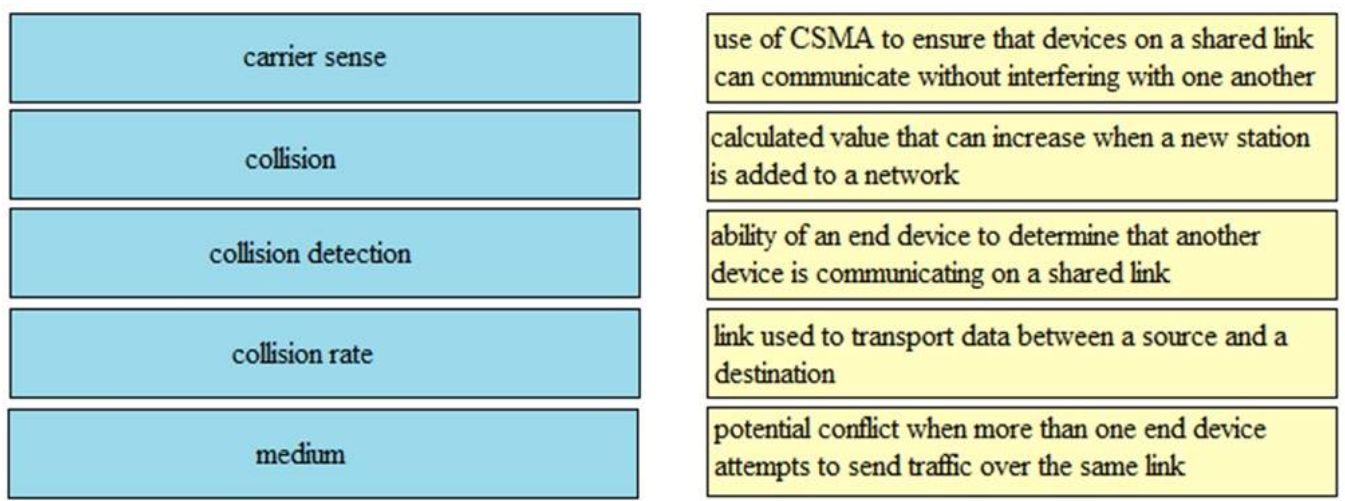
1. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the Ethernet terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
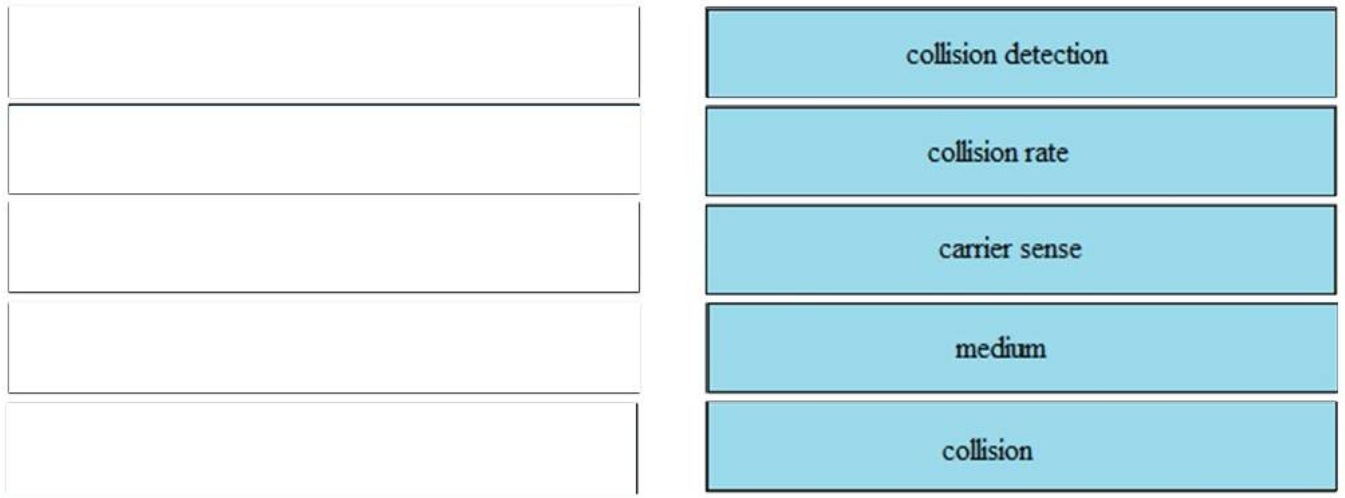
– collision detection: use of CSMA to ensure that devices on a shared link can communicate without interfering with one another
– collision rate: calculated value that can increase when a new station is added to a network
– carrier sense: ability of an end device to determine that another device is communicating on a shared link
– medium: link used to transport data between a source and a destination
– collision: potential conflict when than one end device attempts to send traffic over the same link
2. DRAG DROP. Refer to the exhibit.
Select and Place:
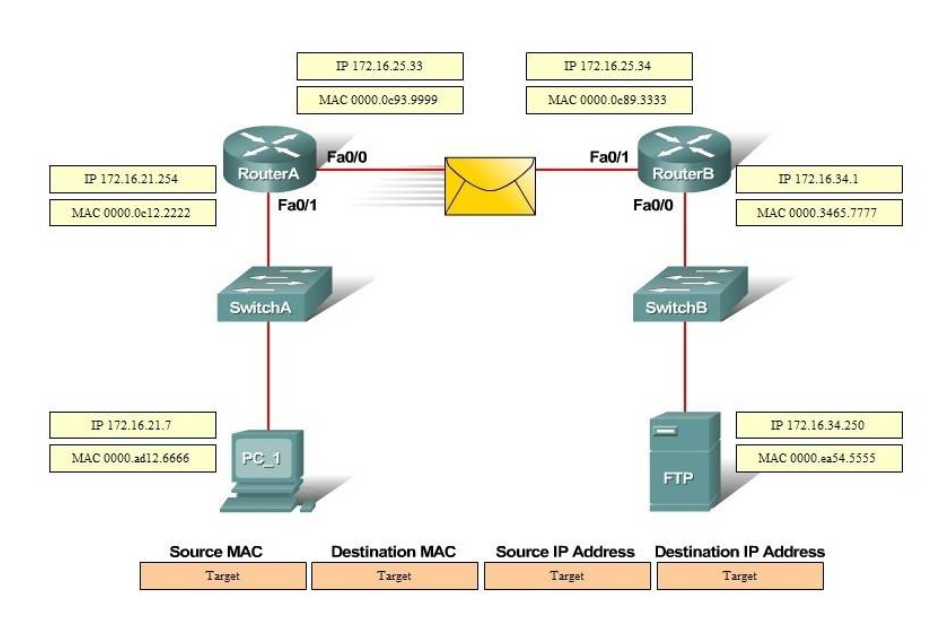
Correct Answer:
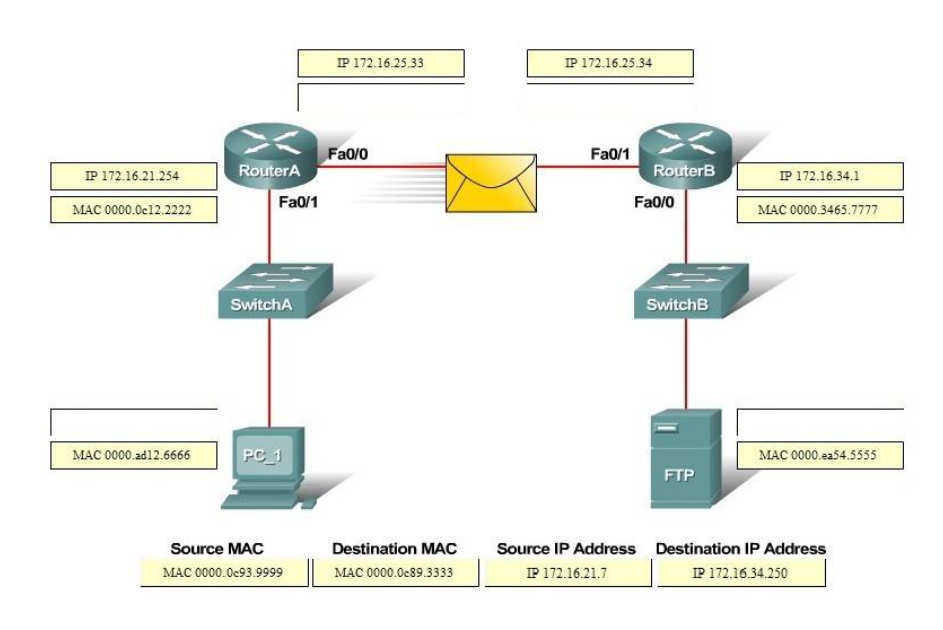
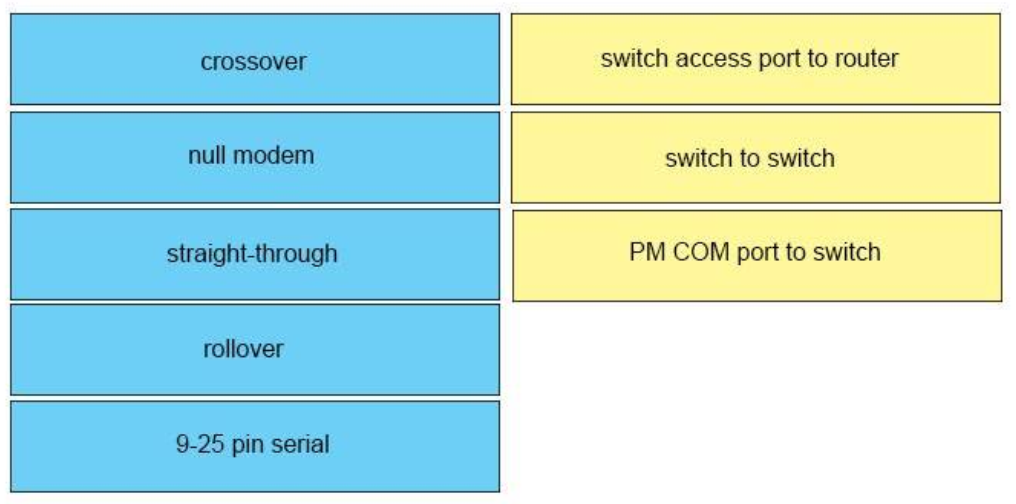
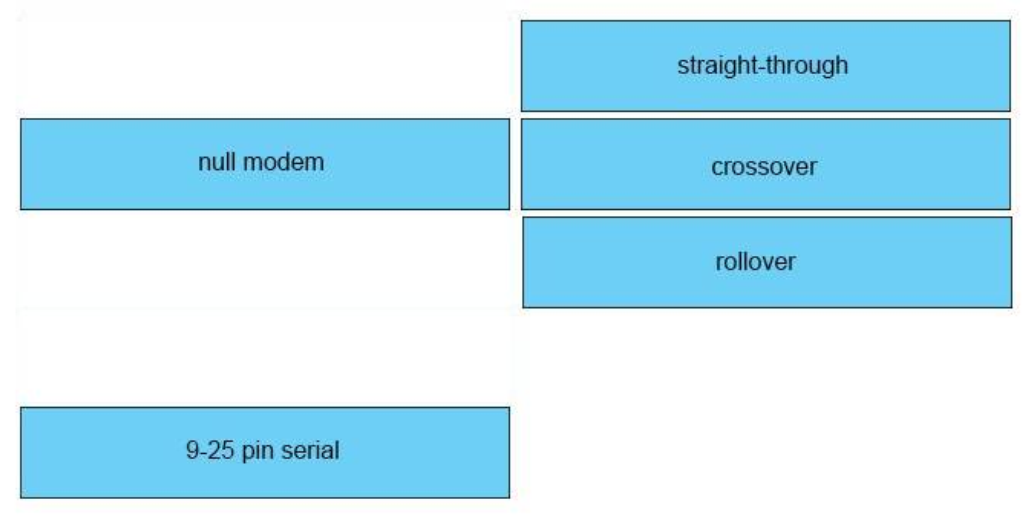
3. DRAG DROP. Drag the cable type on the left to the purpose for which is the best suited on the right. Not all options are used.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
+ switch access port to router: straight-through
+ switch to switch: crossover
+ PC COM to switch Console port: rollover
– To connect two serial interfaces of 2 routers we use serial cable
– To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
For example: we use straight-through cable to connect switch to router, switch to host, hub to host, hub to server… and we use crossover cable to connect switch to switch, switch to hub, router to router, host to host… )
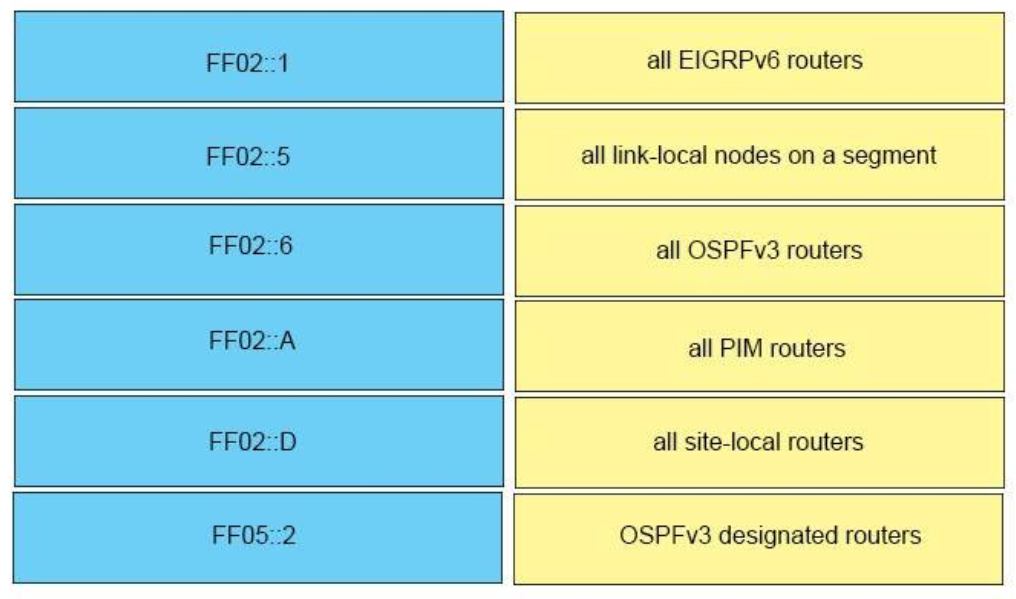
4. DRAG DROP. Drag the IPv6 multicast address type on the left to their purpose on the right..
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
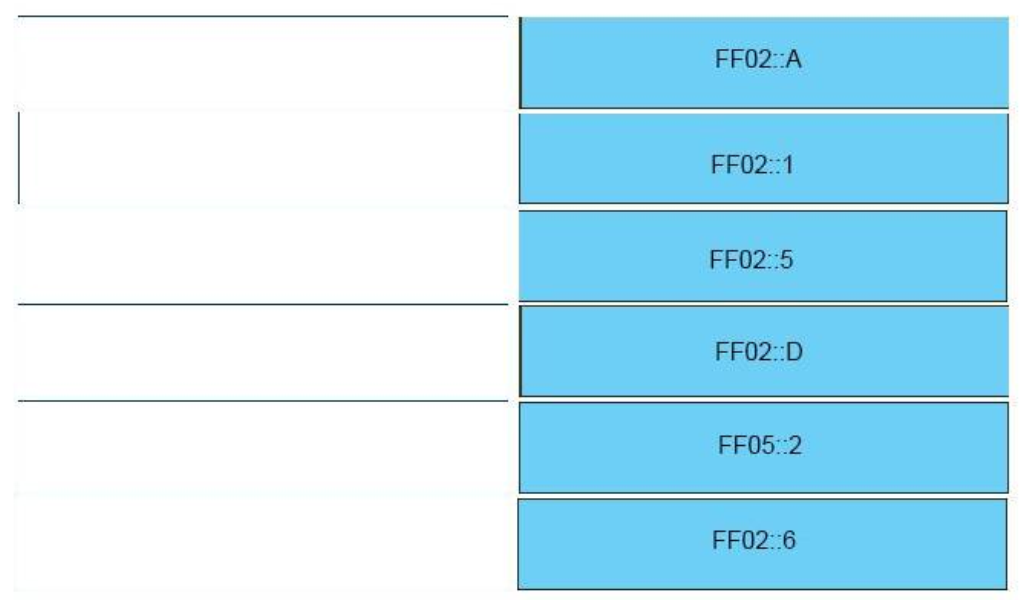
– FF02::A -> all EIGRPv6 routers
– FF02::1 -> all link-local nodes on a segment
– FF02::5 -> all OSPFv3 routers
– FF02::D -> all PIM routers
– FF05::2 -> all site-local routers
– FF02::6 -> OSPFv3 designated routers
5. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the IPv6 IP addresses from the left onto the correct IPv6 address types on the right.
Select and Place:
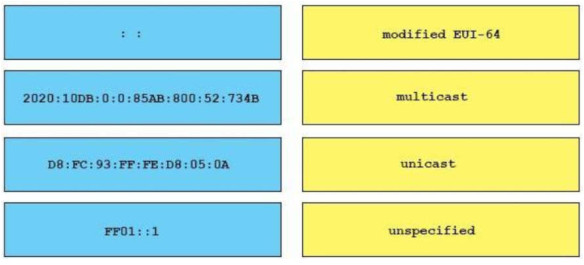
Correct Answer:
+ Modified EUI-64: DB:FC:93:FF:FE:D8:05:0A
+ multicast: FF01::1
+ unicast: 2020:10D8:0:0:85:800:52:7348
+ unspecified: ::
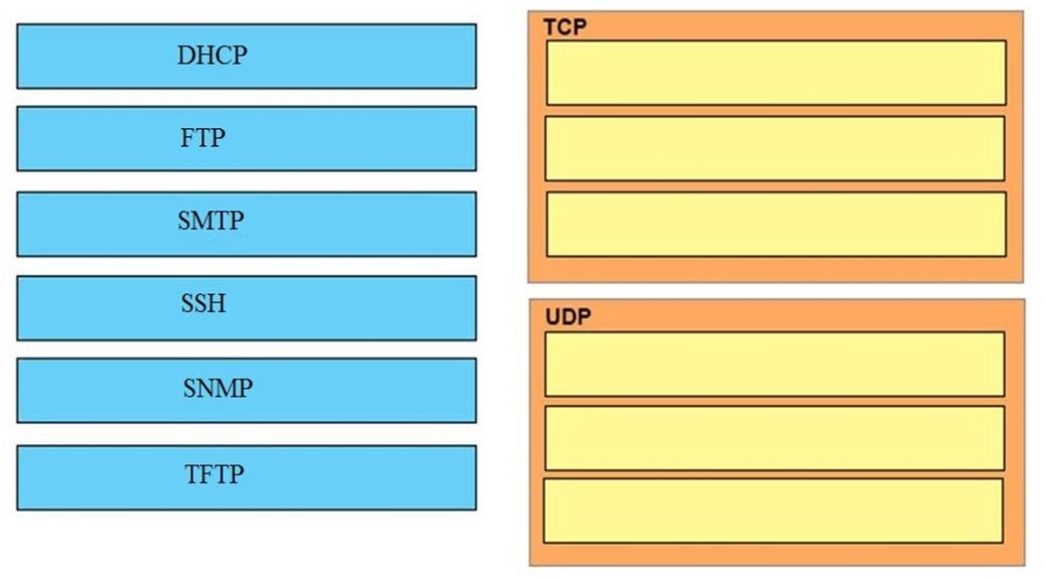
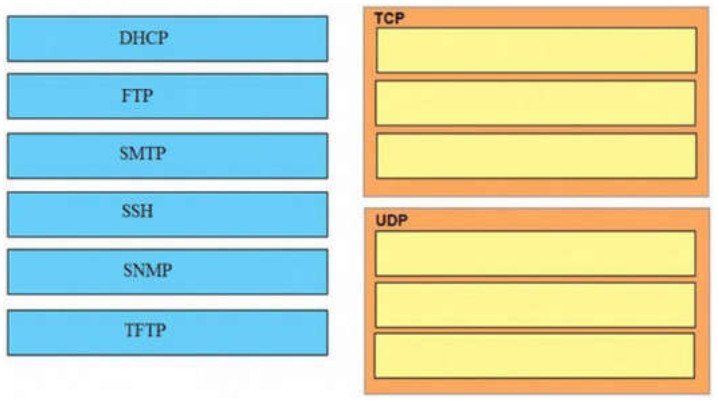
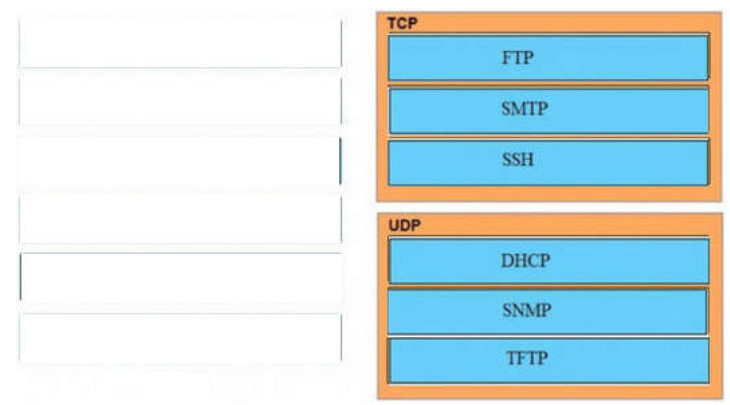
6. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the application protocols from the left onto the transport protocols that is uses on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
TCP:
+ SMTP
+ SSH
+ FTP
UDP:
+ SNMP
+ DHCP
+ TFTP
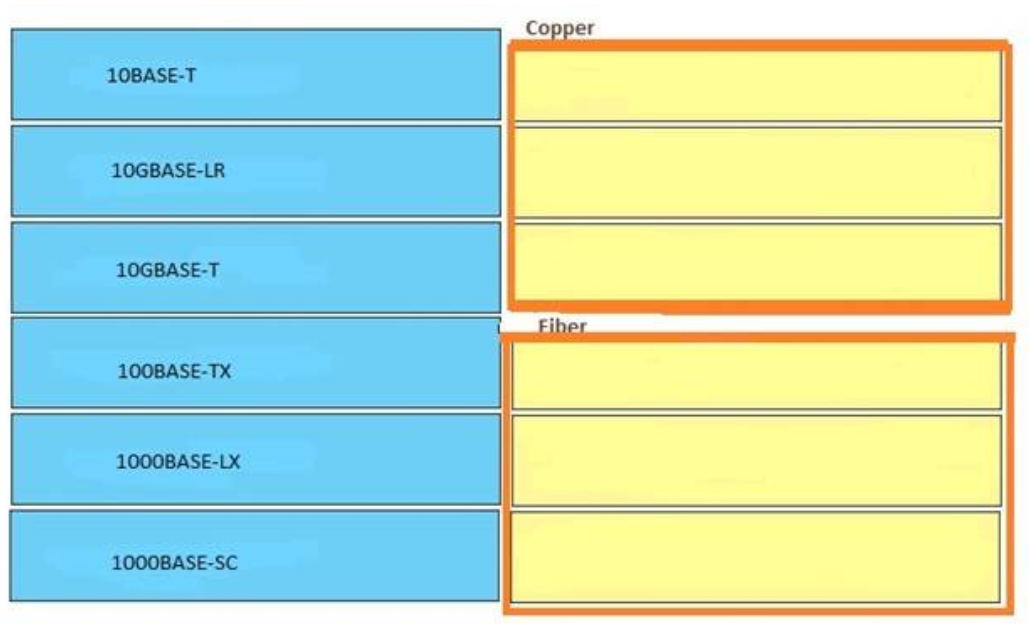
7. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the IEEE standard cable names from the left onto the correct cable types on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:

