Time limit: 0
Quiz-summary
0 of 214 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
Information
Section I: Network Fundamentals - Test Online
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 214 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 214
1. Question
1 pointsIn which two formats can the IPv6 address fd15:0db8:0000:0000:0700:0003:400F:572B be written? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In this case we use two rules: + Leading zeros in a field are optional + Successive fields of 0 are represented as ::, but only once in an address If you are not sure about IPV6, please read our IPv6 tutorial. -
Question 2 of 214
2. Question
1 pointsWhat are three characteristics of the TCP protocol? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Note: Answer F is not correct because TCP does not require applications to determine the retranmission. TCP itself will determine if the data packets should be retransmitted or not. -
Question 3 of 214
3. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit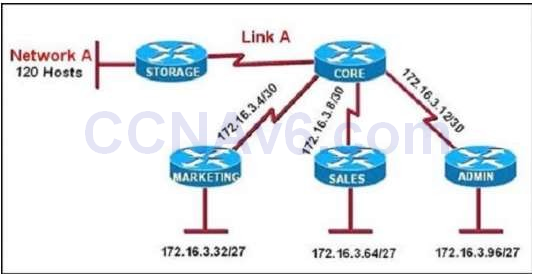 All of the routers in the network are configured with the ip subnet-zero command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two.) Correct
All of the routers in the network are configured with the ip subnet-zero command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two.) Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Network A needs 120 hosts < 128 = 27 -> Need a subnet mask of 7 bit 0s -> “/25″. Because the ip subnet-zero command is used, network 172.16.3.0/30 can be used. Answer E “Link A – 172.16.3.40/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to MARKETING subnet (172.16.3.32/27). Answer F “Link A – 172.16.3.112/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to ADMIN subnet (172.16.3.96/27). -
Question 4 of 214
4. Question
1 pointsWhich type of device can be replaced by the use of subinterfaces for VLAN routing?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 5 of 214
5. Question
1 pointsWhat are two benefits of private IPv4 IP addresses? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Usually using private IPv4 addresses in a organization is free so surely they are less costly than public IP addresses which you have to buy -> B is correct. Also we can use private IPv4 addresses to devices that do not need to connect to the Internet because Internet requires public IPv4 addresses -> C is correct. Answer D is not correct as we still need to use NAT policies to limit which private IPv4 addresses in our company can access our resources. -
Question 6 of 214
6. Question
1 pointsWhich two server types are used to support DNS lookup? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 7 of 214
7. Question
1 pointsWhich three statements about IPv6 prefixes are true? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect

Hint
-
Question 8 of 214
8. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit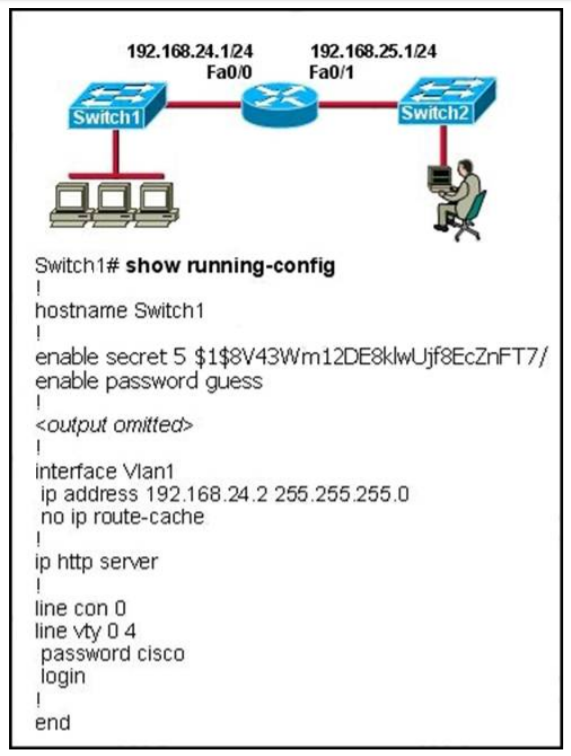 The network administrator cannot connect to Switch 1 over a Telnet session, although the hosts attached to Switch1 can ping the interface Fa0/0 of the router. Given the information in the graphic and assuming that the router and Switch2 are configured properly, which of the following commands should be issued on Switch1 to correct this problem? Correct
The network administrator cannot connect to Switch 1 over a Telnet session, although the hosts attached to Switch1 can ping the interface Fa0/0 of the router. Given the information in the graphic and assuming that the router and Switch2 are configured properly, which of the following commands should be issued on Switch1 to correct this problem? Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 9 of 214
9. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about IPv6 and routing protocols are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Link-local addresses only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is only valid on the current subnet. It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address). -
Question 10 of 214
10. Question
1 pointsWhat will happen if a private IP address is assigned to a public interface connected to an ISP?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 11 of 214
11. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about wireless LAN controllers are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Cisco Wireless is designed to provide 802.11 wireless networking solutions for enterprises and service providers. Cisco Wireless simplifies deploying and managing large-scale wireless LANs and enables a unique best-in-class security infrastructure. The operating system manages all data client, communications, and system administration functions, performs radio resource management (RRM) functions, manages system-wide mobility policies using the operating system security solution, and coordinates all security functions using the operating system security framework. Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-2/config-guide/b_cg82/b_cg82_chapter_01.html -
Question 12 of 214
12. Question
