Chapter 2 – Sections & Objectives
- 2.1 Static Routing Implementation
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing.
- Explain the purpose of different types of static routes.
- 2.2 Configure Static and Default Routes
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 static routes by specifying a next-hop address.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 default routes.
- Configure a floating static route to provide a backup connection.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 static host routes that direct traffic to a specific host
- 2.3 Troubleshoot Static and Default Route Issues
- Explain how a router processes packets when a static route is configured.
- Troubleshoot common static and default route configuration issues.
2.1 Static Routing Implementation
2.1.1 Static Routing
Reach Remote Networks
A router can learn about remote networks in one of two ways:
- Manually – Remote networks are manually entered into the route table using static routes.
- Dynamically – Remote routes are automatically learned using a dynamic routing protocol.
Why Use Static Routing?
Static routing provides some advantages over dynamic routing, including:
- Static routes are not advertised over the network, resulting in better security.
- Static routes use less bandwidth than dynamic routing protocols, no CPU cycles are used to calculate and communicate routes.
- The path a static route uses to send data is known.
When to Use Static Routes
Static routing has three primary uses:
- Providing ease of routing table maintenance in smaller networks.
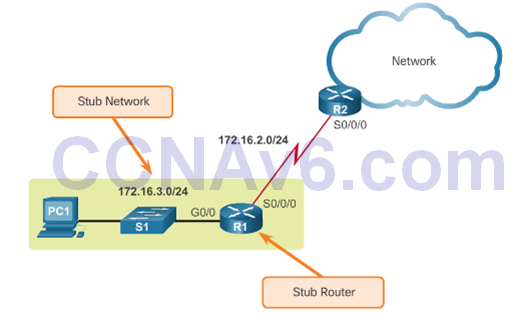
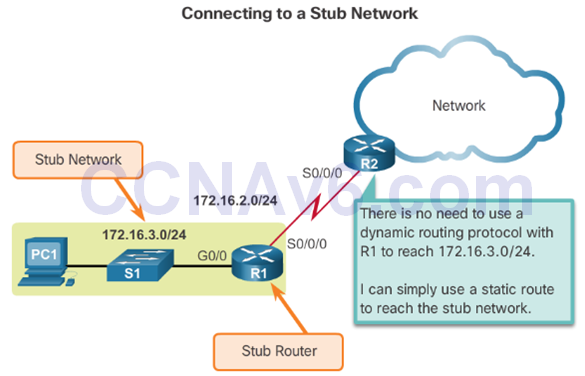
- Routing to and from stub networks. A stub network is a network accessed by a single route, and the router has no other neighbors.
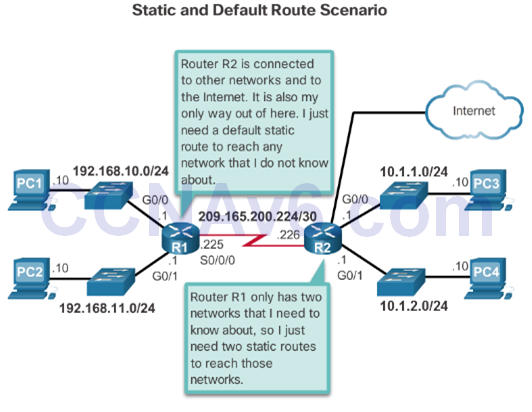
- Using a single default route to represent a path to any network that does not have a more specific match with another route in the routing table.
2.1.2 Types of Static Routes
Static Route Applications
- Static Routes are often used to:
- Connect to a specific network.
- Provide a Gateway of Last Resort for a stub network.
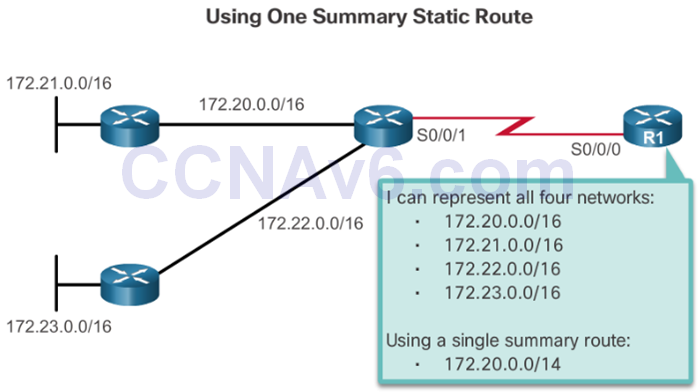
- Reduce the number of routes advertised by summarizing several contiguous networks as one static route.
