7.6.1 Packet Tracer – Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Answers
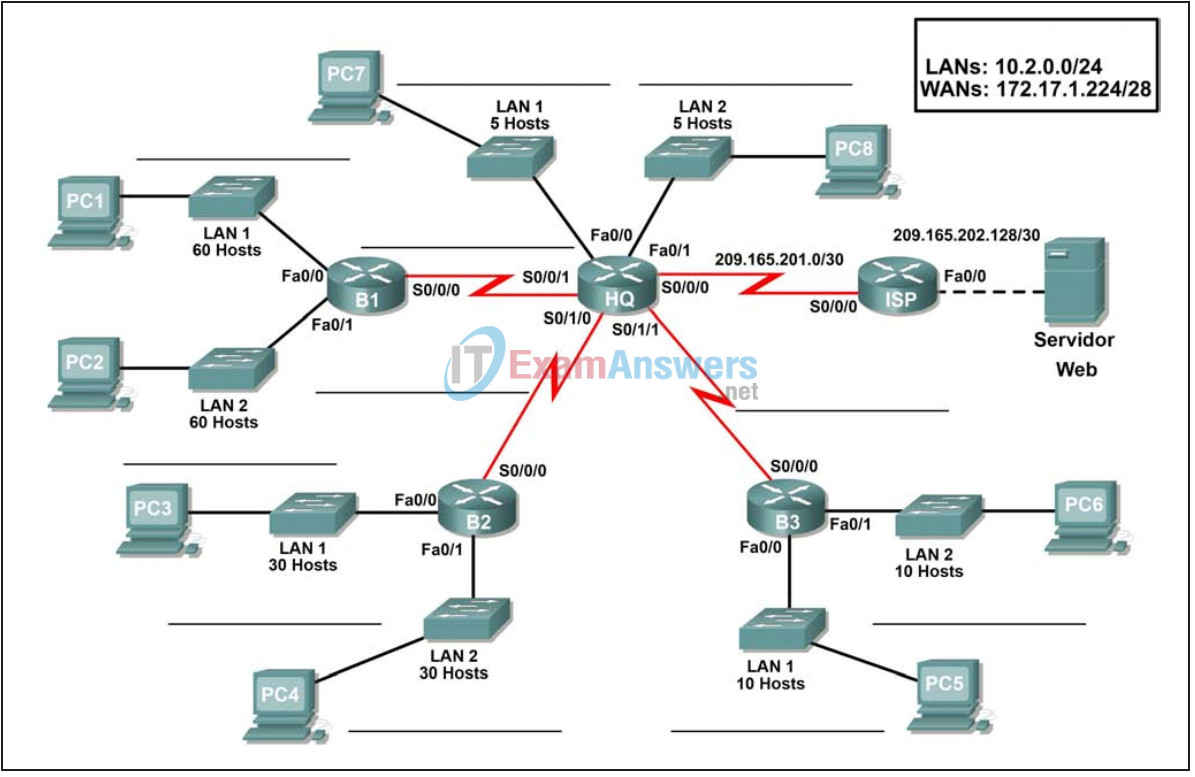
Topology
Addressing table
| Device | Interface | IP address | Subnet mask | Default gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | Fa0/0 | 10.2.0.225 | 255.255.255.248 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 10.2.0.233 | 255.255.255.248 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 209.165.201.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 172.17.1.225 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/1/0 | 172.17.1.229 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/1/1 | 172.17.1.233 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| B1 | Fa0/0 | 10.2.0.1 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 10.2.0.65 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 172.17.1.226 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| B2 | Fa0/0 | 10.2.0.129 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 10.2.0.161 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 172.17.1.230 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| B3 | Fa0/0 | 10.2.0.193 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 10.2.0.209 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 172.17.1.234 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| ISP | Fa0/0 | 209.165.202.129 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 209.165.201.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Web server | NIC | 209.165.202.130 | 255.255.255.252 | 209.165.202.129 |
| PC1 | NIC | 10.2.0.62 | 255.255.255.192 | 10.2.0.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 10.2.0.126 | 255.255.255.192 | 10.2.0.64 |
| PC3 | NIC | 10.2.0.158 | 255.255.255.224 | 10.2.0.129 |
| PC4 | NIC | 10.2.0.190 | 255.255.255.224 | 10.2.0.161 |
| PC5 | NIC | 10.2.0.206 | 255.255.255.240 | 10.2.0.193 |
| PC6 | NIC | 10.2.0.222 | 255.255.255.240 | 10.2.0.209 |
| PC7 | NIC | 10.2.0.230 | 255.255.255.248 | 10.2.0.225 |
| PC8 | NIC | 10.2.0.238 | 255.255.255.248 | 10.2.0.233 |
Introduction:
This Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity is very similar to the activities you have created in prior chapters. To allow you to better practice your skills, the scenario is slightly different. In this activity, you build a network from the ground up. Starting with a given address space and network requirements, you must implement a network design that satisfies the specifications. Next, you implement an effective RIPv2 routing configuration with static and default routing for Internet access.
Learning Objectives:
- Design and document an addressing scheme based on requirements.
- Select appropriate equipment and cable the devices.
- Apply a basic configuration to the devices.
- Test connectivity between directly connected devices.
- Configure RIPv2 routing.
- Configure static and default routing for Internet access.
- Verify full connectivity between all devices in the topology.
Task 1: Design and document an addressing scheme.
Step 1 – Design an addressing scheme.
Based on the network requirements shown in the topology, design an appropriate addressing scheme.
Step 2 – Document the addressing scheme.
- Use the blank spaces on the topology to record the network addresses in dotted-decimal/slash format.
- Use the table provided in the printed instructions to document the IP addresses, subnet masks and default gateway addresses.
Task 2: Select equipment and cable devices.
Step 1 – Select the necessary equipment.
Select the remaining devices you will need and add them to the working space inside Packet Tracer.
Step 2 – Finish cabling the devices.
Cable the networks according to the topology taking care that interfaces match your documentation in Task 1.
Task 3: Apply a basic configuration.
Step 1 – Configure the routers.
Using your documentation, configure the routers with basic configurations.
Step 2 – Configure the PCs.
Using your documentation, configure the PCs with an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
Task 4: Test connectivity.
Before continuing, make sure that each device can ping its directly connected neighbor.
Task 5: Configure and verify RIPv2 routing.
Step 1 – Configure RIPv2.
Configure all devices with RIPv2 routing. In your configuration, make sure you include the following:
- Disable automatic summarization.
- Stop routing updates on interfaces that are not connected to RIP neighbors.
- Set a default route from HQ to ISP using the next-hop IP address.
- Configure static routes on ISP using the outbound interface.
- Redistribute default route from HQ.
Step 2 – Verify RIPv2.
Use verification commands to check your configuration. All routers should be converged on all the 10.2.0.0/24 and 172.17.1.224/28 subnets.
Task 6: Configure static and default routing.
Step 1 – Test connectivity and examine the configuration.
Test connectivity and examine the configuration.