1 pointsWhich step in the router boot process searches for an IOS image to load into the router?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The following details the router boot process: 1. The router is powered on. 2. The router first runs Power-On Self Test (POST) 3. The bootstrap checks the Configuration Register value to specify where to load the IOS. By default (the default value of Configuration Register is 2102, in hexadecimal), the router first looks for “boot system” commands in startup-config file. If it finds these commands, it will run boot system commands in order they appear in startup-config to locate the IOS. If not, the IOS image is loaded from Flash . If the IOS is not found in Flash, the bootstrap can try to load the IOS from TFTP server or from ROM (mini-IOS). 4. After the IOS is found, it is loaded into RAM. 5. The IOS attempts to load the configuration file (startup-config) from NVRAM to RAM. If the startup-config is not found in NVRAM, the IOS attempts to load a configuration file from TFTP. If no TFTP server responds, the router enters Setup Mode (Initial Configuration Mode). For more information about booting process please read our Cisco Router Boot Sequence tutorial. -
Question 13 of 214
13. Question
1 pointsWhich protocol advertises a virtual IP address to facilitate transparent failover of a Cisco routing device?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
First Hop Redundancy Protocol (FHRP) is a protocol that enables two or more devices to work together in a group, sharing a single IP address, the virtual IP address. One router is elected to handle all requests sent to the virtual IP address. With HSRP, this is the active router. An HSRP group has one active router and at least one standby router. -
Question 14 of 214
14. Question
1 pointsRefer to exhibit. Which command can you enter to verify link speed and duplex setting on the interface?R1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1. 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#speed 100 R1(config-if)#duplex full
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The “show interfaces …” command gives us information about speed and duplex mode of the interface. In the output below, the link speed is 100Mbps and it is working in Full-duplex mode.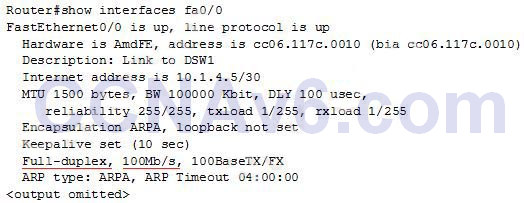
-
Question 15 of 214
15. Question
1 pointsWhich utility can you use to determine whether a switch can send echo requests and replies?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
“ping” command is used to send echo requests and receive echo replies. -
Question 16 of 214
16. Question
1 pointsIf computer A is sending traffic to computer B, which option is the source IP address when a packet leaves R1 on interface F0/1?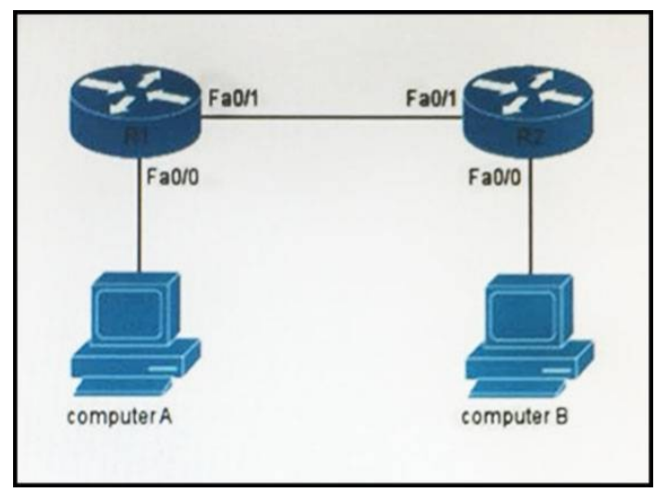 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In all the way on the path, the source and destination IP addresses never change, only the source and destination MAC address are changed on each segment. -
Question 17 of 214
17. Question
1 pointsWhich functionality does split horizon provide?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 18 of 214
18. Question
1 pointsWhich MAC protocol sets a random timer to reattempt communication ?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 19 of 214
19. Question
1 pointsHow many host addresses are available on the network 192.168.1.0 subnet 255.255.255 240?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 20 of 214
20. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about unique local IPv6 addresses are true?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
A IPv6 Unique Local Address is an IPv6 address in the block FC00::/7. It is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address. It is not routable on the global Internet.Note: In the past, Site-local addresses (FEC0::/10) are equivalent to private IP addresses in IPv4 but now they are deprecated. -
Question 21 of 214
21. Question
1 pointsIf three devices are plugged into one port on a switch and two devices are plugged into a different port, how many collision domains are on the switch?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 22 of 214
22. Question
1 pointsHow does a router handle an incoming packet whose destination network is missing from the routing table?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Change from “it discards the packet” to “it routes the packet to the default route” because there is new question Which definition of default route is true? with answer “A route used when a destination route is missing.” -
Question 23 of 214
23. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about Ethernet standards are true?(choose two)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 24 of 214
24. Question
1 pointsWhich command enables IPv6 forwarding on a Cisco router?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
An example of configuring RIPng (similar to RIPv2 but is used for IPv6) is shown below: Router(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing (Enables the forwarding of IPv6 unicast datagrams globally on the router) Router(config)#interface fa0/0 Router(config-if)#ipv6 rip 9tut enable (9tut is the process name of this RIPng) -