- Create a backup route in case a primary route link fails.
Standard Static Route
Default Static Route
- A default static route is a route that matches all packets.
- A default route identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets that it does not have a learned or static route.
- A default static route is simply a static route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination IPv4 address.
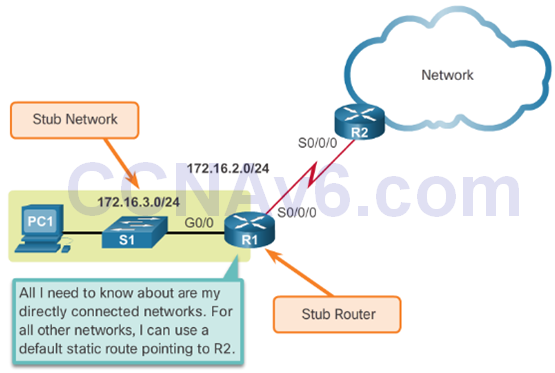
Summary Static Route
Floating Static Route
2.2 Configure Static and Default Routes
2.2.1 Configure IPv4 Static Routes
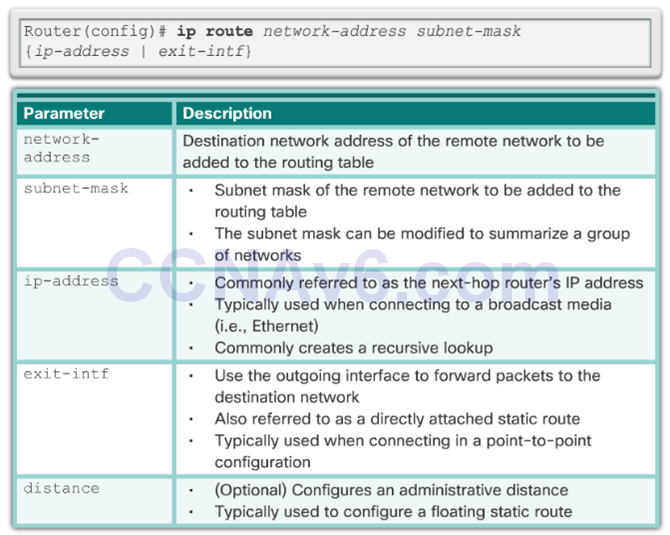
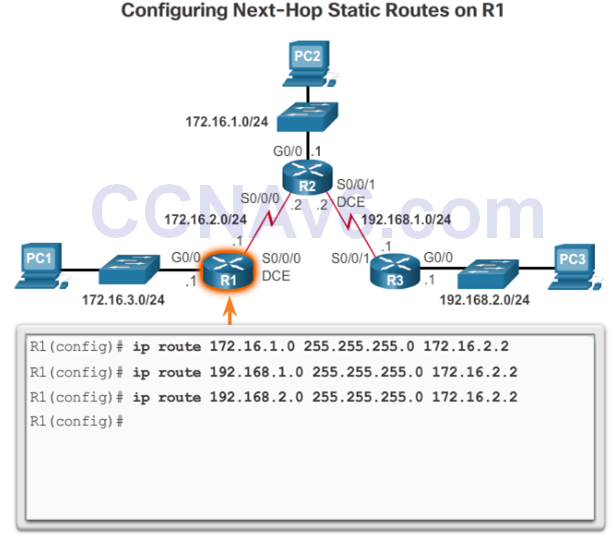
Ip route Command
Next-Hop Options
- The next hop can be identified by an IP address, exit interface, or both. How the destination is specified creates one of the three following route types:
- Next-hop route – Only the next-hop IP address is specified.