Answer:
Copper:
+ 10BASE-T
+ 100BASE-TX
+ 10GBASE-T
Fiber:
+ 10GBASE-LR
+ 1000BASE-LX
+ 1000BASE-SC
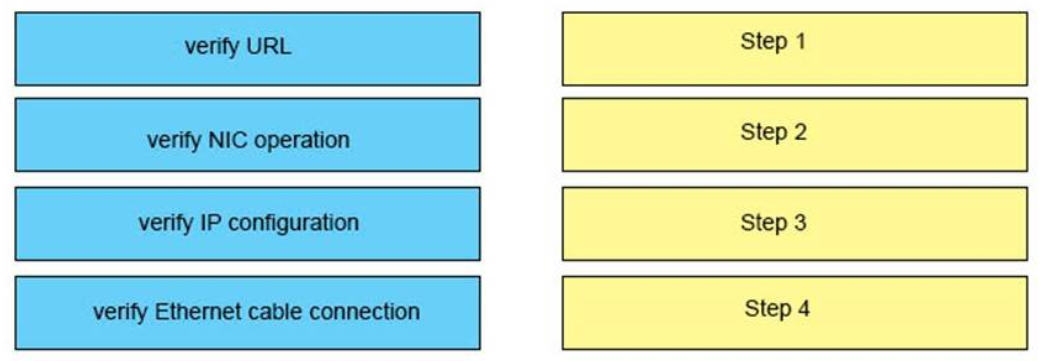
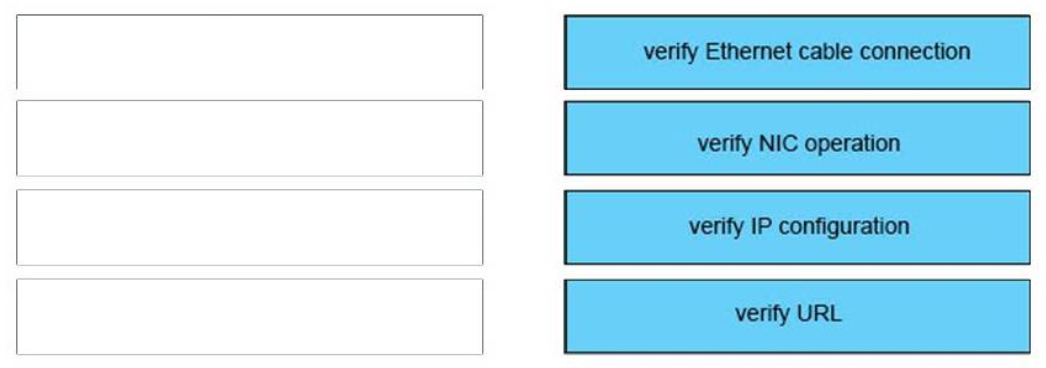
8. DRAG DROP. A user is unable to connect to the Internet. Based on the layered approach to troubleshooting and beginning with the lowest layer, drag each procedure on the left to its proper category on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
1) Verify Ethernet cable connection: Step 1
2) Verify NIC operation: Step 2
3) Verify IP configuration: Step 3
4) Verify URL: Step 4
Next we “verify NIC operation”. We do this by simply making a ping to the loopback interface 127.0.0.1. If it works then the NIC card (layer 1,2) and TCP/IP stack (layer 3) are working properly.
Verify IP configuration belongs to layer 3. For example, checking if the IP can be assignable for host, the PC’s IP is in the same network with the gateway…
Verifying the URL by typing in your browser some popular websites like google.com, microsoft.com to assure that the far end server is not down (it sometimes make we think we can’t access to the Internet). We are using a URL so this step belongs to layer 7 of the OSI model.
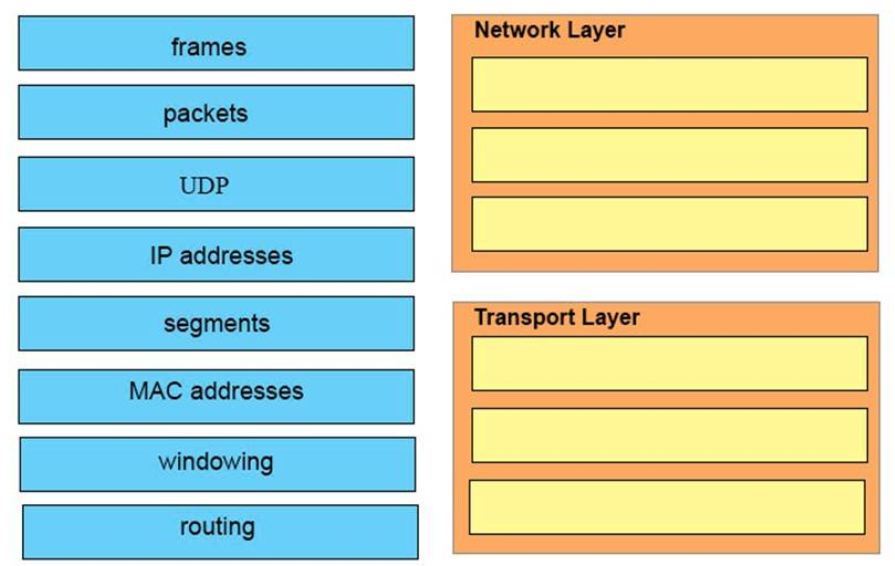
9. DRAG DROP. Drag the terms on the left onto the appropriate OSI layer on the right. (Not all options are used.)
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
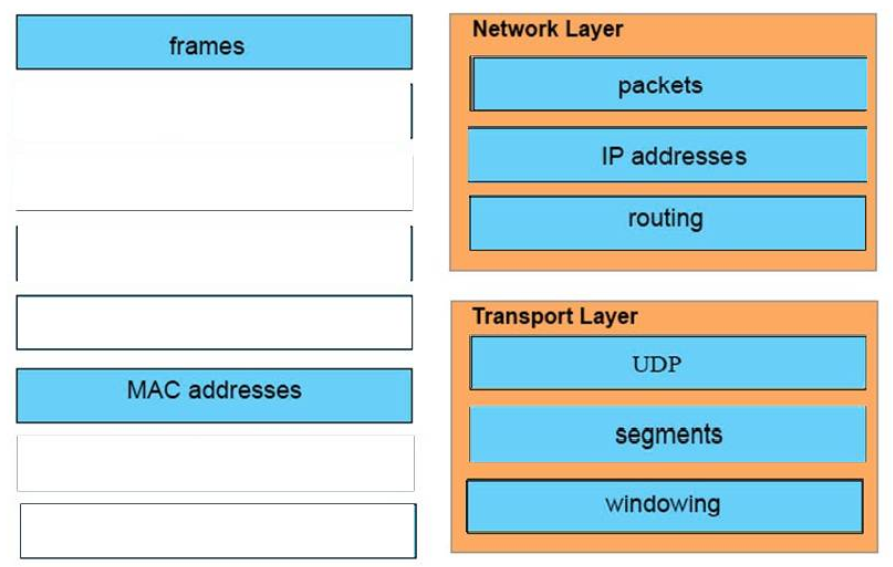
Answer:
Network Layer:
+ packets
+ IP address
+ routing
Transport Layer:
+ udp
+ segments
+ windowing
10. DRAG DROP. Refer to the exhibit.
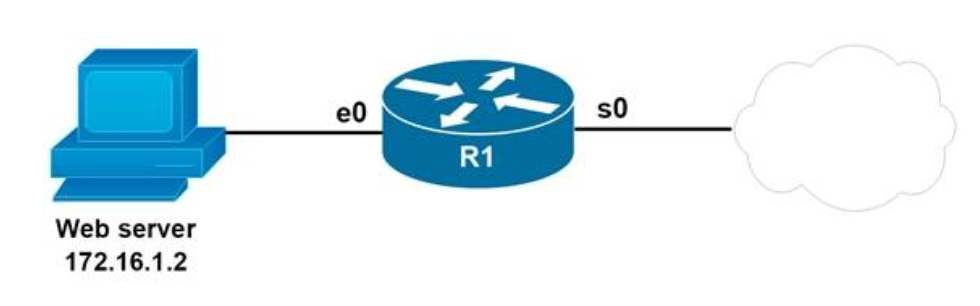
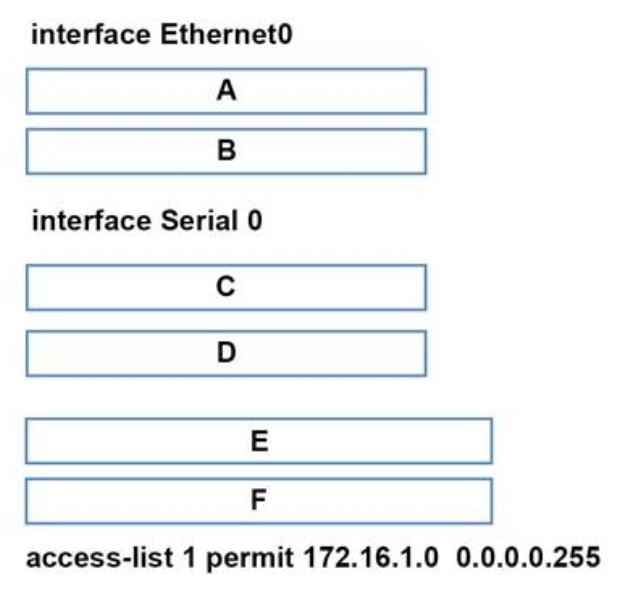
You are configuring the router to provide Static NAT for the web server.
Drag and drop the configuration commands from left onto the letters that correspond to its position in the
configuration on the right.
Select and Place:
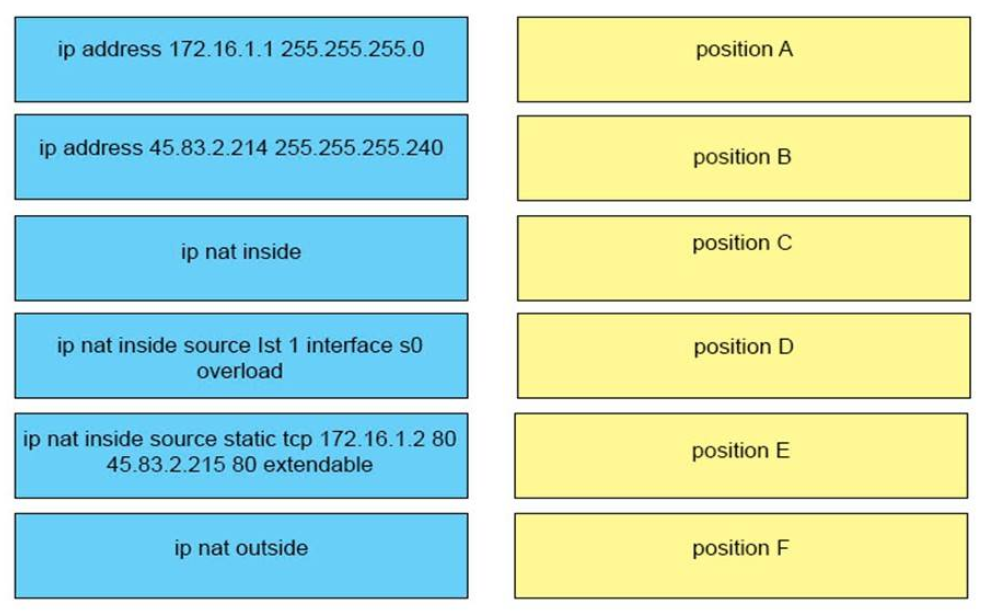
Correct Answer:

+ position A: ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
+ position B: ip nat inside
+ position C: ip address 45.83.2.214 255.255.255.240
+ position D: ip nat outside
+ position E: ip nat inside source static tcp 172.16.1.2 80 45.83.2.215 80 extendable
+ position F: ip nat inside source Ist 1 interface s0 overload
11. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop each cable type from the left onto the type of connection for which it is best suited on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
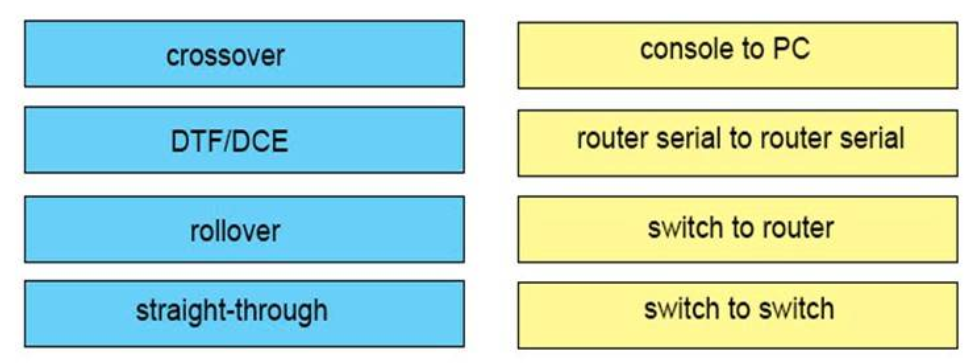
crossover: switch to switch
DTE/DCE: Serial to Serial
straight-through: PC to router
rollover: PC to Console
– To connect two serial interfaces of 2 routers we use serial cable
– To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
For example: we use straight-through cable to connect switch to router, switch to host, hub to host, hub to server… and we use crossover cable to connect switch to switch, switch to hub, router to router, host to host… )
Note: The correct cable type of PC – Router should be crossover. But it was use for switch – switch (which is surely correct) so this question contains a bug.
12. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the characteristics of a cloud environment from the left onto the correct examples on the right
Select and Place:
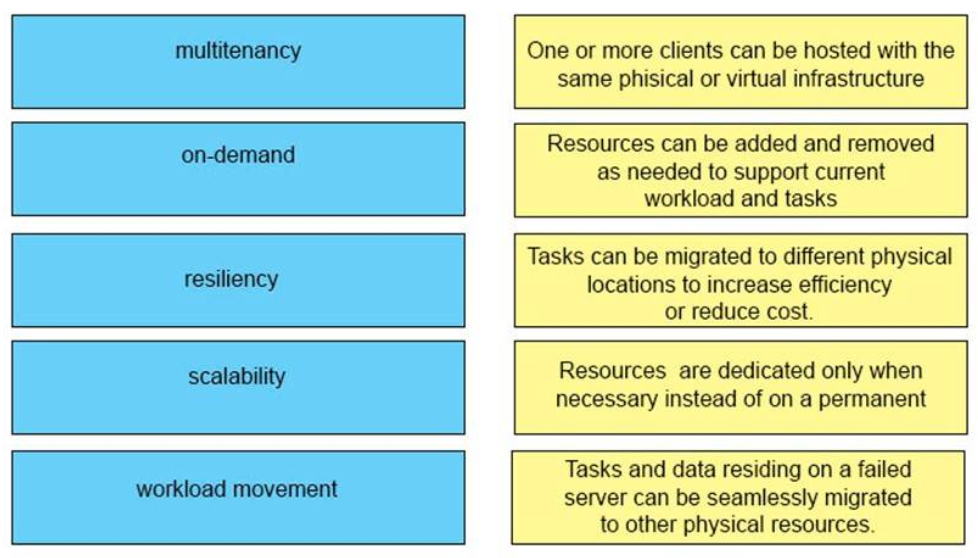
Correct Answer:

Answer:
+ Multitenancy: One or more clients can be hosted with the same physical or virtual infrastructure
+ Scalability: Resources can be added and removed as needed to support current workload and tasks
+ Workload movement: Tasks can be migrated to different physical locations to increase efficiency or reduce cost
+ On-demand: Resources are dedicated only when necessary instead of on a permanent basis
+ Resiliency: Tasks and data residing on a failed server can be seamlessly migrated to other physical resources
13. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop each broadcast IP address on the left to the Broadcast Address column on the right. Not alloptions are used.
Select and Place:

Correct Answer:

Answer:
10.63.255.255/10
172.16.255.39/29
172.20.255.255/16
192.168.255.127/25
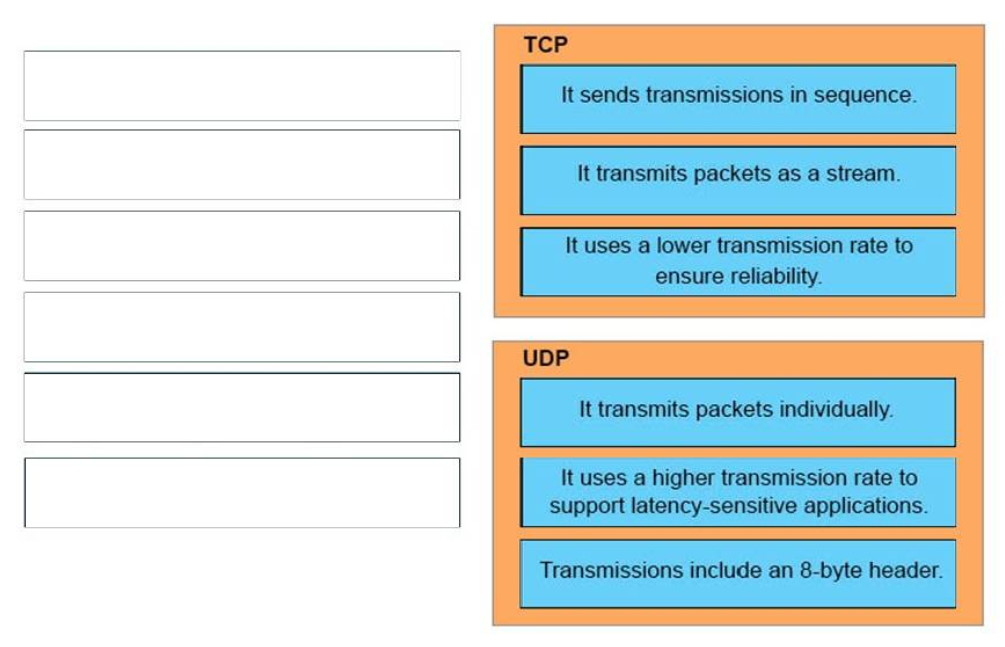
14. DRAG DROP. Drag and Drop the descriptions of IP protocol transmissions from the left onto the correct IP traffic types on the right.
Select and Place:
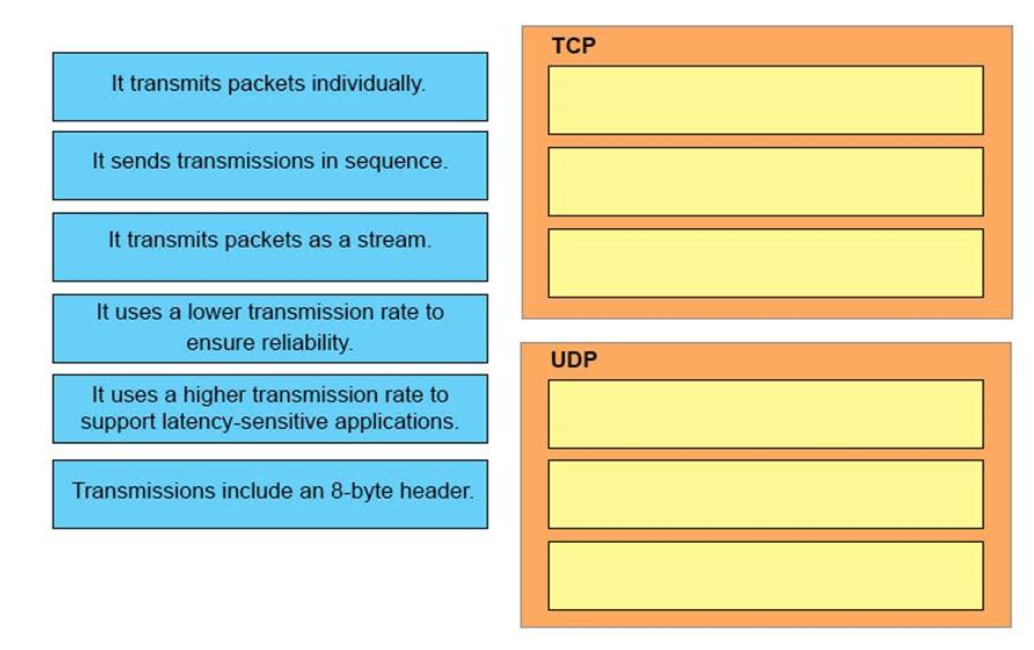
Correct Answer:
Answer:
TCP:
+ It sends transmissions in sequence.
+ It transmits packets as a stream.
+ It uses a lower transmission rate to ensure reliability.
UDP:
+ It transmits packets individually.
+ It uses a higher transmission rate to support latency-sensitive applications.
+ Transmissions include an 8-byte header.
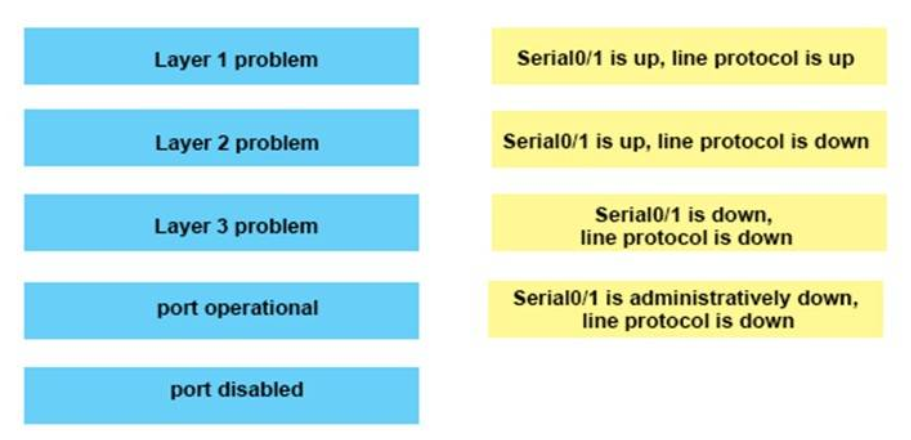
15. DRAG DROP. Drag each category on the left to its corresponding router output line on the right. Each router output line is in the result of a show ip interface command. Not all categories are used.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up : port operational
Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down : Layer 2 problem
Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down : Layer 1 problem
Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down : port disabled
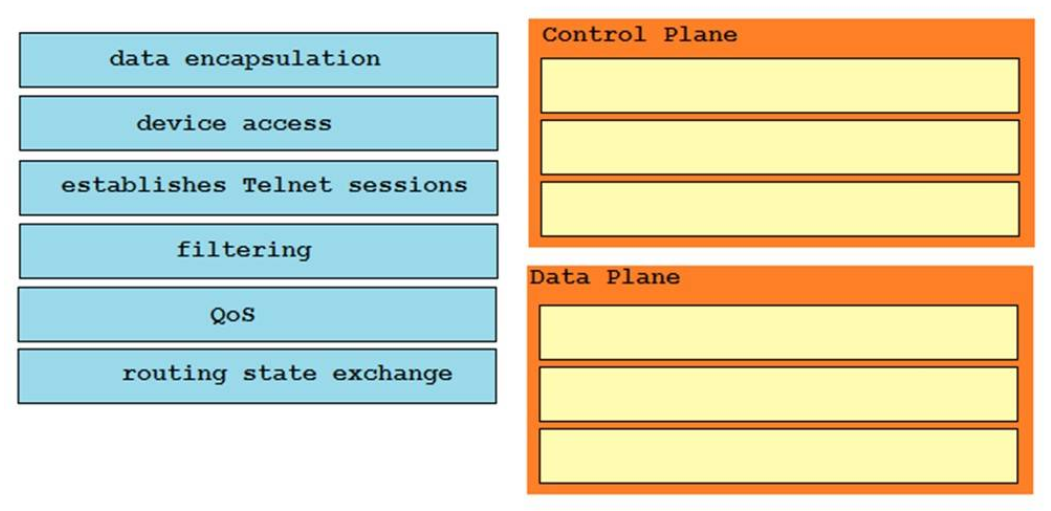
16. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the networking features of functions from the left onto the planes on which they operate on the
right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:

Answer:
Control Plane:
Filtering
Routing state exchange
Device access
Data Plane:
QoS
Establishes telnet session
Data Encapsulation
The data plane: The data plane is the forwarding plane, which is responsible for the switching of packets through the router (that is, process switching and CEF switching). In the data plane, there could be features that could affect packet forwarding such as quality of service (QoS) and access control lists (ACLs).
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2272154&seqNum=3
17. DRAG DROP. You are connecting a variety of devices on your network. Drag and drop the combinations of devices from the left onto the correct cable types on the right.
Select and Place:
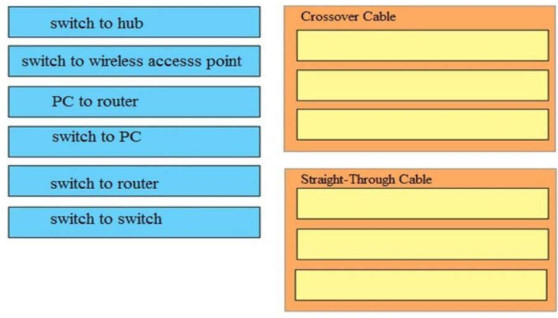
Answer:
Crossover Cable:
+ PC to router
+ switch to hub
+ switch to switch
Straight-Through Cable:
+ switch to PC
+ switch to router
+ switch to wireless accesss point
18. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the STP features from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
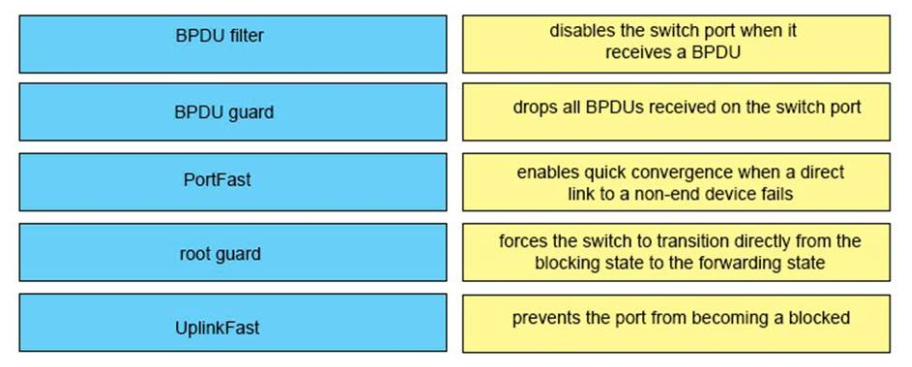
Correct Answer:
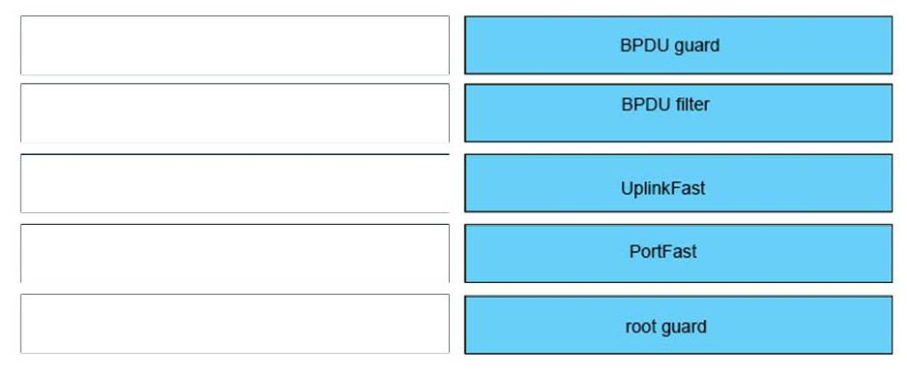
Answer:
+ BPDU Filter: drops all BPDU received on the switch port
+ BPDU guard: disables the switch port when it receives a BPDU
+ PortFast: forces the switch to transition directly from the blocking state to the forwarding state
+ Root guard: prevents the port from becoming a locked port
+ UplinkFast: enables quick convergence when a direct link to a non-end device fails
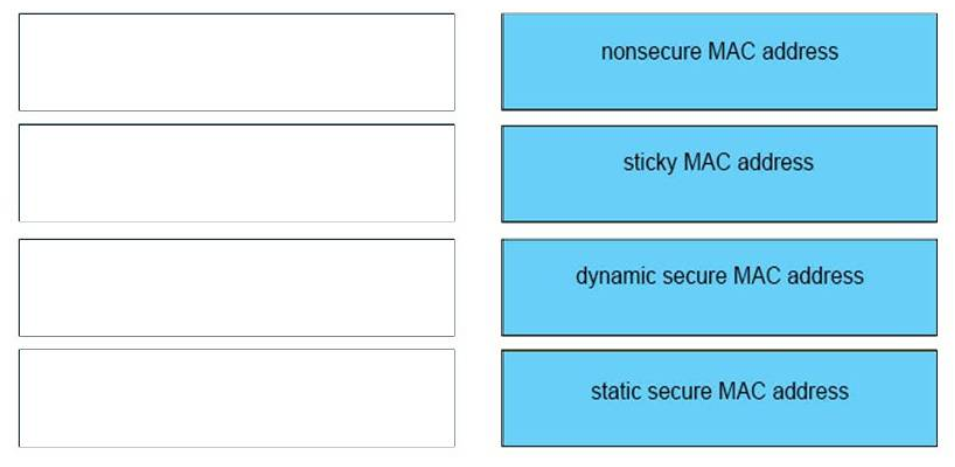
19. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the MAC address types from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right?
Select and Place:
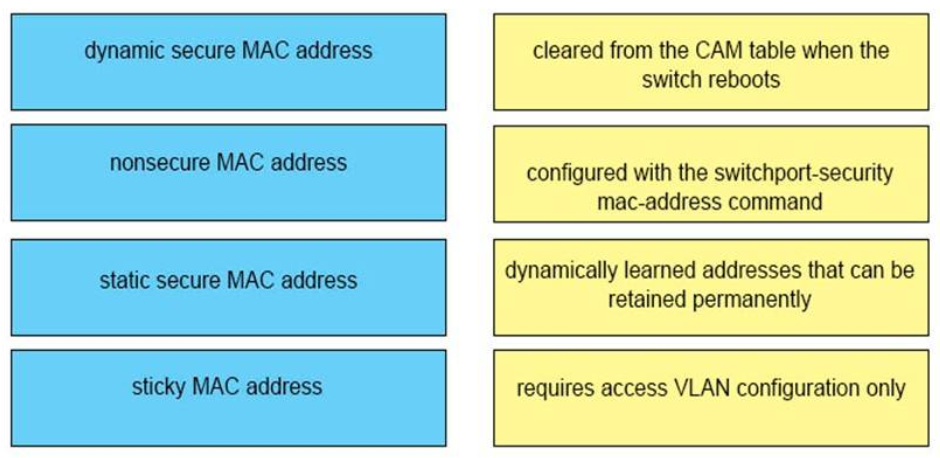
Correct Answer:
Answer:
– cleared from the CAM table when the switch reboots : nonsecure MAC address
– configured with the switchport-security mac-address command : sticky MAC address
– dynamically learned addresses that can be retained permanently : dynamic secure MAC address
– requires access VLAN configuration only : static secure MAC address
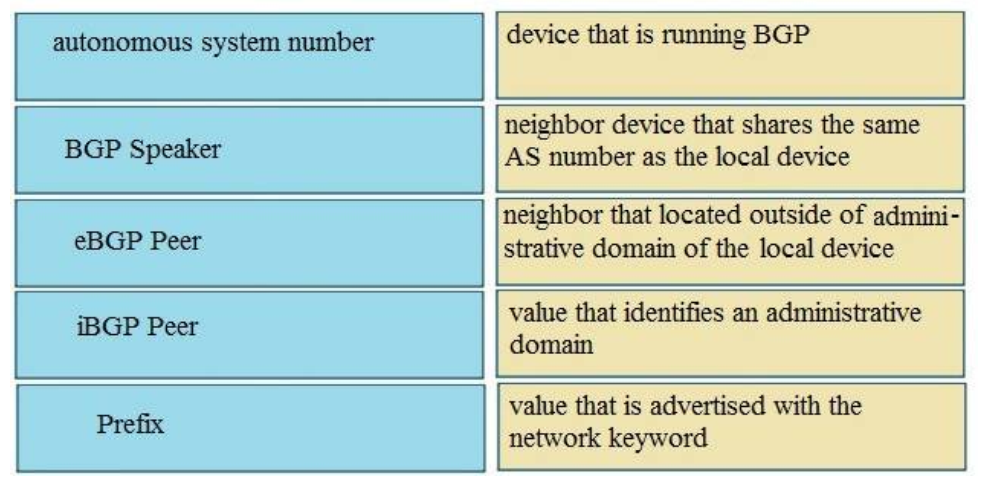
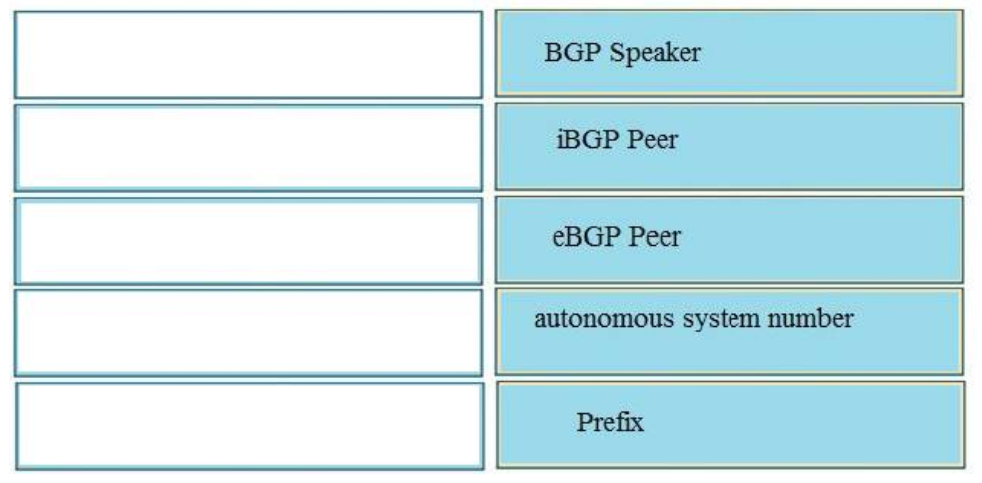
20. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the BGP components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
+ Device that running BGP: BGP speakers
+ Neighbor that share the same AS number as a local device: iBGP peer
+ Neighbor that located outside of AD domain of the local device: eBGP peer
+ Value that identify an AD: Autonomous system number
+ Value that is advertise with network keyword: Prefix
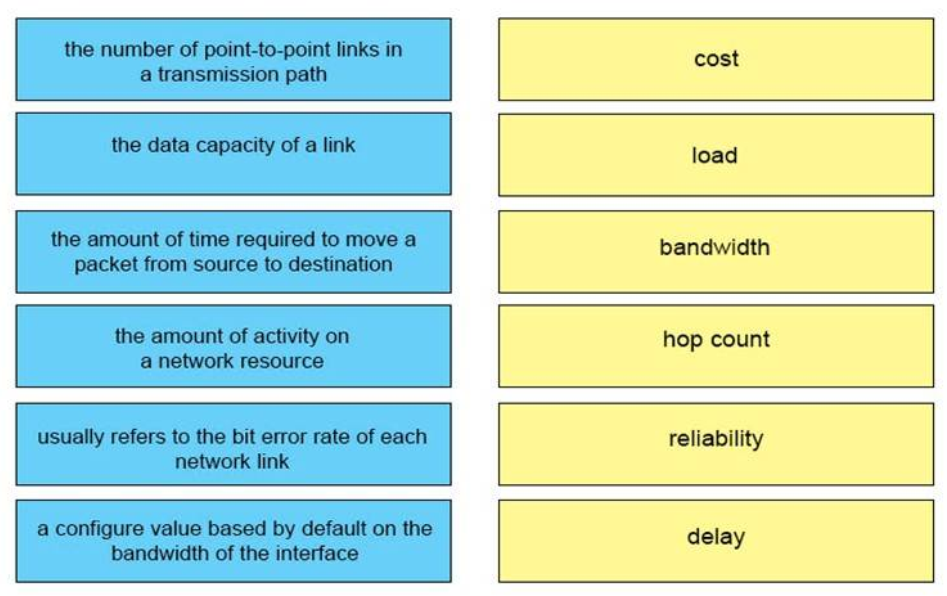
21. DRAG DROP. Drag each definition on the left to the matching term on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
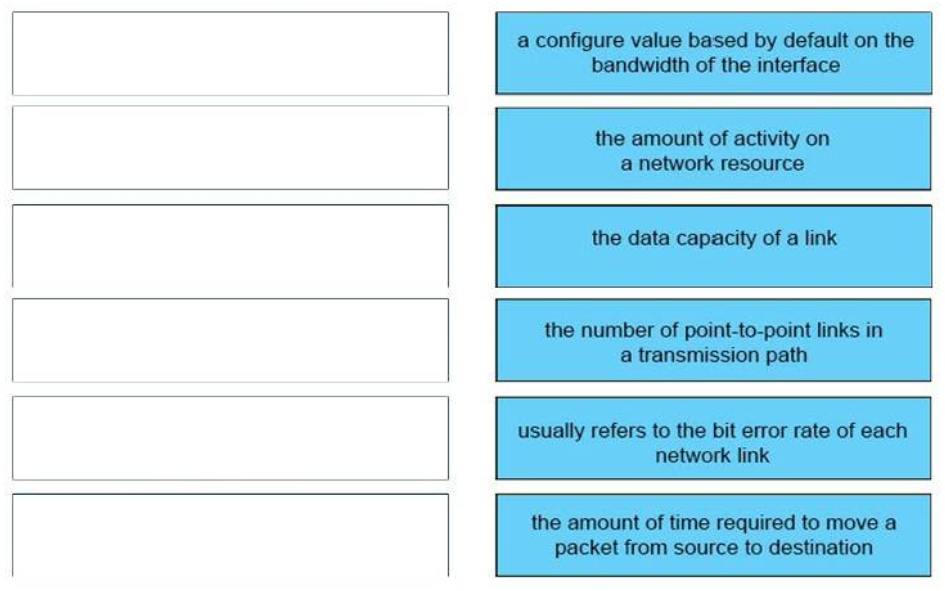
– cost : a configure value based by default on the bandwidth of the interface
– load : the amount of activity on a network resource
– bandwidth : the data capacity of a link
– hop count : the number of point-to-point links in a transmission path
– reliability : usually refers to the bit error rate of each network link
– delay : the amount of time required to move a packet from source to destination
22. DRAG DROP. Drag the Cisco default administrative distance to the appropriate routing protocol or route. (Not all options are
used.)
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
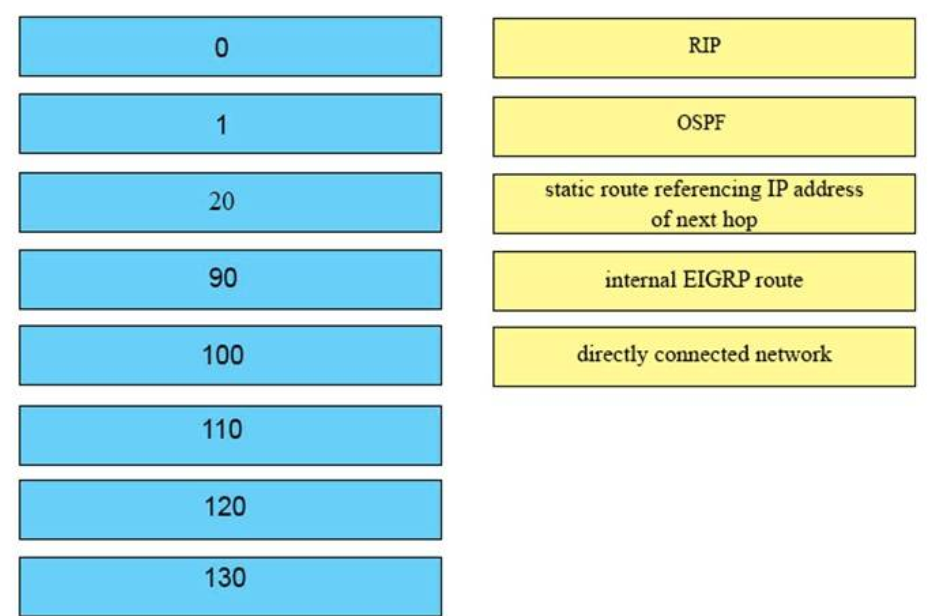
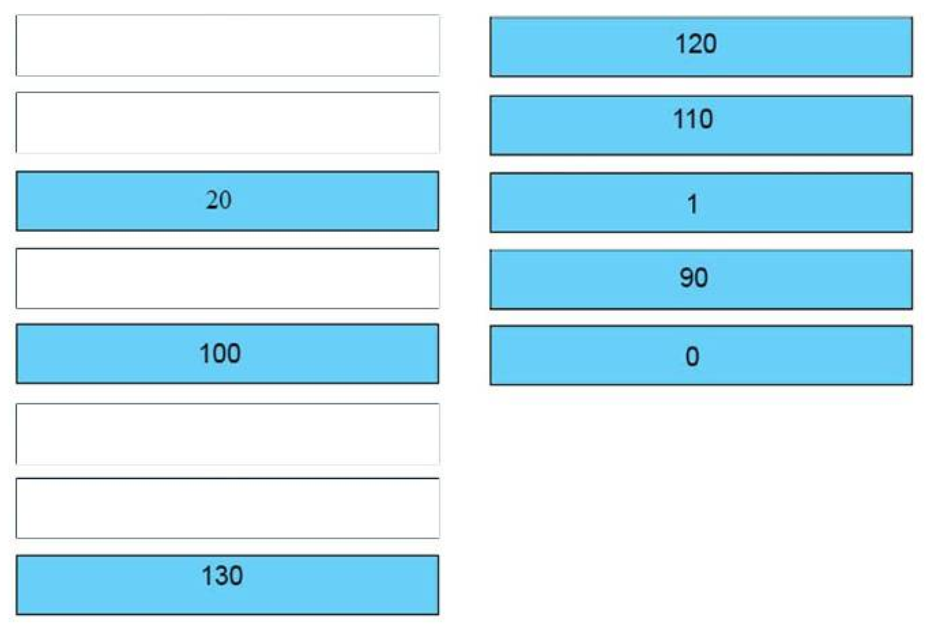
+ RIP : 120
+ OSPF : 110
+ static route referencing IP address of next hop : 1
+ internal EIGRP route : 90
+ directly connected network : 0
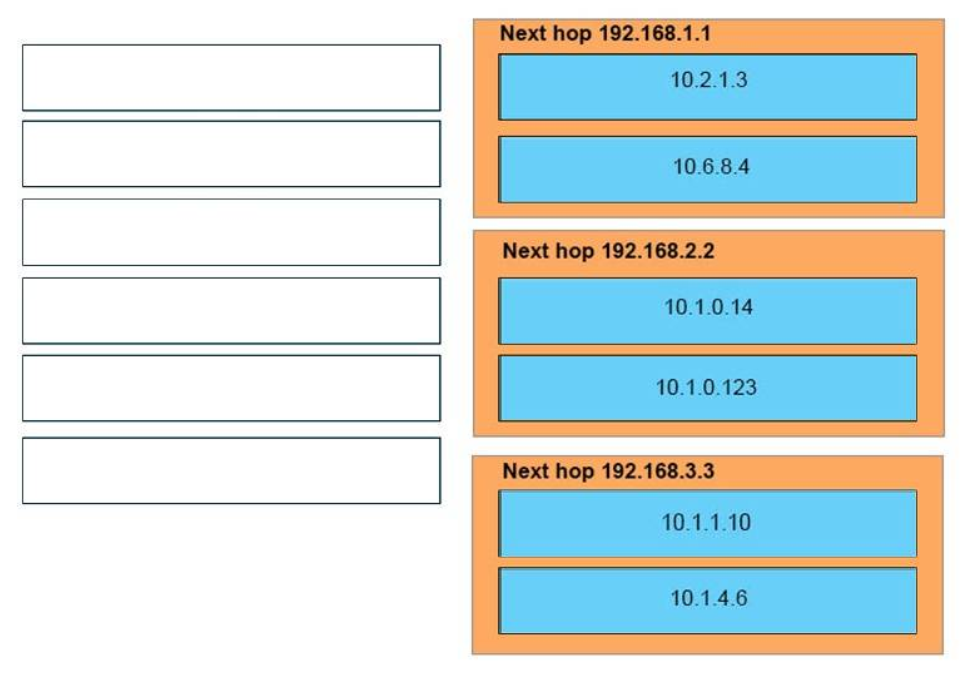
23. DRAG DROP. Routing has been configured on the local router with these commands:

Drag each destination IP address on the left to its correct next hop address on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
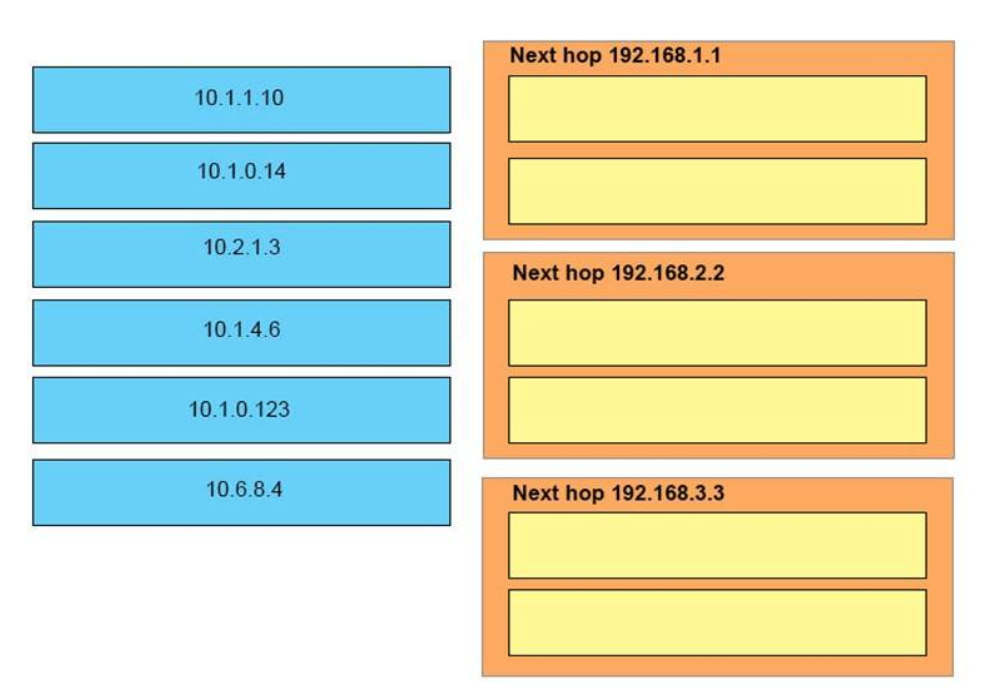
Next hop 192.168.1.1
10.2.1.3
10.6.8.4
Next hop 192.168.2.2
10.1.0.14
10.1.0.123
Next hop 192.168.3.3
10.1.1.10
10.1.4.6
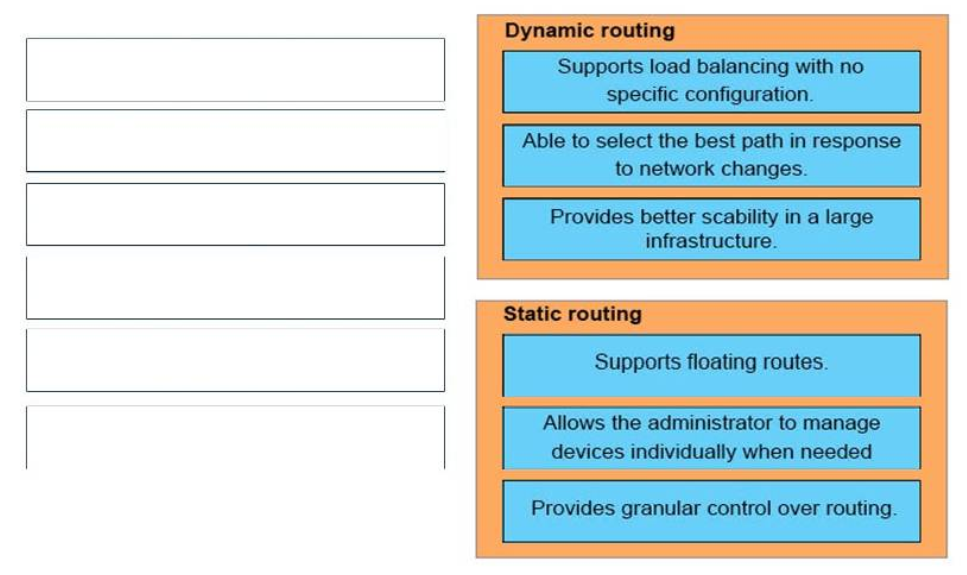
24. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop each advantage of static or dynamic routing from the left onto the correct routing type on the right.Select and Place:
 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
Static Routing:
+ Allows the administrator to manage devices individually when needed
+ Supports floating routes
+ Provides granular control over routing
Dynamic Routing:
+ Able to select the best path in response to network changes
+ Supports load balancing with no specific configuration
+ Provides better scalability in a large infrastructure
25. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the BGP terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.Select and Place:
 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
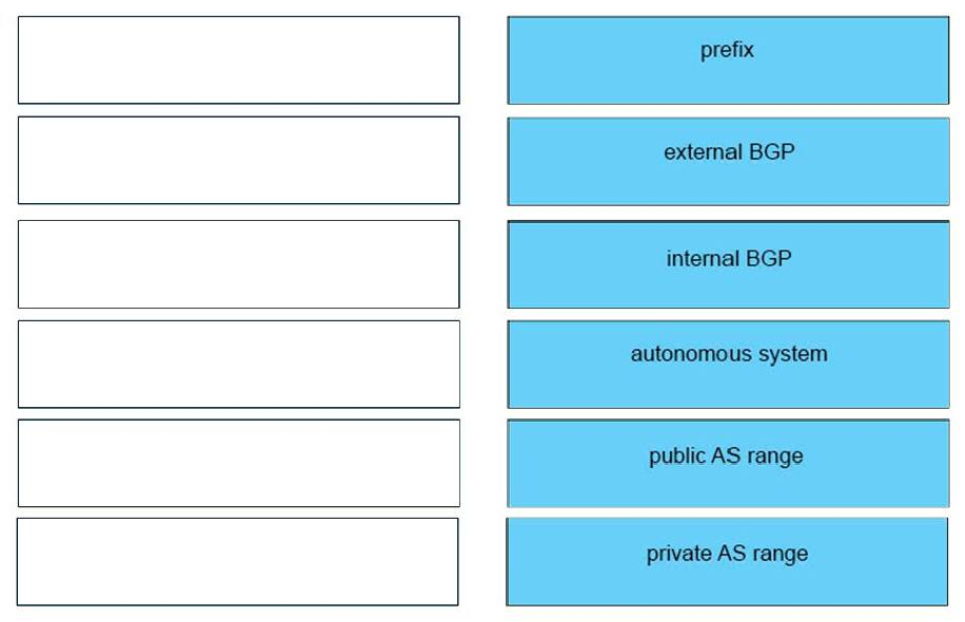
iBGP <-> relationship between peers in same autonomous system
eBGP <-> relationship between peers in different autonomous system
Prefix <-> block of IP addresses
Private AS range <-> Value between 64,512 and 65,535
Public AS range <-> Value between 1 and 64,511
Autonomous System <-> separate network operating within one administrative domain
26. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the values in a routing table from the left onto the correct meanings on the right.Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
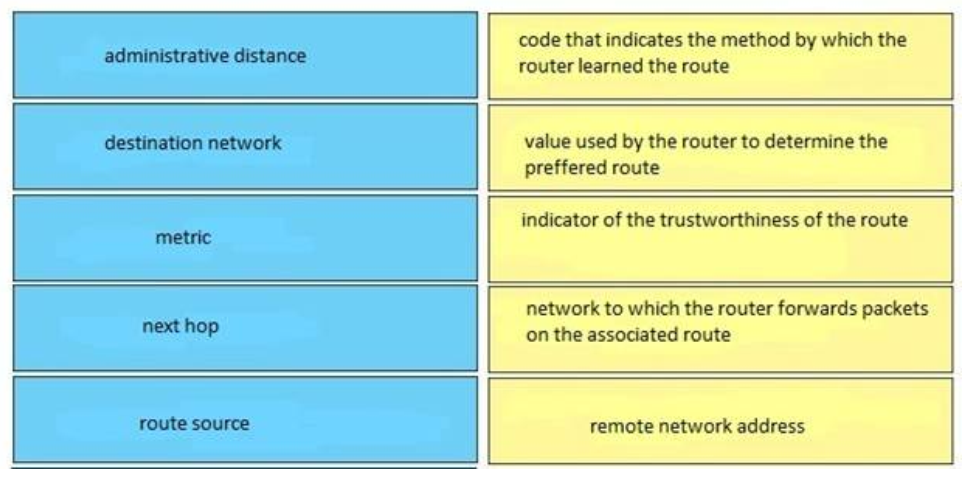
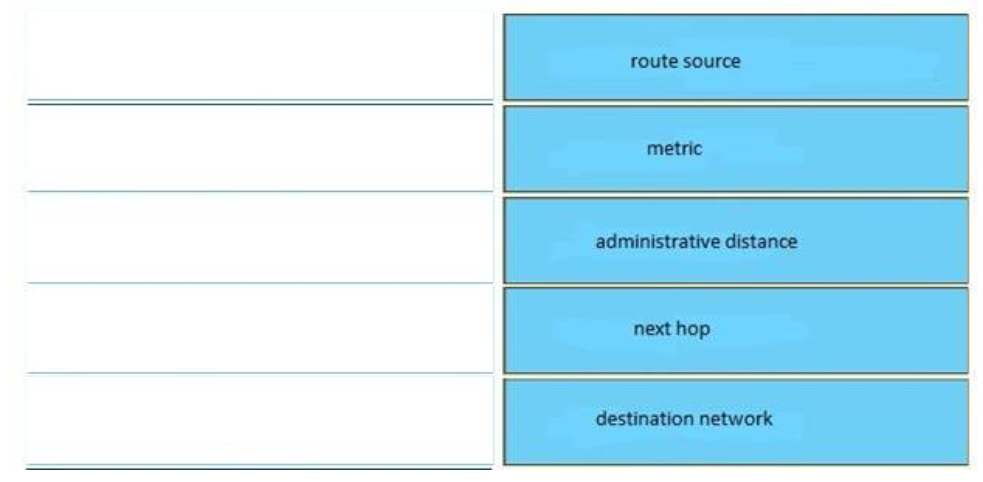
+ Administrative distance: indicator of the trustworthiness of the route
+ Destination network: remote network address
+ Metric: value used by the router to determine the preferred route
+ Next hop: network to which the router forwards packets on the associated route
+ Route source: code that indicates the method by which the router learned the route
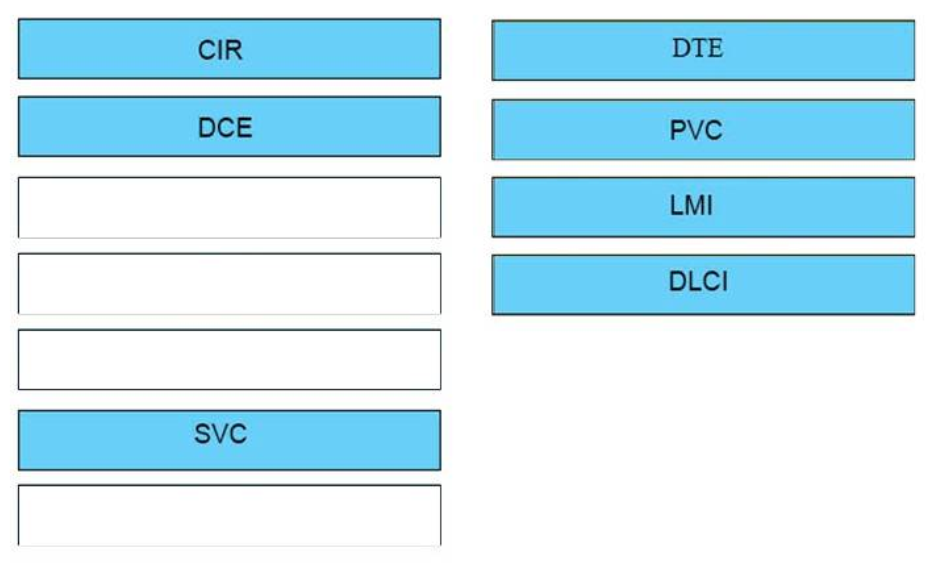
27. DRAG DROP. Drag the frame relay acronym on the left to match its definition on the right. (Not all acronyms are used.)Select and Place:
 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
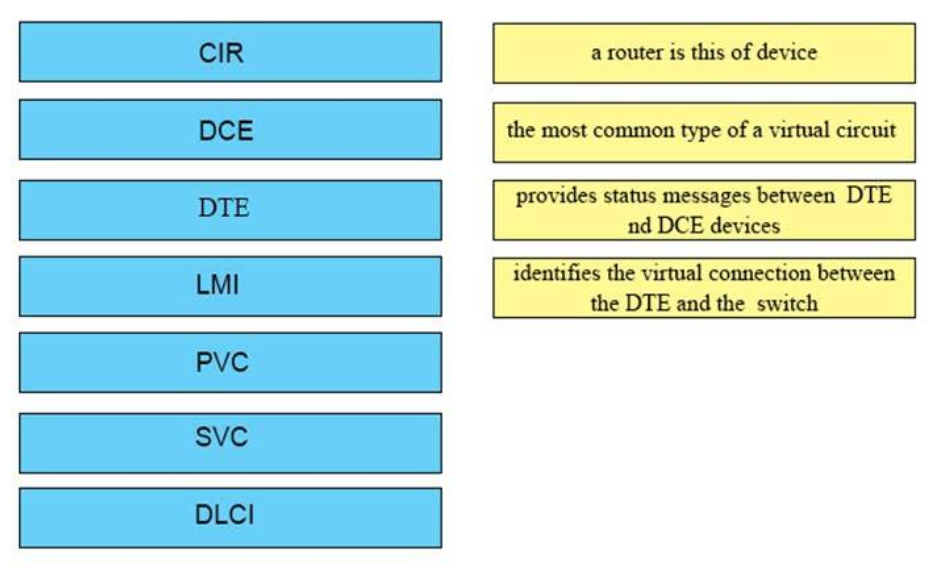
a router is this of device <-> DTE
the most common type of a virtual circuit <-> PVC
provides status messages between DTE nd DCE devices <-> LMI
identifies the virtual connection between the DTE and the switch <-> DLCI
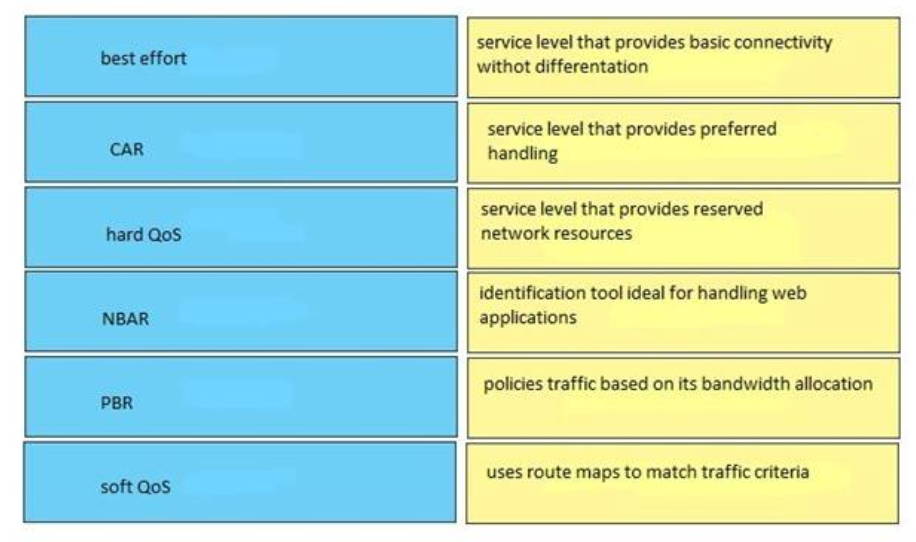
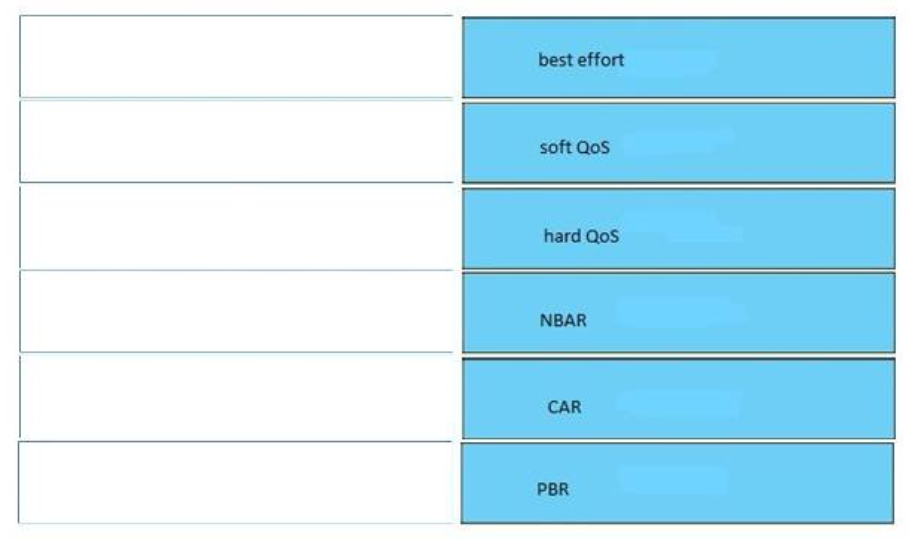
28. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the QoS features from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.Select and Place:
 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
+ CAR: policies traffic based on its bandwidth allocation
+ Best effort: service level that provides basic connectivity without differentiation
+ Soft QoS: service level that provides preferred handling
+ Hard QoS: service level that provides reserved network resources
+ PBR: uses route maps to match traffic criteria
+ NBAR: identification tool ideal for handling web applications
Note:
+ Committed Access Rate (CAR)
+ Network-based application recognition (NBAR)
+ Policy-based routing (PBR)
+ Soft QoS: also known as Differentiated Services (Diffserv), which ensures resources for
applications based on available bandwidth
+ Hard QoS: Differentiated Service (DiffServ) is an appropriate example for this type of QoS service
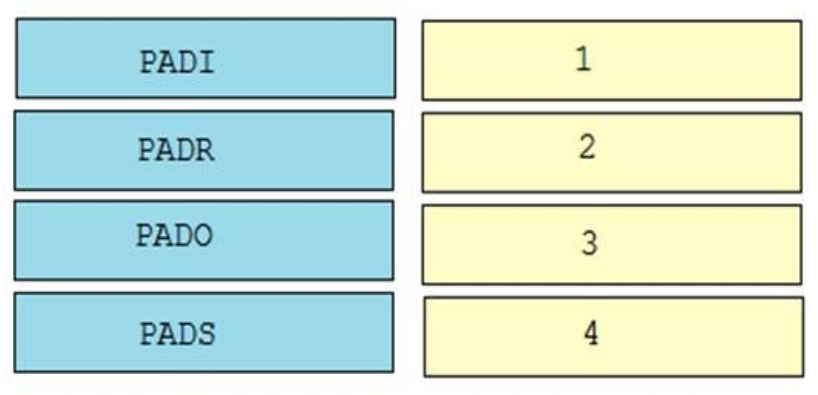
29. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the PPPoE message types from the left into the sequence in which PPPoE messages are sent on the right.Select and Place:
 Correct Answer:
Correct Answer:
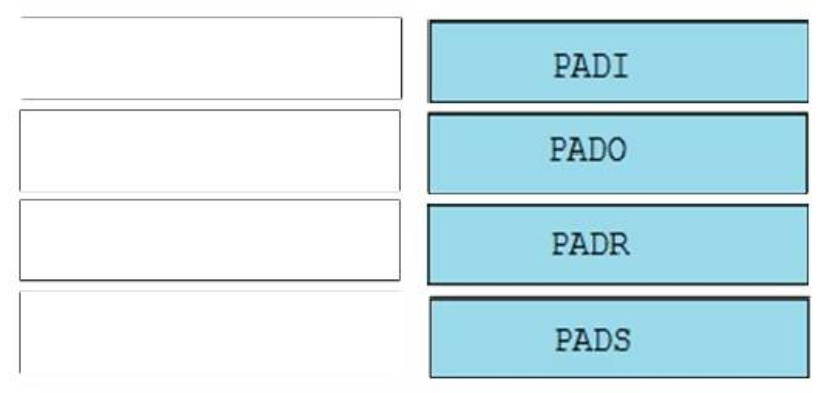
Answer:
1. PADI
2. PADO
3. PADR
4. PADS
30. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the DHCP client states from the left into the standard order in which the client passes through
them on the right.
Select and Place:
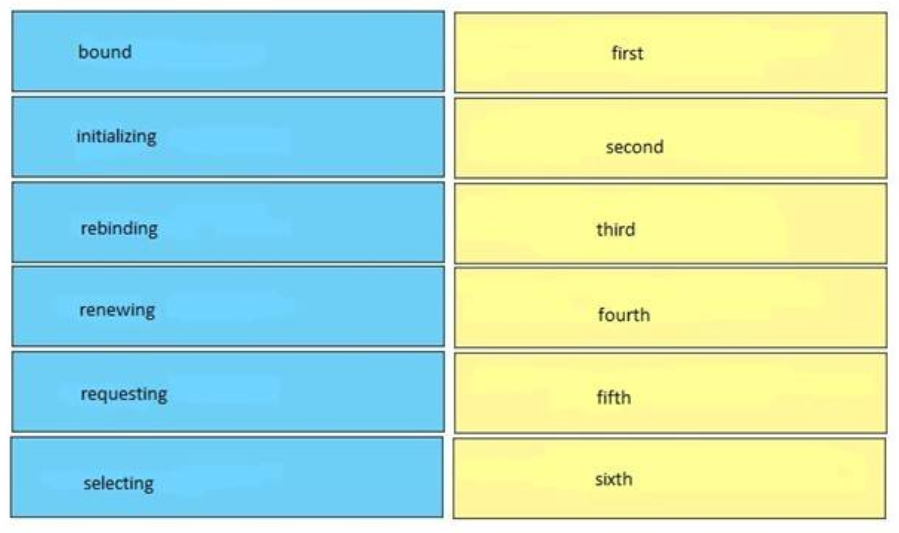
Correct Answer:

Answer:
initializing – first
selecting – second
requesting – third
bound – fourth
renewing – fifth
rebinding – sixth
31. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the DNS lookup commands from the left onto the correct effects on the right.
Select and Place:
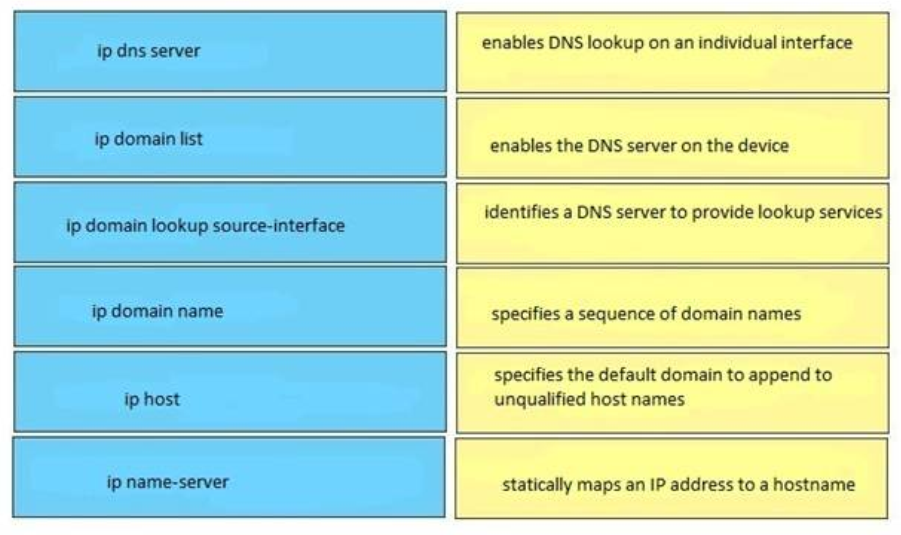
Correct Answer:

Answer:
enables DNS lookup on an individual interface <-> ip domain lookup source-interface
enables the DNS server on the device <-> ip dns server
identifies a DNS server to provide lookup services <-> ip name-server
specifies a sequence of domain names <-> ip domain list
specifies the default domain to append to unqualified host names <-> ip domain name
statically maps an IP address to a hostname <-> ip host
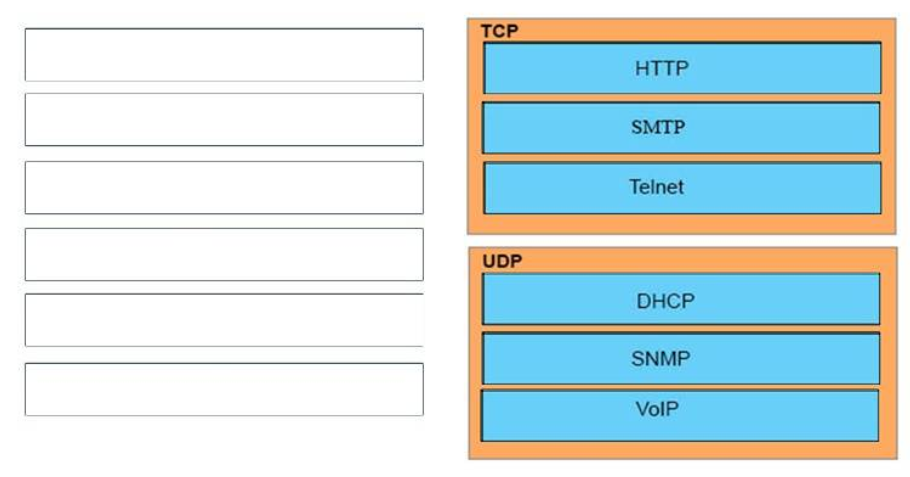
32. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the protocols from the left onto the correct IP traffic types on the right.
Select and Place:
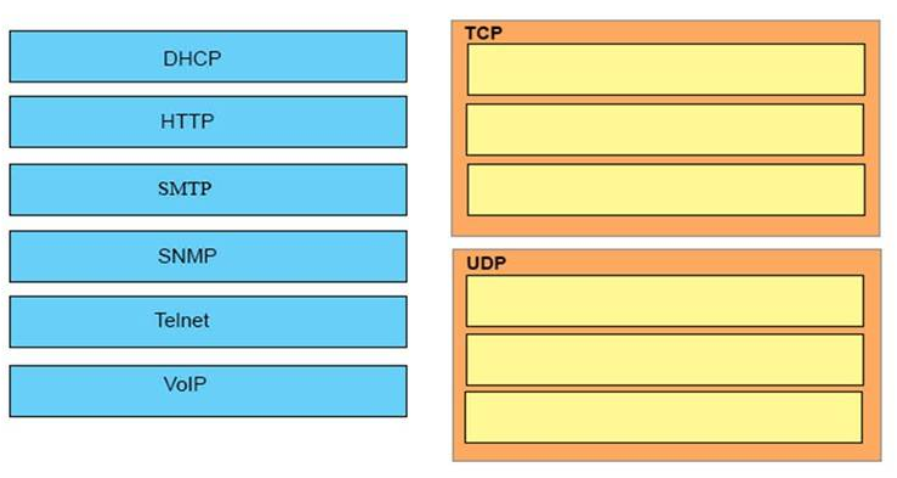
Correct Answer:
Answer:
TCP:
+ HTTP
+ SMTP
+ Telnet
UDP:
+ DHCP
+ SNMP
+ VoIP
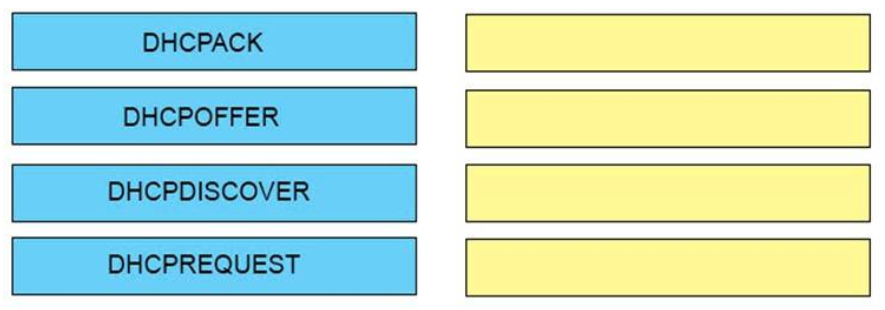
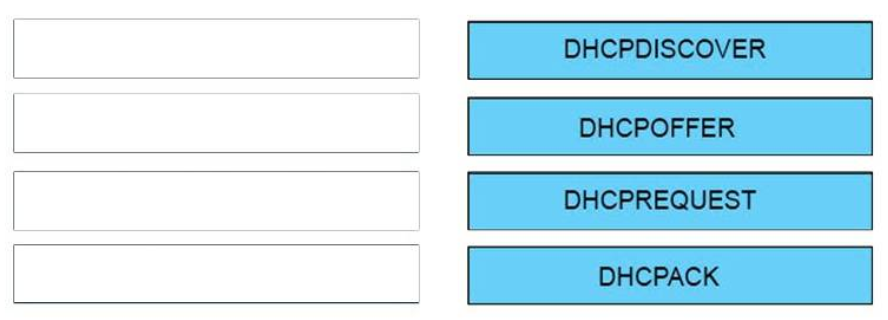
33. DRAG DROP. Order the DHCP message types as they would occur between a DHCP client and a DHCP server.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
DHCPDISCOVER
DHCPOFFER
DHCPREQUEST
DHCPACK
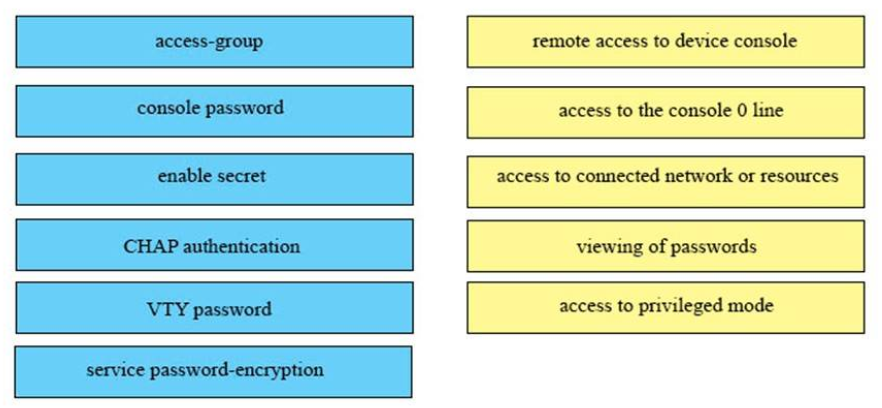
34. DRAG DROP. Drag the security features on the left to the specific security risks they help protect against on the right. (Not all options are used.)
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
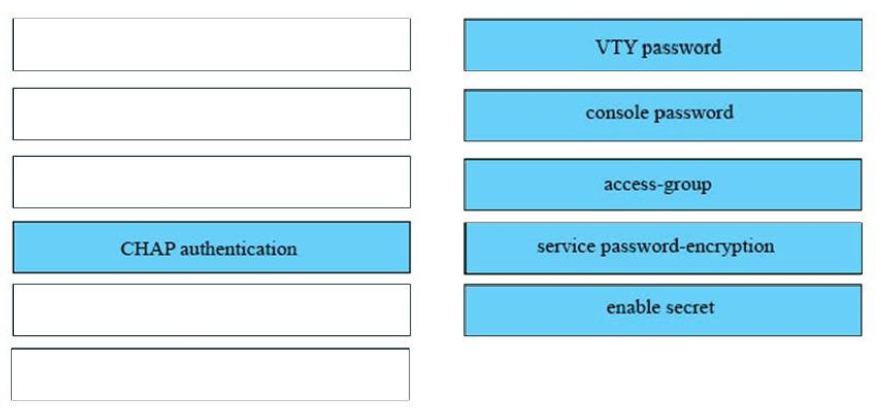
Answer:
1) VTY password: remote access to device console
2) console password: access to the console 0 line
3) access-group: access to connected networks or resources
4) service password-encryption: viewing of passwords
5) enable secret: access to privileged mode
The unselected left-box – CHAP – is used to verify the identity of the peer by means of a three-way handshake.
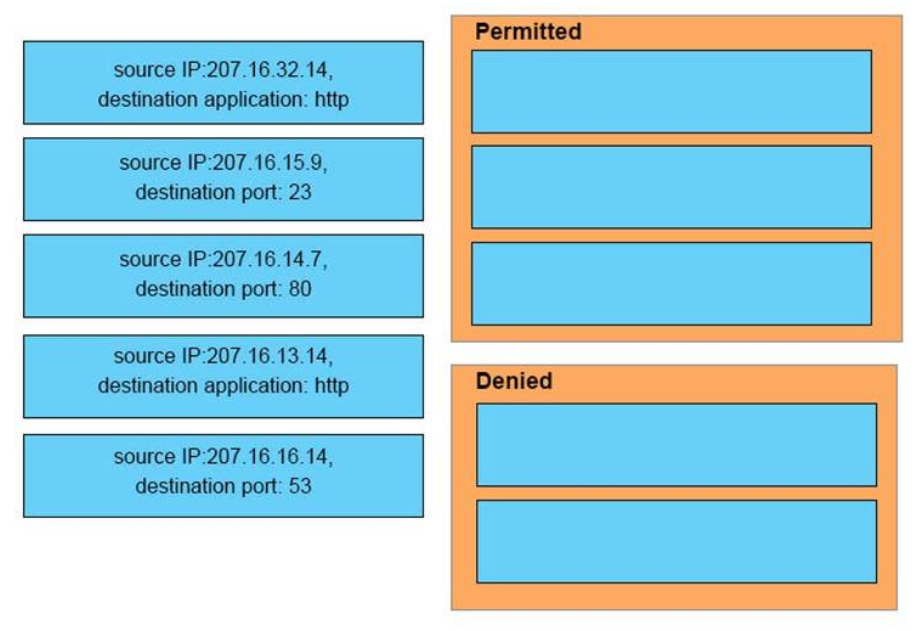
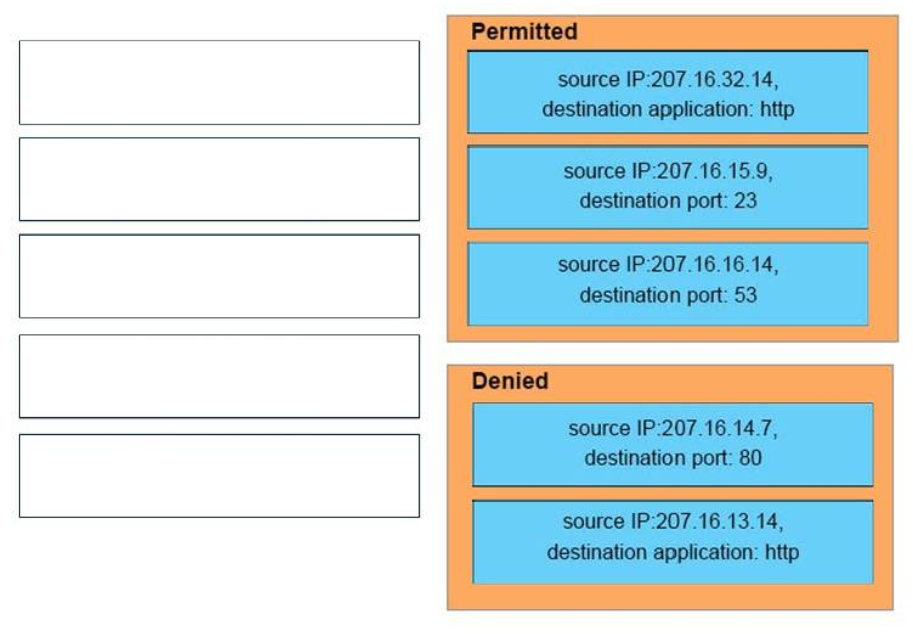
35. DRAG DROP. An interface has been configured with the access list that is shown below. On the basis of that access list,drag each information packet on the left to the appropriate category on the right.

Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
Answer:
Permitted
– source IP:207.16.32.14, destination application: http
– source IP:207.16.15.9, destination port: 23
– source IP:207.16.16.14, destination port: 53
Denied
– source IP:207.16.14.7, destination port: 80
– source IP:207.16.13.14, destination application: http
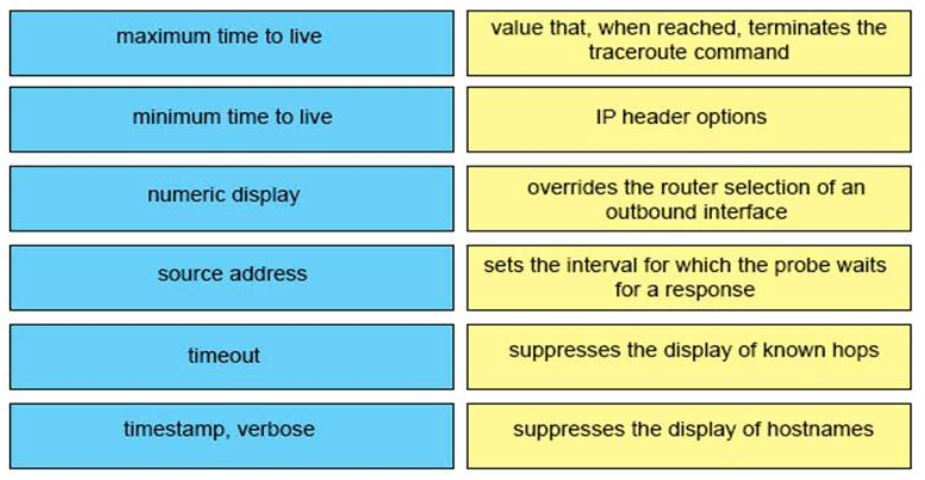
36. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the extended traceroute options from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
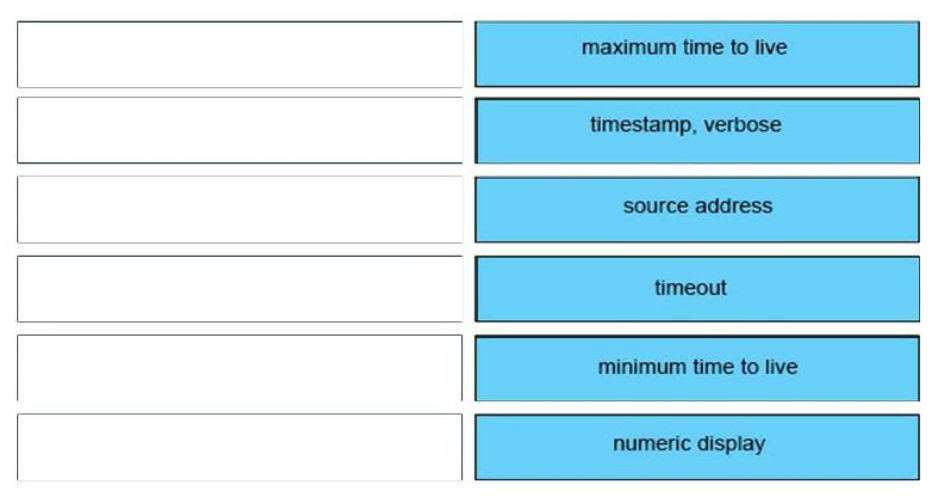
Answer:
+ Maximum time to live: value that, when reached, terminates the traceroute command
+ Minimum time to live: suppresses the display of known hops
+ Numeric display: suppresses the display of hostnames
+ Source address: overrides the router selection of an outbound interface
+ Timeout: sets the interval for which the probe waits for a response
+ Timestamp, verbose: IP header options
Numeric display: The default is to have both a symbolic and numeric display; however, you can suppress the symbolic display.
37. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the descriptions of performing an initial device configuration from the left onto the correct features or components on the right.
Select and Place:
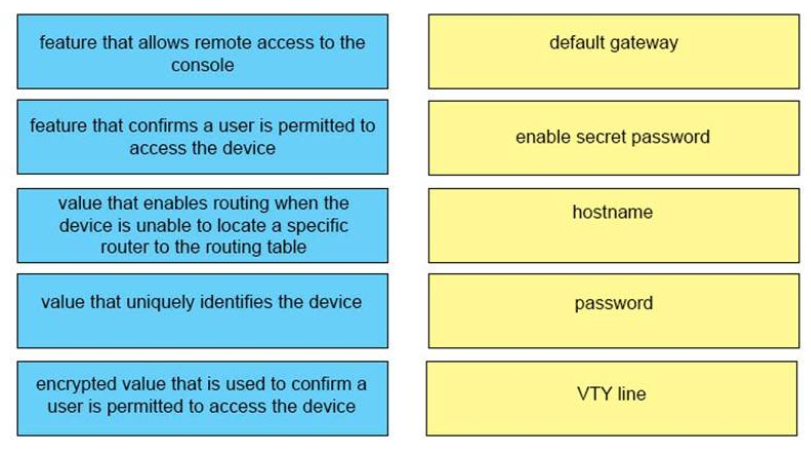
Correct Answer:
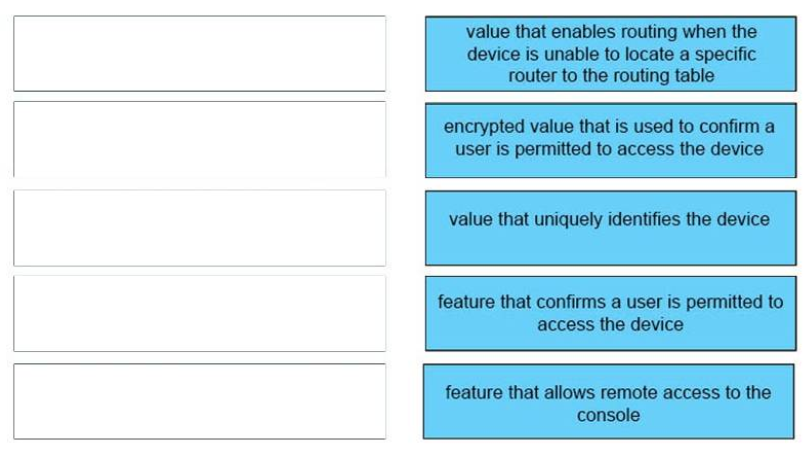
Answer:
default gateway <-> value that enables routing when the device is unable to locate a specific router to the routing table
enable secret password <-> encrypted value that is used to confirm a user is permitted to access the device
hostname <-> value that uniquely identifies the device
password <-> feature that confirms a user is permitted to access the device
VTY line <-> feature that allows remote access to the console
38. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the descriptions of logging from the left onto the correct logging features or components on the right.
Select and Place:
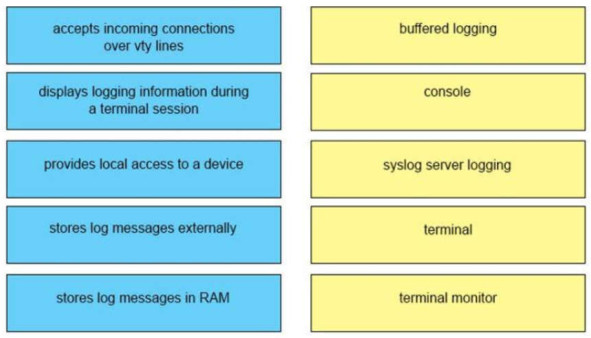
Answer:
buffered logging <-> stores log messages in RAM
console <-> provides local access to a device
syslog server logging <-> stores log messages externally
terminal <-> accepts incoming connections over vty lines
terminal monitor <-> displays logging information during a terminal session
39. DRAG DROP. You are performing the initial configuration on a new Cisco device. Drag the task from the left onto the required or optional category on the right.
Select and Place:
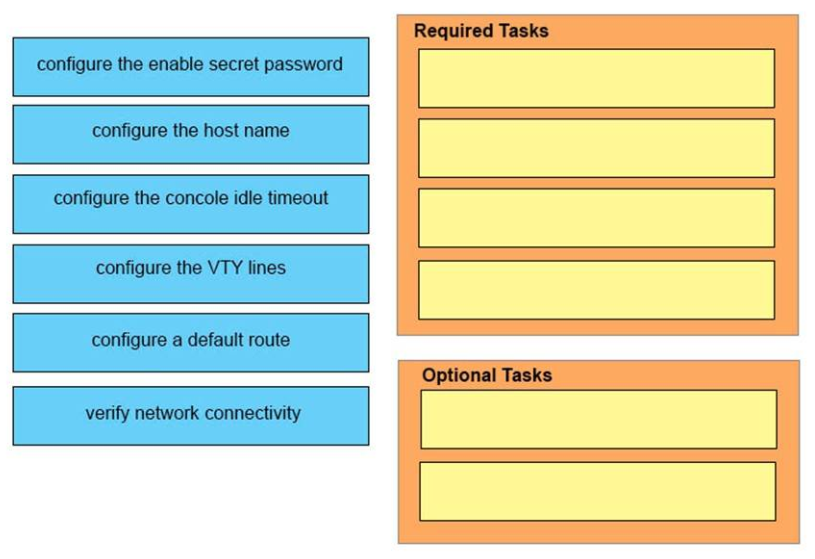
Correct Answer:
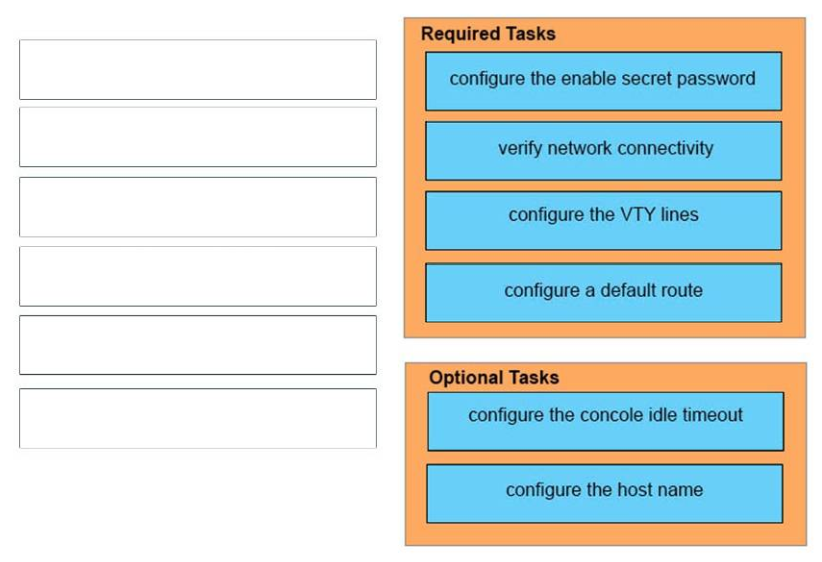
Required Tasks :
+ configure the enable secret password
+ verify network connectivity
+ configure the VTY lines
+ configure a default route
Optional Tasks :
+ configure the concole idle timeout
+ configure the host name
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/access/2900/hardware/installation/guide/
Hardware_Installation_Guide/Configure.html#91811
40. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop the network programmability features from the left onto the correct description on the right.
Select and Place:
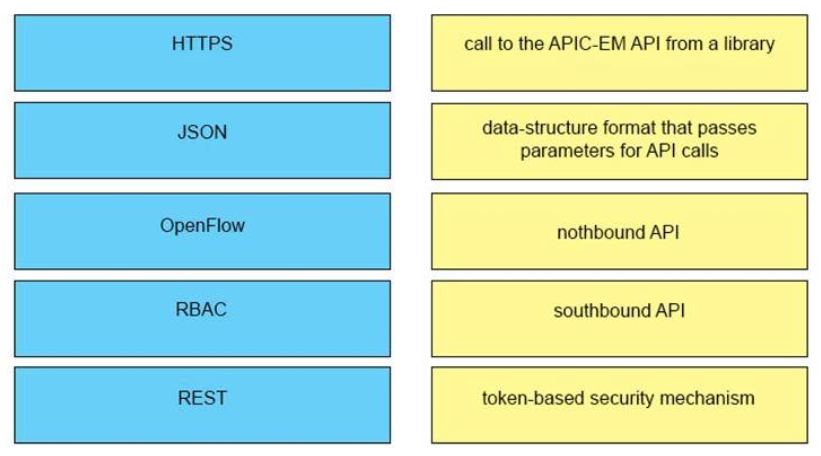
Correct Answer:

Answer:
+ HTTPS: token-based security mechanism
+ JSON: data-structure format that passes parameters for API calls
+ OpenFlow: southbound API
+ RBAC: call to the APIC-EM API from a library
+ REST: northbound API
Javascript Object Notation (JSON) is used to pass parameters when making API calls and is also the returned data format.
What’s RBAC?
The Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) mechanism utilizes security tokens that the controller issues upon successful authentication of a user of the APIC-EM controller. All subsequent requests from the authenticated user must provide a valid token.
41. DRAG DROP. Drag and drop each WAN design option on the left onto the correct description on the right.
Select and Place:
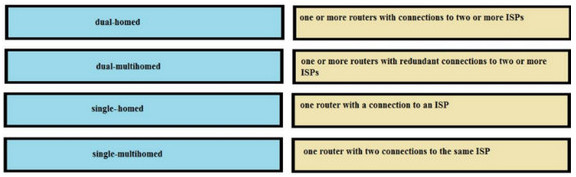
Correct Answer:
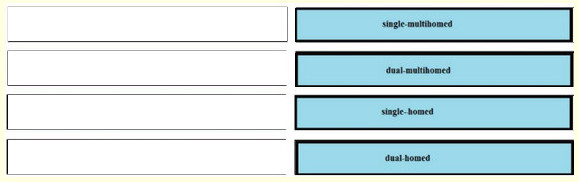
Answer:
one or more routers with connections to two or more ISPs <-> single-multihomed
one or more routers with redundant connections to two or more ISPs <-> dual-multihomed
one router with a connection to an ISP <-> single-homed
one router with two connections to the same ISP <-> dual-homed
42. DRAG DROP.
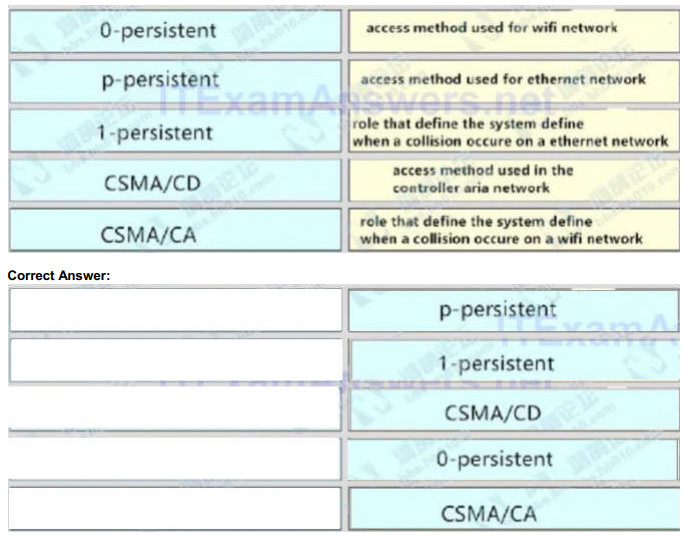
access method used for wifi network <-> p-persistent
access method used for ethernet network <-> 1-persistent
role that define the system define when a collision occure on a ethernet network <-> CSMA/CD
access method used in the controller aria network <-> 0-persistent
role that define the system define when a collision occure on a wifi network <-> CSMA/CA
44. Drag and drop the application protocols from the left onto the transport protocols that is uses on the right.
Correct Answer:
45.
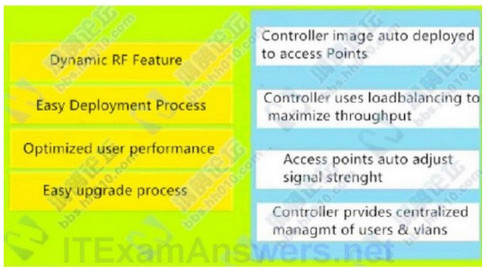
Correct Answer:
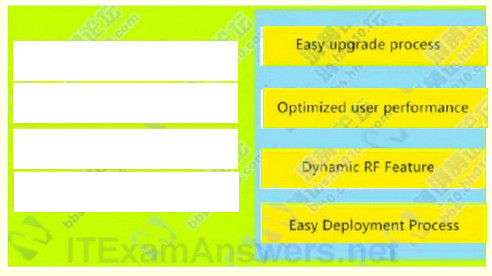
Controller image auto deployed to access Points : Easy upgrade process
Controller uses loadbalancing to maximize throughput : Optimized user performance
Access points auto adjust signal strenght : Dynamic RF Feature
Controller prvides centralized managmt of users & vlans : Easy Deployment Process
46.

Correct Answer:
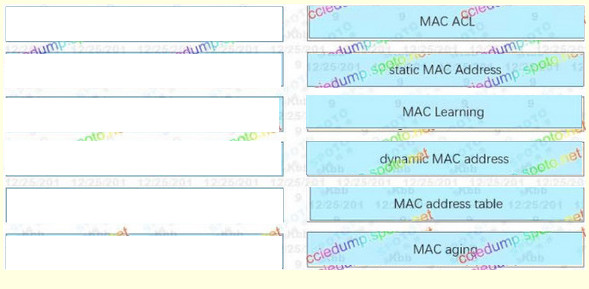
mac address that is learned by the switch through normal traffic flows : Dynamic mac address
associates a learned mac address with its connected interface : Mac address table
removing an inactive mac after a specified time : Mac aging
feature that determines whether incoming traffic will be allowed : Mac ACL
adding a previously unknown mac into the address table : Mac learning
mac address that remains in the mac address table after reboot : Static mac
47.

Correct Answer:

– Discover to server : initializing
– from Offer from server : selecting
– Request to server : requesting
– from Ack from server : bound
– from same dhcp server : renewing
– from different dhcp server : rebinding
48.
RIPV1 :
– classful
– Non support authentication
Updates send in broadcast
– Non support VLSM
RIPV2:
– ciassiess
– support authentication
– Updates send in multicast
– Support VLSM
49.
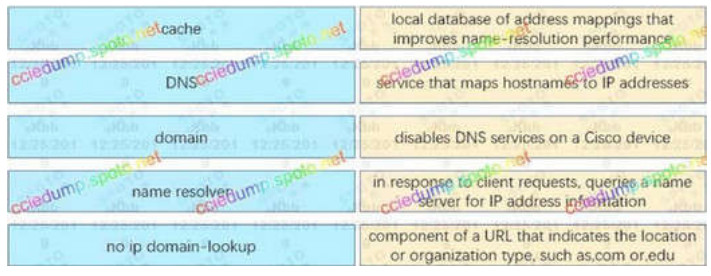
Correct Answer:

– Local database of address mappings that improves name-resolution performance : cache
– Service that maps hostnames to IP addresses : DNS
– Disables DNS services on a cisco device : no ip domain-lookup
– In response to client requests, queries a name server for IP address information : name resolver
– Component of e URL that indicates the location or organization type, such as .com or. edu : domain
50.
Drag drop about RADIUS & TACACS+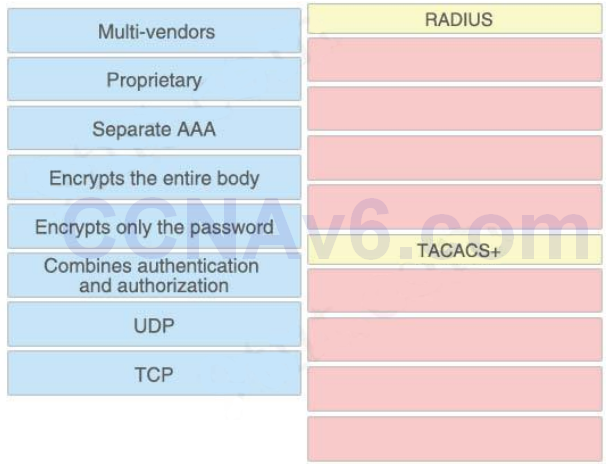
Answer:
RADIUS:
+ Multi-vendors
+ UDP
+ Combines authentication and authorization
+ Encrypts only the password
TACACS+:
+ Proprietary
+ Separate AAA
+ Encrypts the entire body
+ TCP
51.

Correct Answer:
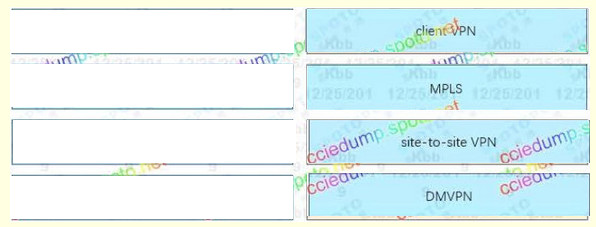
– Enable moble devices to connect to an enterprise network : client VPN
– Use the logical ful-mesh network of a service provider across an enterprise headquarters and remote stes : MPLS
– Securely connect two networks over an untrusted network. : site-to-site VPN
– Use GRE tunnels and IPSEC to create a ful-mesh network through a central location : DMVPN
52.
All nodes of Link Local –> FF02::1
All EIGRPv3 Routers –> FF02::A
All OSPFV3 Designated Routers –> FF02::6
All PIM Routers –> FF02::D
All OSPFv3 Routers –> FF02::5
All Routers of site local –> FF05::2
53. Refer to the exhibit

Drag and drop the routing table components on the left onto the corresponding letter from the exhibit on the right. Not all options are used.
Select and Place – Your Response

Correct Answer:
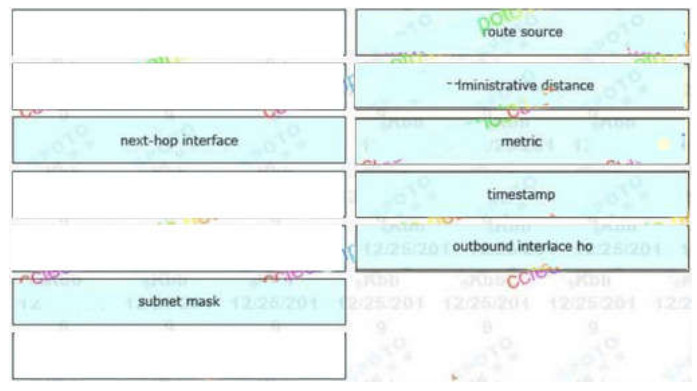
A: route source
B: administrative distance
C: metric
D: timestamp
E: outbound interlace ho
54. Drag and drop the source from the left to the numbers on the right. Beginning with the lowest and ending with highest administrative distance.
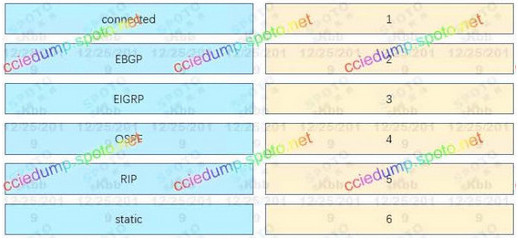
Correct Answer:

1: connected
2: static
3: EBGP
4: EIGRP
5: OSPF
6: RIP
55. You are configuration a switch so that it accepts traffic from a maximum of two dynamic MAC addresses. Drag and drop the required configuration commands on the left into the correct sequence on the right. (Not all commands are used)

Correct Answer:
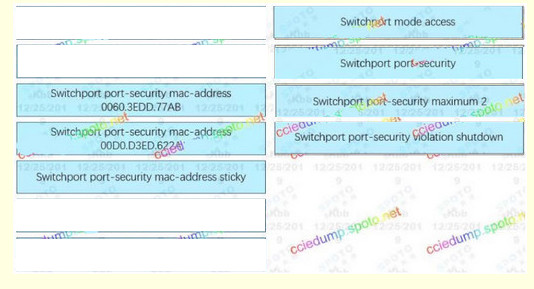
1: switchport mode access
2: switchport port-security
3: switchport port-security mac-address sticky
4: switchport port-security maximum 2
switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]
If we don’t specify the MAC address (like in this question) then the switch will dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into your running-configuration

Q 19
cleared from the CAM table when the switch reboots nonsecure MAC address
configured with the switchport-security mac-address command sticky MAC address
dynamically learned addresses that can be retained permanently dynamic secure MAC address
requires access VLAN configuration only static secure MAC address
Command configured with the switchport-security mac-address without word “sticky” as part of the command adding just static secure MAC address.
so it’s
switchport-security mac-address 00:00:00:00:00:00
or
switchport-security mac-address sticky
And dynamically learned addresses that can be retained permanently only if sticky command is used, e.i. address appears in running config
Question 46
On the image, it’s shown that “MAC Learning” has been dragged onto “Mac that is learned by the switch through normal traffic flow” while on the transcription of the question it is different, it is “Dynamic MAC address” has been dragged onto “Mac that is learned by the switch through normal traffic flow”. I wanted to know which version is right because for me it seems like any one of them works.
fixed, thanks you
For DnD #16, why is filtering in the Control Planes? I was thinking this is similar to ACL thus should be in Data Plane. Not sure though.
Q. 41 also answers are wrong:
https://networklessons.com/cisco/ccna-routing-switching-icnd2-200-105/singledual-homed-and-multi-homed-designs
Question 38. Syslog server logging should not be a external logging?
Is this Drag-Drop valid on this time Thanks