Question 25 of 214
25. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. If R1 receives a packet destined to 172.16.1.1, to which IP address does it send the packet?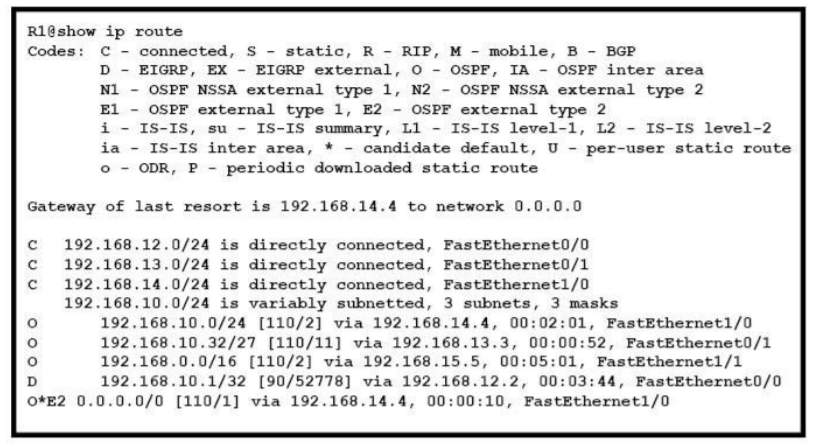 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
It can’t find the address 172.16.1.1 so it will be directed to the Gate of last resort 192.168.14.4 -
Question 26 of 214
26. Question
1 pointsWhat is known as “one-to-nearest” addressing in IPv6?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 27 of 214
27. Question
1 pointsWhen a router is unable to find a known route in the routing table, how does it handle the packet?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In fact this question is not clear. If we understand that “router is unable to find a known route in the routing table” and there is no default route in the routing table then the router will surely discard the packet -> A is correct. But we are not sure if there is a default route or not so let learn more about gateway of last resort. A Gateway of Last Resort is a route used by the router when no other known route exists to send the IP packet. For CCNA level, when ip routing feature is enabled, a gateway of last resort is usually created by: + The “ip default-network” command (but dynamic routing protocols have different behaviors). But in general, the “ip default-network” cannot set the gateway of last resort without a known route in the routing table. + Creating a static route to network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 is another way to set the gateway of last resort on a router. This is the reason why this question is not clear as it does not tell us if a default route exists or not. Maybe in this question a default route does not exist. Otherwise the author would notice and indicate it in the question. For more information about Gateway of Last Resort, please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/routing-information-protocol-rip/16448-default.html -
Question 28 of 214
28. Question
1 pointsIf router R1 knows a static route to a destination network and then learns about the same destination network through a dynamic routing protocol, how does R1 respond?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
By default the administrative distance of a static route is 1, meaning it will be preferred over all dynamic routing protocols. If you want to have the dynamic routing protocol used and have the static route be used only as a backup, you need to increase the AD of the static route so that it is higher than the dynamic routing protocol. -
Question 29 of 214
29. Question
1 pointsWhich option is the correct CIDR notation for 192.168.0.0 subnet 255.255.255.252?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 30 of 214
30. Question
1 pointsWhich six-byte field in a basic Ethernet frame must be an individual address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The picture below shows the fields in IEEE 802.1Q frame.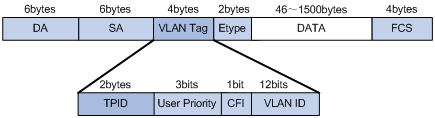 The SA field is the source address field. The field should be set to the MAC address of the switch port that transmits the frame. It is a 48-bit value (6 bytes). The receiving device may ignore the SA field of the frame.
In fact there is another correct answer for this question: DA (Destination Address) which also consists of 6 bytes. Maybe there is a mistake or typo in this question.
The SA field is the source address field. The field should be set to the MAC address of the switch port that transmits the frame. It is a 48-bit value (6 bytes). The receiving device may ignore the SA field of the frame.
In fact there is another correct answer for this question: DA (Destination Address) which also consists of 6 bytes. Maybe there is a mistake or typo in this question. -
Question 31 of 214
31. Question
1 pointsIf a router has four interfaces and each interface is connected to four switches, how many broadcast domains are present on the router?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Remember that only route interface can separate broadcast domain (while switch interface separate collision domain) so the broadcast domains are equal to the number of router interfaces, which is four in this case. -
Question 32 of 214
32. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. What is the most appropriate summarization for these routes?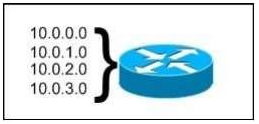 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The 10.0.0.0/22 subnet mask will include the 10.0.0.0, 10.0.1.0, 10.0.2.0, and 10.0.3.0 networks, and only those four networks. -
Question 33 of 214
33. Question
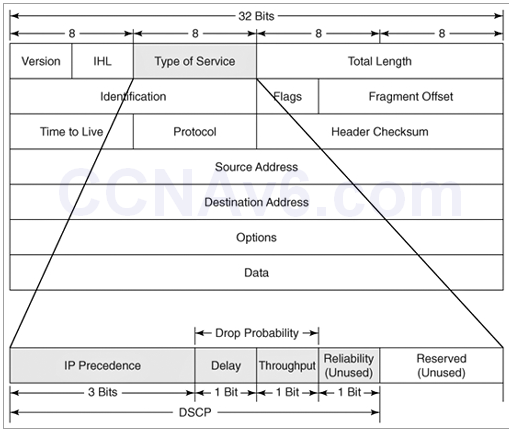
1 pointsWhat 8-bit field exists in IP packet for QoS?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The IP datagram header contains an 8-bit field called ToS (Type of Service). The field has been part of the IP header since the beginning, but it was rarely used until the recent introduction of Differentiated Services (Diff-Serv).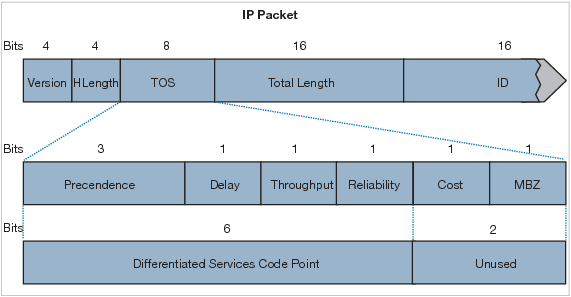 Note:
+ CoS does not exists in an IP header. It appears in the header of a 802.1Q frame only. CoS is used for QoS on a trunk link.