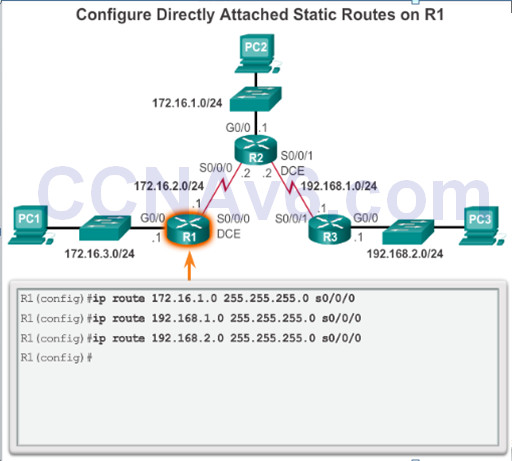
- Directly connected static route – Only the router exit interface is specified.
- Fully specified static route – The next-hop IP address and exit interface are specified.
Configure a Next-Hop Static Route
Configure Directly Connected Static Route
Configure a Fully Specified Static Route
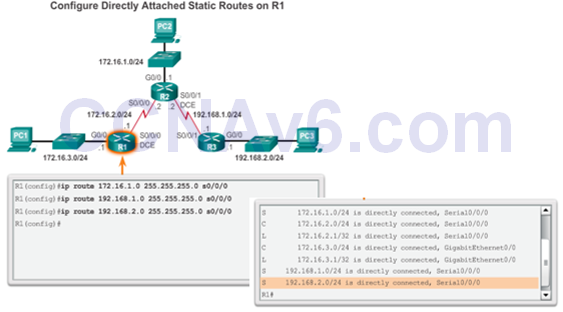
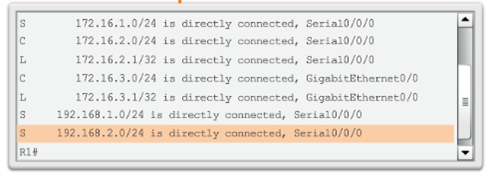
Verify a Static Route
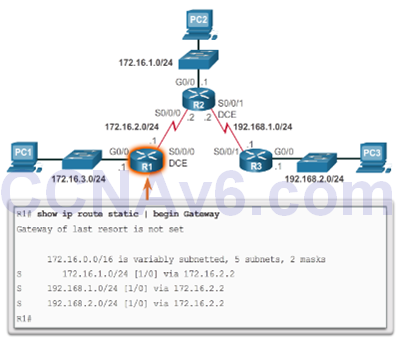
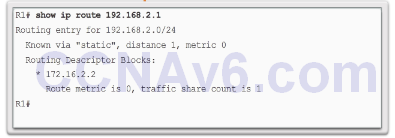
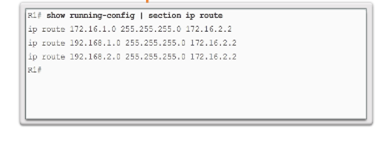
Default Static Route
