7.4.3 Packet Tracer – Routing Table Corruption Answers
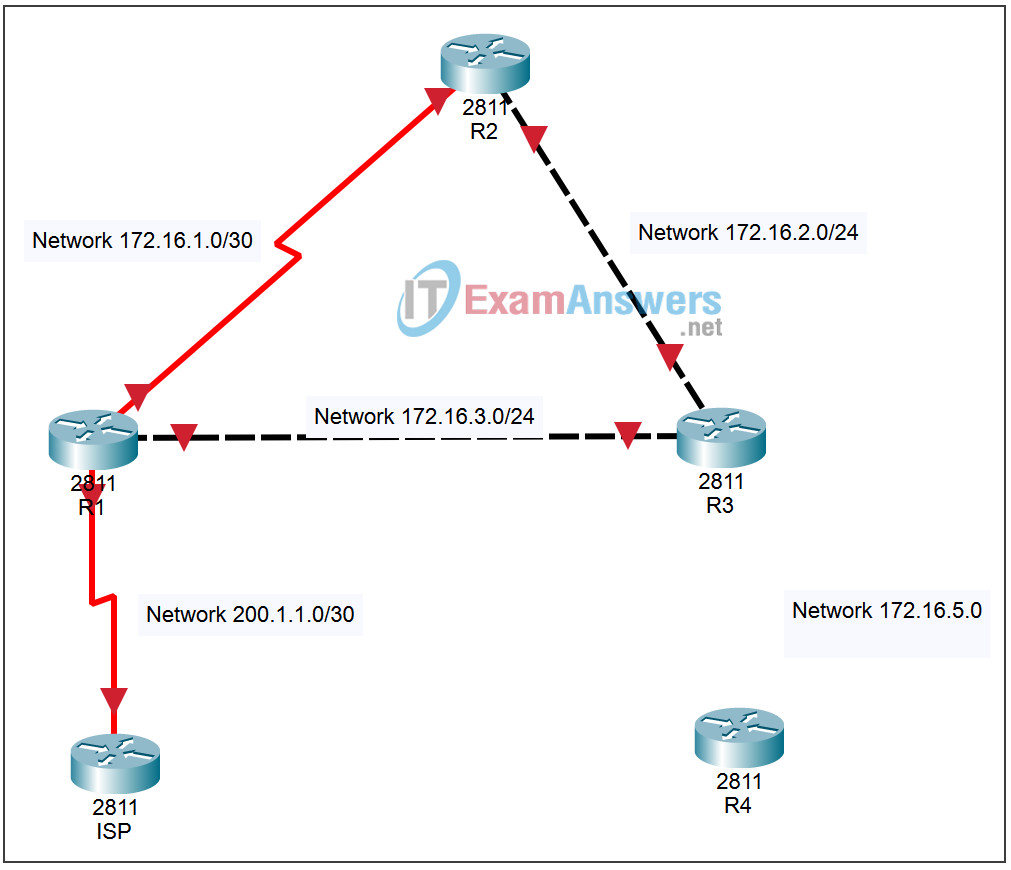
Topology
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISP | Lo0 | 199.199.199.1 | 255.255.255.255 |
| S0/0/0 | 200.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | |
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/2/0 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| S0/2/1 | 200.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | |
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/2/0 | 172.16.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| R3 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.3.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| Fa0/1 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa1/0 | 172.16.5.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| R4 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.5.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
Learning Objectives
- Create a default route.
- Propogate a default route to the routing domain.
Introduction:
This activity focuses on how Internet Service Providers use static routes to communicate with their customers, and how Customers use the default route to communicate with their service provider. The lab shows how the border router builds a default route and propagates it to all other routers in the routing domain. After the network has been established a new router R4 is added to the network, but this router has an erroneous default route not pointing to the ISP. You will view the routing table entries to determine the result this has on your network, and examine ping responses. Initially, all interfaces have been configured with correct addressing. RIP will be configured as the routing protocol.