+ DSCP uses the first 6 bits of the TOS field.
Note:
+ CoS does not exists in an IP header. It appears in the header of a 802.1Q frame only. CoS is used for QoS on a trunk link.
+ DSCP uses the first 6 bits of the TOS field. -
Question 34 of 214
34. Question
1 pointsWhat feature uses a random time to re-send a frame?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 35 of 214
35. Question
1 pointsTwo hosts are attached to a switch with the default configuration. Which statement about the configuration is true?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
All ports on a Layer 2 switch are in the same broadcast domain. Only router ports separate broadcast domains. -
Question 36 of 214
36. Question
1 pointsIf a router has 3 hosts connected in one port and two other hosts connected in another port, how may broadcast domains are present on the router?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 37 of 214
37. Question
1 pointsWhat are three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
IPv6 includes two different unicast address assignments: + Global unicast address + Link-local address The global unicast address is globally unique in the Internet. The example IPv6 address that is shown below is a global unicast address.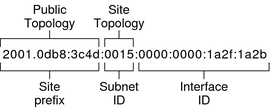 + Site prefix (global routing prefix): defines the public topology of your network to a router. You obtain the site prefix for your enterprise from an ISP or Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
+ Site Topology and Subnet ID: the subnet ID defines an administrative subnet of the network and is up to 16 bits in length. You assign a subnet ID as part of IPv6 network configuration. The subnet prefix defines the site topology to a router by specifying the specific link to which the subnet has been assigned
+ Interface ID: identifies an interface of a particular node. An interface ID must be unique within the subnet.
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23823_01/html/816-4554/ipv6-overview-10.html
+ Site prefix (global routing prefix): defines the public topology of your network to a router. You obtain the site prefix for your enterprise from an ISP or Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
+ Site Topology and Subnet ID: the subnet ID defines an administrative subnet of the network and is up to 16 bits in length. You assign a subnet ID as part of IPv6 network configuration. The subnet prefix defines the site topology to a router by specifying the specific link to which the subnet has been assigned
+ Interface ID: identifies an interface of a particular node. An interface ID must be unique within the subnet.
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23823_01/html/816-4554/ipv6-overview-10.html -
Question 38 of 214
38. Question
1 pointsYou have been asked to come up with a subnet mask that will allow all three web servers to be on the same network while providing the maximum number of subnets. Which network address and subnet mask meet this requirement?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 39 of 214
39. Question
1 pointsWhat is the correct routing match to reach 172.16.1.5/32?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Although all above answers are correct but 172.16.1.0/26 is the best choice as it is the most specific prefix-match one. -
Question 40 of 214
40. Question
1 pointsWhich layer in the OSI reference model is responsible for determining the availability of the receiving program and checking to see if enough resources exist for that communication?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 41 of 214
41. Question
1 pointsWhat are the address that will show at the show ip route if we configure the above statements? (Choose Three.) Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
With auto-summary feature is turned on, EIGRP will summary these networks to their classful networks automatically. For example: + 172.15.4.0 belongs to class B so it will be summarized to 172.15.0.0 + 10.4.3.0 belongs to class A so it will be summarized to 10.0.0.0 + 192.168.4.0 belongs to class C so it will be summarized to 192.168.4.0 (same) -
Question 42 of 214
42. Question
1 pointsWhich feature facilitates the tagging of frames on a specific VLAN?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 43 of 214
43. Question
1 pointsWhat does split horizon prevent?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Split horizon is used in distance vector routing protocols (like RIP, EIGRP) to prevent routing loops by prohibiting a router from advertising a route back to the interface from which it was learned. -
Question 44 of 214
44. Question
1 pointsWhich IPV6 feature is supported in IPV4 but is not commonly used?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Only three connection types are commonly known and used in Internet Protocol version four (IPv4) networks: unicast, multicast and broadcast. A fourth connection type, Anycast, was unknown until IPv6 made it a standard connection type. Anycast is not standardized in IPv4 but can be emulated. IPv4 Anycast addressing is a good solution to provide localization for services and servers in order to obtain robustness, redundancy and resiliency. The basic idea of Anycast is very simple: multiple servers, which share the same IP address, host the same service. The routing infrastructure sends IP packets to the nearest server (according to the metric of the routing protocol used). The major benefits of employing Anycast in IPv4 are improved latency times, server load balancing, and improved security. Reference: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.116.6367&rep=rep1&type=pdf -
Question 45 of 214
45. Question
1 pointsWhat is the binary pattern of unique ipv6 unique local address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
A IPv6 Unique Local Address is an IPv6 address in the block FC00::/7, which means that IPv6 Unique Local addresses begin with 7 bits with exact binary pattern as 1111 110 -> Answer B is correct. Note: IPv6 Unique Local Address is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address. It is not routable on the global Internet. -
Question 46 of 214
46. Question
1 pointsDescribe the best way to troubleshoot and isolate a network problem?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In fact all three of the above answers are in the problem-solving process but “gather facts” is at Step 2 while “Create an action plan” and “Implement an action plan” is at step 4 & 5 of this link http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1901.html Step 2 Gather the facts that you need to help isolate possible causes. Ask questions of affected users, network administrators, managers, and other key people. Collect information from sources such as network management systems, protocol analyzer traces, output from router diagnostic commands, or software release notes. -
Question 47 of 214
47. Question
1 pointsn which byte of an IP packet can traffic be marked?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
-
Question 48 of 214
48. Question
1 pointsWhat are two benefits of Private IPv4 Addresses? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
http://smallbusiness.chron.com/advantages-disadvantages-using-private-ip-address-space-46424.html -
Question 49 of 214
49. Question
1 pointsHow many bits represent network id in a IPv6 address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Each ISP receives a /32 and provides a /48 for each site-> every ISP can provide 2(48-32) = 65,536 site addresses (note: each network organized by a single entity is often called a site).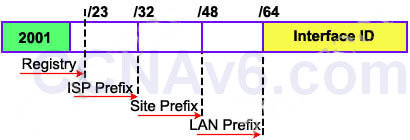 Each site provides /64 for each LAN -> each site can provide 2(64-48) = 65,536 LAN addresses for use in their private networks.