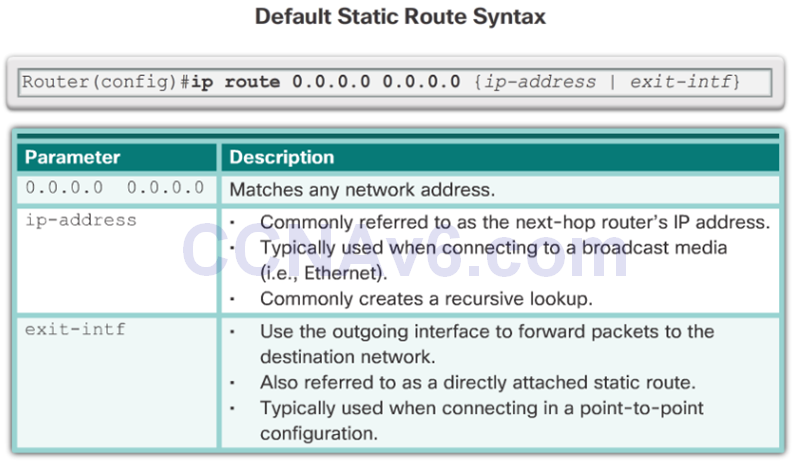
Configure a Default Static Route
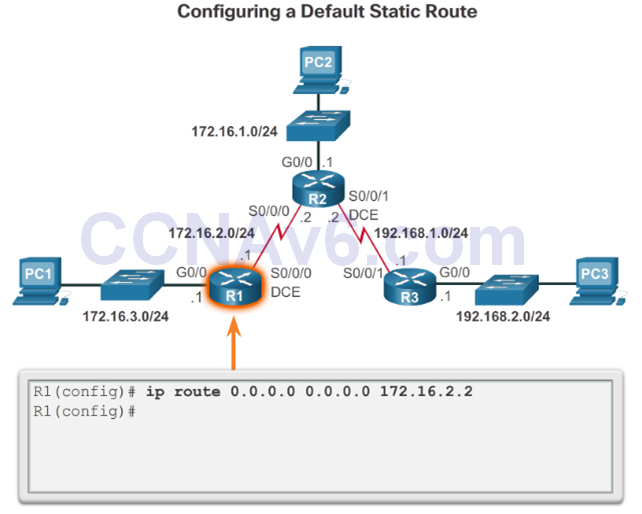
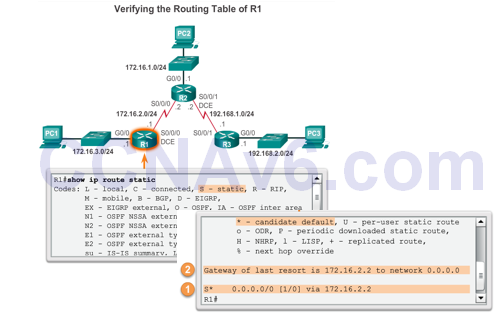
Verify a Default Static Route
2.2.2 Configure IPv6 Static Routes
The ipv6 route Command
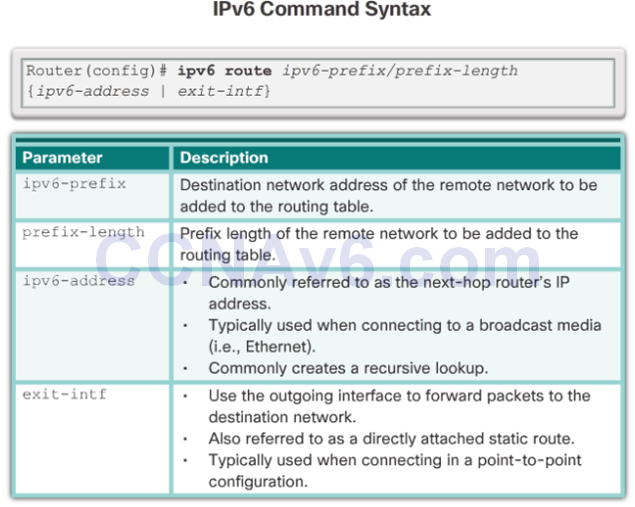
Next-Hop Options
- Next-hop static IPv6 route – Only the next-hop IPv6 address is specified
- Directly connected static IPv6 route – Only the router exit interface is specified
- Fully specified static IPv6 route – The next-hop IPv6 address and exit interface are specified
