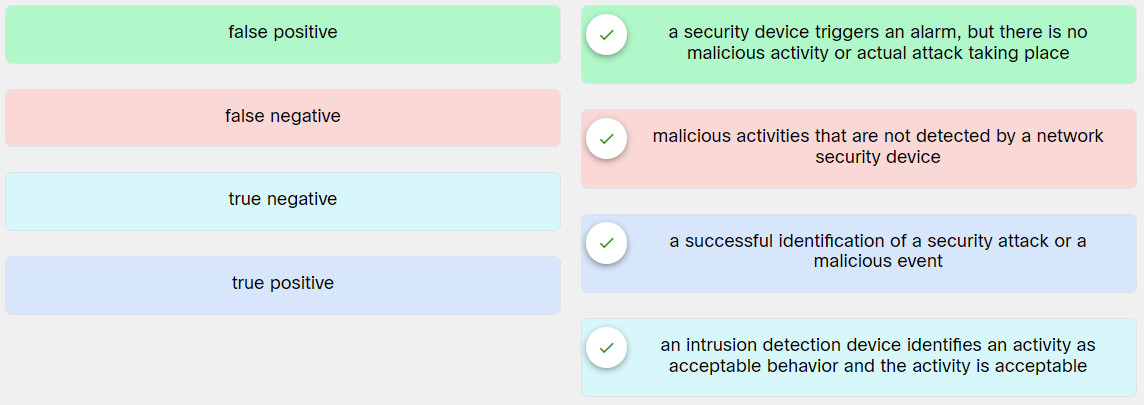
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| false negative |
malicious activities that are not detected by a network security device |
| true negative |
an intrusion detection device identifies an activity as acceptable behavior and the activity is acceptable |
| false positive |
a security device triggers an alarm, but there is no malicious activity or actual attack taking place |
| true positive |
a successful identification of a security attack or a malicious event |
16. Which kind of event is also called a “benign trigger”?
- false positive
- false negative
- true positive
- true negative
Explanation: False positives are “false alarms” or “benign triggers.” They are problematic because triggering unjustified alerts diminishes the value and urgency of real alerts.
17. What kind of events diminishes the value and urgency of real alerts?
- false positives
- false negatives
- true negatives
- true positives
Explanation: False positives are situations in which a security device triggers an alarm, but no malicious activity or actual attack occurs. They are problematic because triggering unjustified alerts diminishes the value and urgency of real alerts.
18. Which kinds of events are malicious activities not detected by a network security device?
- false positives
- false negatives
- true negatives
- true positives
Explanation: False negatives are malicious activities not detected by a network security device. False positives are situations in which a security device triggers an alarm, but no malicious activity or actual attack occurs. True positives are successfully identifying a security attack or a malicious event. True negatives occur when an intrusion detection device identifies an activity as acceptable behavior, and the activity is acceptable.
19. Which kind of event occurs when an intrusion detection device identifies an activity as acceptable behavior and the activity is acceptable?
- false positives
- false negatives
- true negatives
- true positives
Explanation: True negatives occur when an intrusion detection device identifies an activity as acceptable behavior, and the activity is acceptable. False negatives are malicious activities not detected by a network security device. False positives are situations in which a security device triggers an alarm, but no malicious activity or actual attack occurs. True positives are successfully identifying a security attack or a malicious event.
20. Which kind of event is a successful identification of a security attack?
- false negative
- false positive
- true positive
- true negative
Explanation: True positives are successful identification of security attacks or malicious events. True negatives occurs when an intrusion detection device identifies an activity as acceptable behavior, and the activity is actually acceptable. False negatives are malicious activities that are not detected by a network security device. False positives are situations in which a security device triggers an alarm but there is no malicious activity or actual attack taking place.
21. Which example of technical control is recommended to mitigate and prevent vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting, cross-site request forgery, SQL injection, and command injection?
- user input sanitization
- process-level remediation
- secrets management solution
- certificate management
Explanation: The use of input validation (user input sanitization) best practices is recommended to mitigate and prevent vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting, cross-site request forgery, SQL injection, command injection, XML external entities, and other vulnerabilities.
22. Which example of administrative controls enables administrators to control what users can do at both broad and granular levels?
- RBAC
- secure software development life cycle
- policies and procedures
- minimum password requirements
Explanation: Role-based access control (RBAC) is a control that bases access permissions on a specific role or function. Administrators grant access rights and permissions to roles. Each user is then associated with a role. Users can belong to multiple groups. RBAC enables to control what users can do at both broad and granular levels.
23. A document entitled “Building an Information Technology Security Awareness and Training Program” succinctly defines why security education and training are so important for users. The document defines ways to improve the security operations of an organization. Which document is being described?
- NIST SP 800-50
- NIST SP 800-115
- OWASP WSTG
- CVSS
Explanation: User training is an example of operational controls often allowing organizations to improve security operations. A user should have the training and provide written acknowledgment of rights and responsibilities before being granted access to information and information systems. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) published Special Publication 800-50, “Building an Information Technology Security Awareness and Training Program,” which succinctly defines why security education and training are important.
24. How is the score that CVSS provides interpreted?
- scores are rated from 0 to 100, with 100 being the most severe
- scores are rated from 0 to 100, with 0 being the most severe
- scores are rated from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe
- scores are rated from 0 to 10, with 0 being the most severe
Explanation: Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which was developed and is maintained by FIRST.org, provides a method for calculating a score for the seriousness of a threat. The scores are rated from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe.
25. What control category does system hardening belong to?
- technical
- administrative
- operational
- physical
Explanation: Technical controls make use of technology to reduce vulnerabilities. System hardening is an example of technical control that can be recommended as mitigation and remediation of the vulnerabilities found during a pen test. System hardening involves applying security best practices, patches, and other configurations to remediate or mitigate the vulnerabilities found in systems and applications.