So each LAN can provide 264 interface addresses for hosts.
-> Global routing information is identified within the first 64-bit prefix.
Now let’s see an example of IPv6 prefix: 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64:
Each site provides /64 for each LAN -> each site can provide 2(64-48) = 65,536 LAN addresses for use in their private networks.
So each LAN can provide 264 interface addresses for hosts.
-> Global routing information is identified within the first 64-bit prefix.
Now let’s see an example of IPv6 prefix: 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64:
 In this example, the RIR has been assigned a 12-bit prefix. The ISP has been assigned a 32-bit prefix and the site is assigned a 48-bit site ID. The next 16-bit is the subnet field and it can allow 216, or 65536 subnets. This number is redundant for largest corporations on the world!
The 64-bit left (which is not shown the above example) is the Interface ID or host part and it is much more bigger: 64 bits or 264 hosts per subnet! For example, from the prefix 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64 an administrator can assign an IPv6 address 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD:218:34EF:AD34:98D to a host.
In this example, the RIR has been assigned a 12-bit prefix. The ISP has been assigned a 32-bit prefix and the site is assigned a 48-bit site ID. The next 16-bit is the subnet field and it can allow 216, or 65536 subnets. This number is redundant for largest corporations on the world!
The 64-bit left (which is not shown the above example) is the Interface ID or host part and it is much more bigger: 64 bits or 264 hosts per subnet! For example, from the prefix 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64 an administrator can assign an IPv6 address 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD:218:34EF:AD34:98D to a host. -
Question 50 of 214
50. Question
1 pointsWhat layer of the OSI Model is included in TCP/IP Model’s INTERNET layer?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Internet Layer in TCP/IP Model is equivalent to the Network Layer of the OSI Model.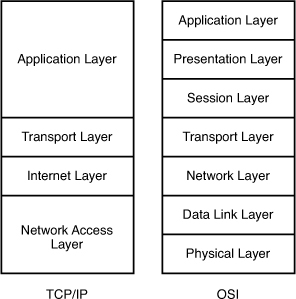
-
Question 51 of 214
51. Question
1 pointsWhich two features can dynamically assign IPv6 addresses? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Answer “DHCP” is not correct because DHCP can only assign IPv4 address. To assign IPv6 address, DHCPv6 should be used instead. Answer “NHRP” is not correct because it is a protocol used in DMVPN. Answer “ISATAP tunneling” is not correct because it is an IPv6 transition mechanism to transmit IPv6 packets between dual-stack nodes on top of an IPv4 network. The two types of autoconfiguration are “stateless” and “stateful.” Stateful autoconfiguration is the IPv6 equivalent of DHCP. A new protocol, called DHCPv6 (and based closely on DHCP), is used to pass out addressing and service information in the same way that DHCP is used in IPv4. This is called “stateful” because the DHCP server and the client must both maintain state information to keep addresses from conflicting, to handle leases, and to renew addresses over time -> Answer “IPv6 stateful autoconfiguration” is correct. Stateless Autoconfiguration allows an interface to automatically “lease” an IPv6 address and does not require the establishment of an server to delve out address space. Stateless autoconfiguration allows a host to propose an address which will probably be unique (based on the network prefix and its Ethernet MAC address) and propose its use on the network. Because no server has to approve the use of the address, or pass it out, stateless autoconfiguration is simpler. This is the default mode of operation for most IPv6 systems, including servers. So answer “IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration” is correct too. -
Question 52 of 214
52. Question
1 pointsHow many usable host are there per subnet if you have the address of 192.168.10.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
From the subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 (/28) we learn there are 24 – 2 = 14 hosts per subnet. -
Question 53 of 214
53. Question
1 pointsWhich type of cable must you use to connect two devices with MDI interfaces?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Use an Ethernet straight-through cable to connect an medium dependent interface (MDI) to an MDI-X port. Use a cross-over cable to connect an MDI to an MDI port, or an MDI-X to an MDI-X port. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/asa/hw/maintenance/5505guide/ASA5505HIG/pinouts.html Note: MDI/MDIX is a type of Ethernet port connection using twisted pair cabling. -
Question 54 of 214
54. Question
1 pointsWhich type of IPv6 address also exists in IPv4 but is barely used?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 55 of 214
55. Question
1 pointsWhich IPv6 header field is equivalent to the TTL?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
This field is same as Time To Live (TTL) in IPv4, which is used to stop packet to loop in the network infinitely. The value of Hop Limit field is decremented by 1 when it passes a Layer 3 device (like a router). When this field reaches 0 the packet is dropped. -
Question 56 of 214
56. Question
1 pointsWhich IP configuration does the CIDR notation 192.168.1.1/25 refer?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
“/25” means 1111 1111.1111 1111.1000 0000 in binary or 255.255.255.128 in decimal. -