Configure a Next-Hop Static IPv6 Route
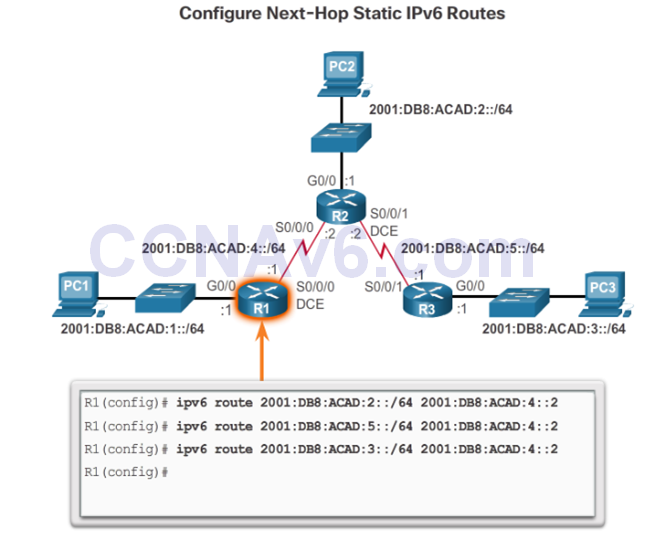
Directly Connected Static IPv6 Route
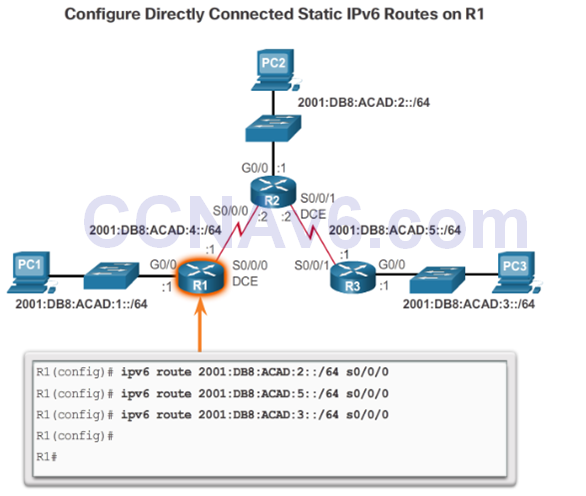
Fully Specified Static IPv6 Route
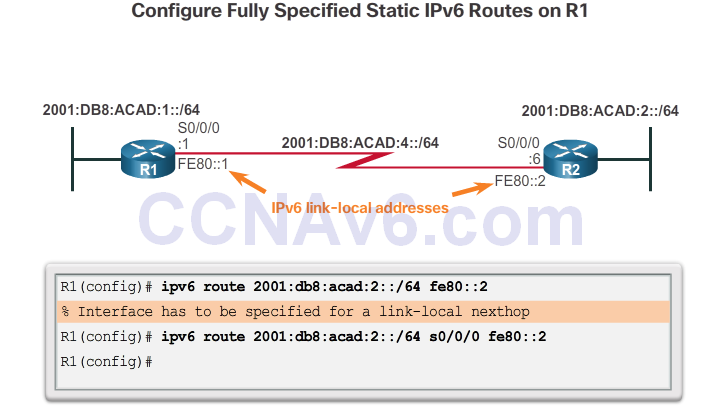
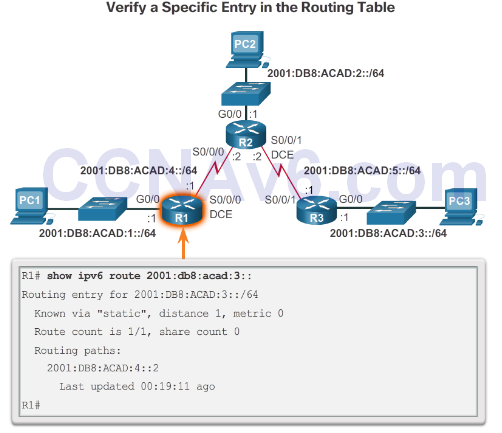
Verify IPv6 Static Routes
- In addition to ping and traceroute, commands to verify static routes include:
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 route static
- show ipv6 route network
2.2.3 Configure IPv6 Default Routes
Default Static IPv6 Route
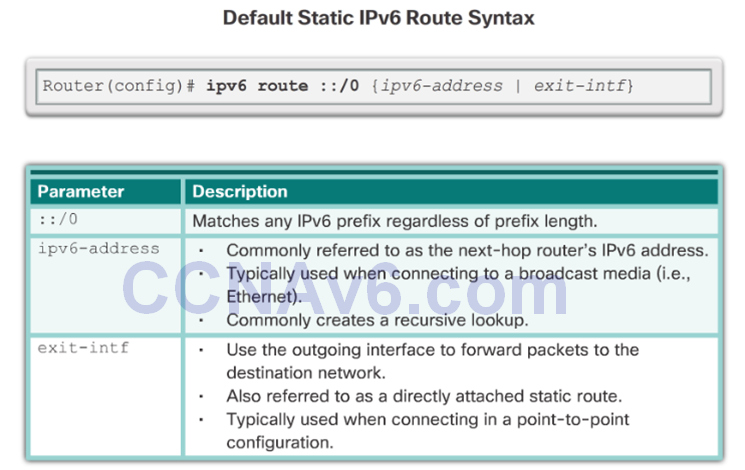
Configure a Default Static IPv6 Route
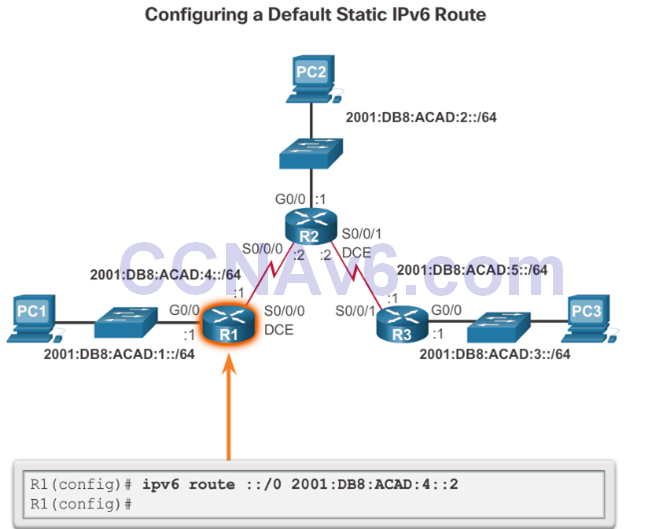
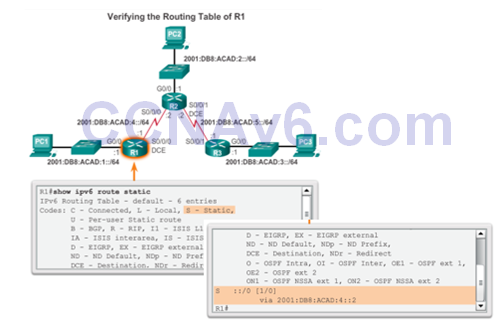
Verify a Default IPv6 Static Route
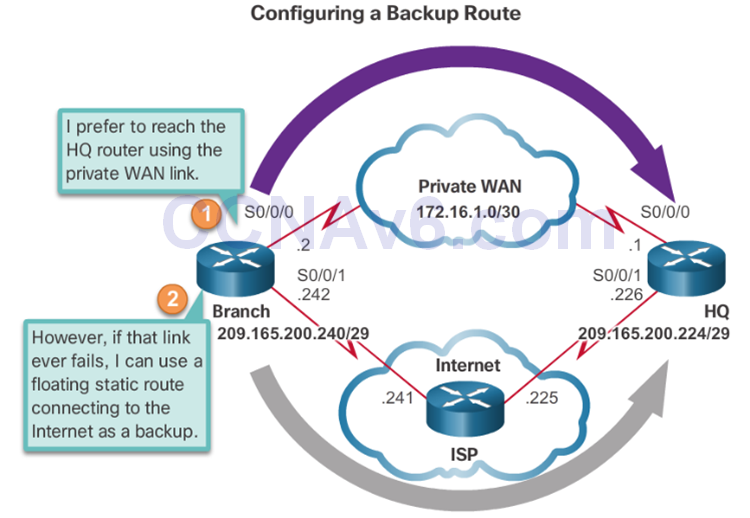
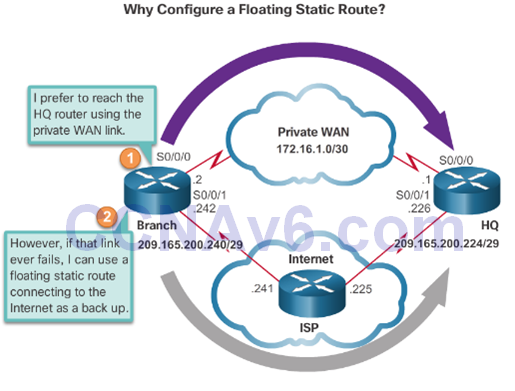
Floating Static Routes
- Floating static routes have an administrative distance greater than the administrative distance of another static route or dynamic routes.
- The static route “floats” and is not used when the route with the better administrative distance is active.
- If the preferred route is lost the floating static route can take over.