Question 57 of 214
57. Question
1 pointsWhich option is the correct CIDR notation for 192.168.0.0 subnet 255.255.255.252?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 58 of 214
58. Question
1 pointsWhich two functions can be performed by a local DNS server? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 59 of 214
59. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Which three statements correctly describe Network Device A? (Choose three.)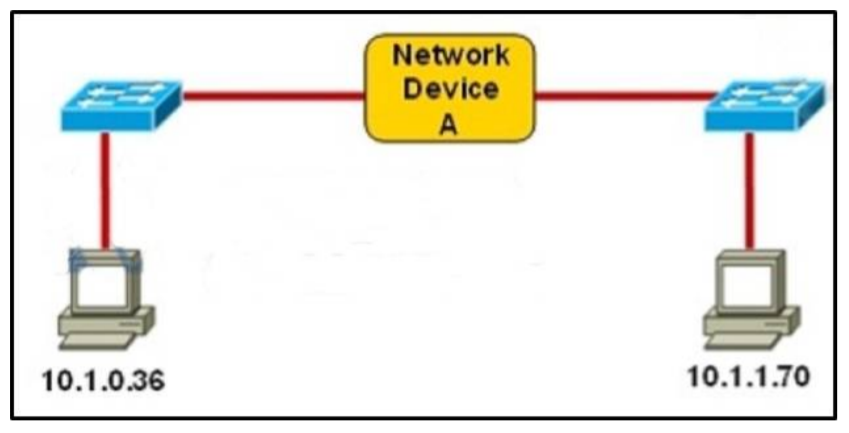 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The principle here is if the subnet mask makes two IP addresses 10.1.0.36 and 10.1.1.70 in the same subnet then the Network device A does not need to have IP addresses on its interfaces (and we don’t need a Layer 3 device here). A quick way to find out the correct answers is notice that all 255.255.255.x subnet masks will separate these two IP addresses into two separate subnets so we need a Layer 3 device here and each interface must require an IP address on a unique IP subnet -> A, C are not correct while B, D are correct. With 255.255.254.0 subnet mask, the increment here is 2 in the third octet -> the first subnet is from 10.1.0.0 to 10.1.1.255, in which two above IP addresses belong to -> each interface of Network device A does not require an IP address -> E is correct. -
Question 60 of 214
60. Question
1 pointsWhich two tasks does a router perform when it receives a packet that is being forwarded from one network to another? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 61 of 214
61. Question
1 pointsWhich three encapsulation layers in the OSI model are combined into the TCP/IP application layer? (Choose three)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
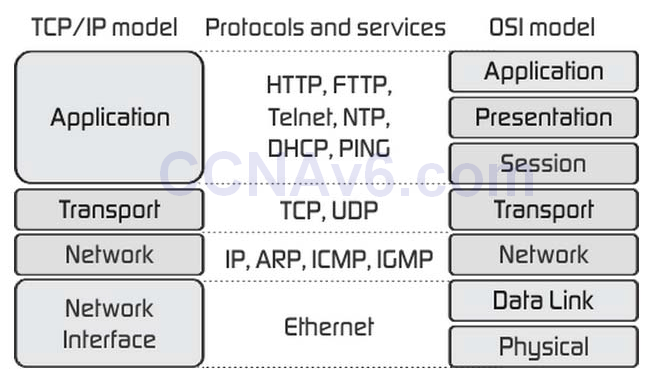
-
Question 62 of 214
62. Question
1 pointsWhen is the most appropriate time to escalate an issue that you troubleshooting?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
From this paragraph: Step 2. Resolve or escalate: Problem isolation should eventually uncover the root cause of the problem – that is, the cause which, if fixed, will resolve the problem. In short, resolving the problem means finding the root cause of the problem and fixing that problem. Of course, what do you do if you cannot find the root cause, or fix (resolve) that root cause once found? Escalate the problem. Most companies have a defined escalation process, with different levels of technical support and management support depending on whether the next step requires more technical expertise or management decision making. Reference: ICND1 100-105 Official Cert Guide Also from this link: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1578504&seqNum=2 “After you have clearly defined the problem, you have one more step to take before starting the actual troubleshooting process. You must determine whether this problem is your responsibility or if it needs to be escalated to another department or person. For example, assume the reported problem is this: “When user Y tries to access the corporate directory on the company intranet, she gets a message that says permission is denied. She can access all other intranet pages.” You are a network engineer, and you do not have access to the servers. A separate department in your company manages the intranet servers. Therefore, you must know what to do when this type of problem is reported to you as a network problem. You must know whether to start troubleshooting or to escalate it to the server department. It is important that you know which type of problems is your responsibility to act on, what minimal actions you need to take before you escalate a problem, and how you escalate a problem.” So we can say answer A is the most suitable choice. -
Question 63 of 214
63. Question
1 pointsWhich address class includes network 191.168.0.1/27?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
This is a tricky question if you don’t have a close look on the network. The first octet is 191, not 192 so it belongs to class B, not class C. -
Question 64 of 214
64. Question
1 pointsWhich RFC was created to alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The RFC 1518 is Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR), which is created to save the IPv4 addresses because we can now assign IP addresses classless. Therefore, instead of assigning the whole block of a class B or C address, now smaller blocks of a class can be assigned. For example, instead of assigning a whole block of 200.1.45.0/24, a smaller block, like 200.1.45.0/27 or 200.1.45.32/27, can be assigned. The RFC 1918 is Address Allocation for Private Internets, which reserves IP addresses for private and internal use. These addresses can be used for networks that do not need to connect to the Internet. Therefore the RFC 1918 is the best choice to “alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses”. -
Question 65 of 214
65. Question
1 pointsWhich network topology allows all traffic to flow through a central hub?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Star topology is the most popular topology for the network which allows all traffic to flow through a central device.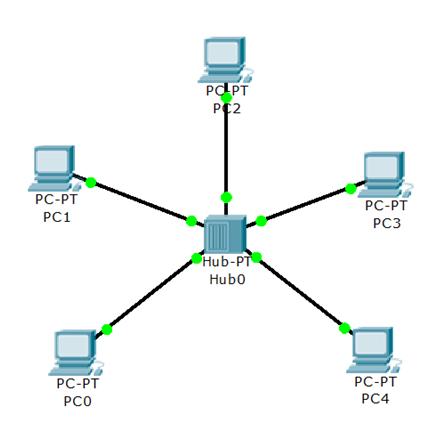
-
Question 66 of 214
66. Question
1 pointsWhich statement about a router on a stick is true?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
https://www.freeccnaworkbook.com/workbooks/ccna/configuring-inter-vlan-routing-router-on-a-stick -
Question 67 of 214
67. Question
1 pointsWhich component of the routing table ranks routing protocols according to their preferences?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Administrative distance – This is the measure of trustworthiness of the source of the route. If a router learns about a destination from more than one routing protocol, administrative distance is compared and the preference is given to the routes with lower administrative distance. In other words, it is the believability of the source of the route -
Question 68 of 214
68. Question
1 pointsWhich two options are the best reasons to use an IPV4 private IP space?(choose two)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 69 of 214
69. Question
1 pointsAssuming a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0, three of the following addresses are valid host addresses. Which are these addresses? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
From the subnet mask of 255.255.248.0 we learn that the increment is 8 therefore 172.16.8.0 is a network address which cannot be assigned to a host. Other network addresses are 172.16.16.0, 172.16.24.0, 172.16.32.0… Notice that 172.16.31.0 is a valid host address (which belongs to 172.16.24.0 to 172.16.31.255 subnet). -
Question 70 of 214
70. Question
1 pointsWhich entity assigns IPv6 addresses to end users?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
According to the official IANA website “Users are assigned IP addresses by Internet service providers (ISPs). ISPs obtain allocations of IP addresses from a local Internet registry (LIR) or National Internet Registry (NIR), or from their appropriate Regional Internet Registry (RIR): https://www.iana.org/numbers -
Question 71 of 214
71. Question
1 pointsWhich networking Technology is currently recognized as the standard for computer networking?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 72 of 214
72. Question
1 pointsWhich two tasks does the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol perform? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Explanation: The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network protocol used to configure devices that are connected to a network (known as hosts) so they can communicate on that network using the Internet Protocol (IP). It involves clients and a server operating in a client-server model. DHCP servers assigns IP addresses from a pool of addresses and also assigns other parameters such as DNS and default gateways to hosts. -
Question 73 of 214
73. Question
1 pointsWhich statement about IPv6 link-local addresses is true ?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Link-local addresses refer only to a particular physical link and are used for addressing on a single link for purposes such as automatic address configuration and neighbor discovery protocol. Link-local addresses can be used to reach the neighboring nodes attached to the same link. The nodes do not need a globally unique address to communicate. Routers will not forward datagram using link-local addresses. All IPv6 enabled interfaces have a link-local unicast address. A link-local address is an IPv6 unicast address that can be automatically configured on any interface using the link-local prefix FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format. Link-local addresses are not necessarily bound to the MAC address (configured in a EUI-64 format). Link-local addresses can also be manually configured in the FE80::/10 format using the “ipv6 address link-local” command. Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-version-6-ipv6/113328-ipv6-lla.html In summary, if you do not configure a link-local on an IPv6 enabled interface, it will automatically use the FE80::/10 and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format to form a link-local address. -
Question 74 of 214
74. Question
1 pointsWhich header field is new on IPv6?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Only three connection types are commonly known and used in Internet Protocol version four (IPv4) networks: unicast, multicast and broadcast. A fourth connection type, Anycast, was unknown until IPv6 made it a standard connection type. Anycast is not standardized in IPv4 but can be emulated. IPv4 Anycast addressing is a good solution to provide localization for services and servers in order to obtain robustness, redundancy and resiliency. The basic idea of Anycast is very simple: multiple servers, which share the same IP address, host the same service. The routing infrastructure sends IP packets to the nearest server (according to the metric of the routing protocol used). The major benefits of employing Anycast in IPv4 are improved latency times, server load balancing, and improved security. Reference: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.116.6367&rep=rep1&type=pdf -
Question 75 of 214
75. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about access points are true? (Choose Two)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 76 of 214
76. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements describe characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses: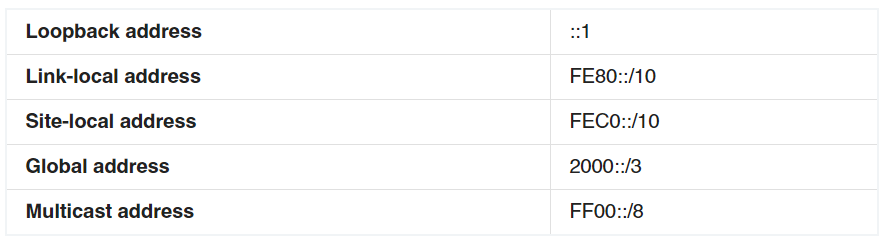 From the above table, we learn that A and D are correct while B and C are incorrect. Notice that the IPv6 unicast loopback address is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1. The IPv6 loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, or ::1.