Configure an IPv4 Floating Static Route
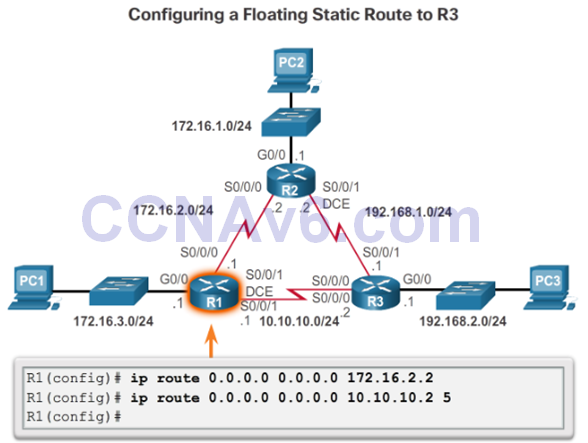
Test the IPv4 Floating Static Route
- To test a floating static route:
- Use the show ip route command to verify that the routing table is using the default static route.
- Use the traceroute command to follow the traffic flow out the primary route.
- Disconnect the link or shutdown the primary interface(s). In the curriculum example the serial interfaces on R2 are shutdown.
- Use a show ip route command to verify that the routing table is using the floating static route.
- Use a traceroute command to follow the traffic flow out the backup route.
2.2.4 Configure Static Host Routes
Automatically Installed Host Routes
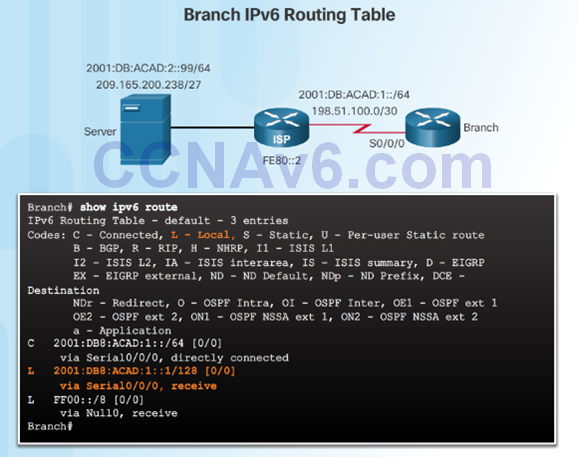
- A host route is an IPv4 address with a 32-bit mask or an IPv6 address with a 128-bit mask.
- Automatically installed when an IP address is configured on the router.
- The local routes are marked with “L” in the output of the routing table.
Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static Host Routes
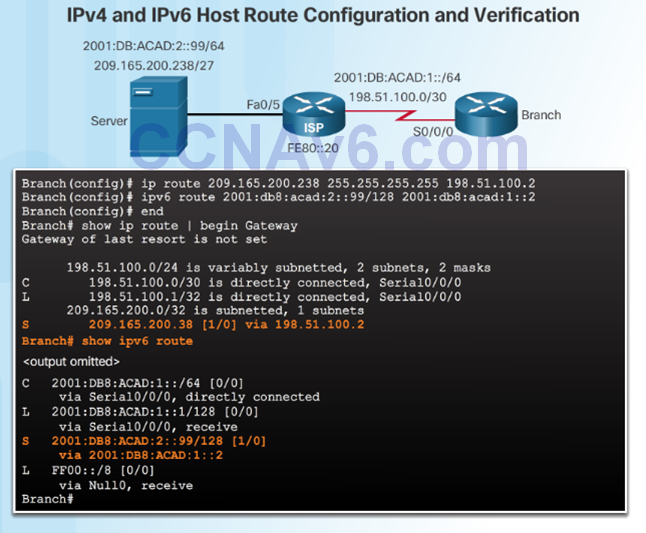
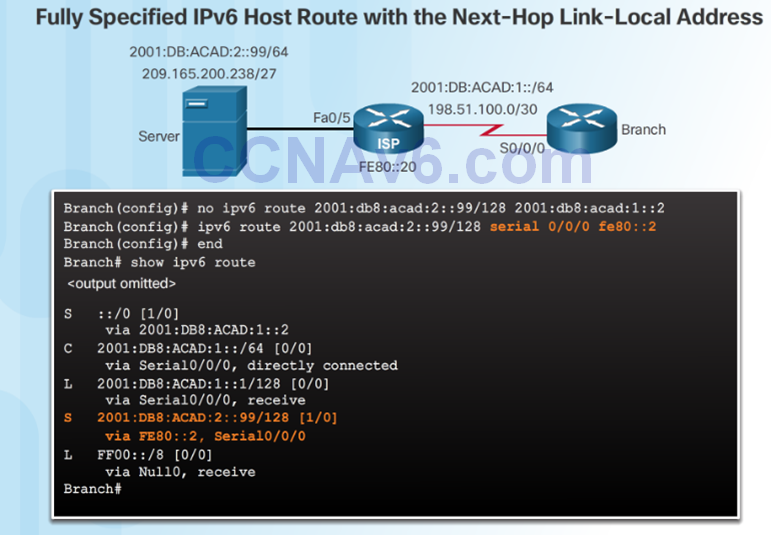
2.3 Troubleshoot Static and Default Route Issues
Packet Processing with Static Routes
Static Routes and Packet Forwarding
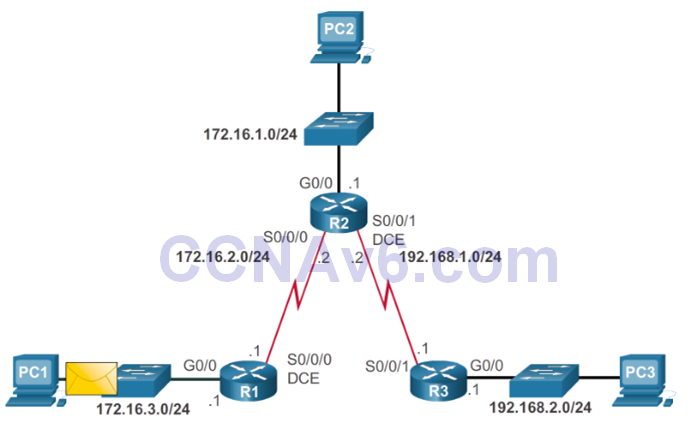
Troubleshoot IPv4 Static and Default Route Configuration
Troubleshoot a Missing Route
- IOS troubleshooting commands include:
- ping
- Extended ping enables you to specify the source IP address for the ping packets.
- traceroute
- show ip route
- show ip interface brief
- show cdp neighbors detail
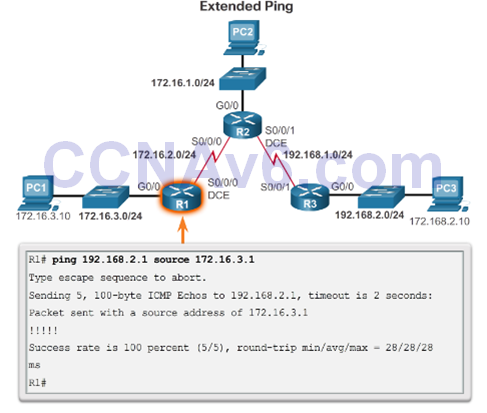
Packet Processing with Static Routes
Solve a Connectivity Problem
- Finding a missing (or misconfigured) route requires using the right tools in a methodical manner.
- Use the ping command to confirm the destination can’t be reached.
- A traceroute would also reveal the closest router (or hop) that fails to respond as expected. In this case, the router would then send an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) destination unreachable message back to the source.
- The next step is to investigate the routing table using the show ip route command. Look for missing or misconfigured routes.
- Incorrect static routes are a common cause of routing problems.
2.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain the advantages and disadvantages of static routing.
- Explain the purpose of different types of static routes.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 static routes by specifying a next-hop address.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 default routes.
- Configure a floating static route to provide a backup connection.
- Configure IPv4 and IPv6 static host routes that direct traffic to a specific host.
- Explain how a router processes packets when a static route is configured.
- Troubleshoot common static and default route configuration issues.
Section 2.1
Terms and Commands
- static route
- administrative distance (AD)
- stub network
- default route
- 0.0.0.0/0
- default static route
- Gateway of Last Resort
- more specific match
- summary static route
- floating static route
Section 2.2
Terms and Commands
- exit-intf
- next hop
- recursive static route
- recursive lookup
- directly connected static route
- CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding)
- FIB (Forwarding Information Base)
- fully specified static route
- edge router
- stub router
- quad-zero route
- ::/0
- destination network
- Ipv6 route command
- Fully specified static IPv6 route
- show ipv6 route
- show ipv6 route static
- show ipv6 route network
- IPv4 Static Host Routes
- IPv6 Static Host Routes
Section 2.3
Terms and Commands
- Extended ping
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