E is not correct because of anycast addresses which are indistinguishable from normal unicast addresses. You can think of anycast addresses like this: “send it to nearest one which have this address”. An anycast address can be assigned to many interfaces and the first interface receives the packet destined for this anycast address will proceed the packet. A benefit of anycast addressing is the capability to share load to multiple hosts. An example of this benefit is if you are a Television provider with multiple servers and you want your users to use the nearest server to them then you can use anycast addressing for your servers. When the user initiates a connection to the anycast address, the packet will be routed to the nearest server (the user does not have to specify which server they want to use).
From the above table, we learn that A and D are correct while B and C are incorrect. Notice that the IPv6 unicast loopback address is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1. The IPv6 loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, or ::1.
E is not correct because of anycast addresses which are indistinguishable from normal unicast addresses. You can think of anycast addresses like this: “send it to nearest one which have this address”. An anycast address can be assigned to many interfaces and the first interface receives the packet destined for this anycast address will proceed the packet. A benefit of anycast addressing is the capability to share load to multiple hosts. An example of this benefit is if you are a Television provider with multiple servers and you want your users to use the nearest server to them then you can use anycast addressing for your servers. When the user initiates a connection to the anycast address, the packet will be routed to the nearest server (the user does not have to specify which server they want to use). -
Question 77 of 214
77. Question
1 pointsWhich three statements about IPv6 address fd14:920b:f83d:4079::/64 are true? (Choose two)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Let’s see an example of IPv6 prefix: 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64: In this example, the RIR has been assigned a 12-bit prefix. The ISP has been assigned a 32-bit prefix and the site is assigned a 48-bit site ID. The next 16-bit is the subnet field and it can allow 216, or 65536 subnets. This number is redundant for largest corporations on the world!
The 64-bit left (which is not shown the above example) is the Interface ID or host part and it is much more bigger: 64 bits or 264 hosts per subnet!
Therefore in this question 4079 is the subnet ID. The FD14 prefix belongs to FC00::/7 which is an IPv6 Unique Local Address (The address block fc00::/7 is divided into two /8 groups which are FC00::/8 & FD00::/8)
In this example, the RIR has been assigned a 12-bit prefix. The ISP has been assigned a 32-bit prefix and the site is assigned a 48-bit site ID. The next 16-bit is the subnet field and it can allow 216, or 65536 subnets. This number is redundant for largest corporations on the world!
The 64-bit left (which is not shown the above example) is the Interface ID or host part and it is much more bigger: 64 bits or 264 hosts per subnet!
Therefore in this question 4079 is the subnet ID. The FD14 prefix belongs to FC00::/7 which is an IPv6 Unique Local Address (The address block fc00::/7 is divided into two /8 groups which are FC00::/8 & FD00::/8) -
Question 78 of 214
78. Question
1 pointsWhich tunneling mechanism embeds an IPv4 address within an IPv6 address?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 79 of 214
79. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following statements describe the network shown in the graphic? (Choose two.)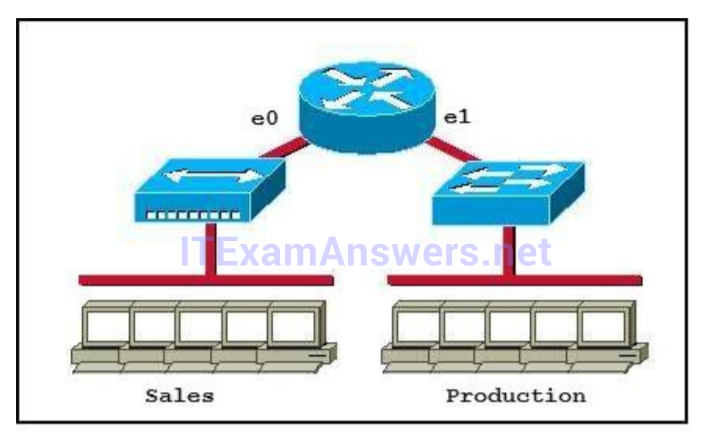 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Only router can break up broadcast domains so in the exhibit there are 2 broadcast domains: from e0 interface to the left is a broadcast domain and from e1 interface to the right is another broadcast domain -> A is correct. Both router and switch can break up collision domains so there is only 1 collision domain on the left of the router (because hub doesn’t break up collision domain) and there are 6 collision domains on the right of the router (1 collision domain from e1 interface to the switch + 5 collision domains for 5 PCs in Production) -> F is correct. -
Question 80 of 214
80. Question
1 pointsWhich protocol does ipv6 use to discover other ipv6 nodes on the same segment?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 81 of 214
81. Question
1 pointsWhat is the most efficient subnet mask for a point to point ipv6 connection?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
On inter-router point-to-point links, it is useful, for security and other reasons, to use 127-bit IPv6 prefixes. Such a practice parallels the use of 31-bit prefixes in IPv4. Reference: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6164 -
Question 82 of 214
82. Question
1 pointsWhat are three features of the IPV6 protocol?(choose three)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 83 of 214
83. Question
1 pointsWhere does routing occur within the DoD TCP/IP reference model?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The picture below shows the comparison between TCP/IP model & OSI model. Notice that the Internet Layer of TCP/IP is equivalent to the Network Layer which is responsible for routing decision.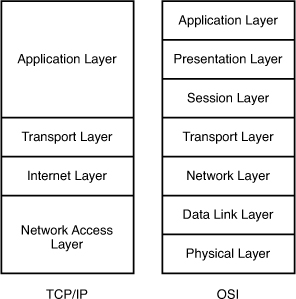
-
Question 84 of 214
84. Question
1 pointsWhich address block identifies all link-local addresses?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Link-local addresses only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is only valid on the current subnet. It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address). -
Question 85 of 214
85. Question
1 pointsFor which two reasons was RFC 1918 address space define (Choose two)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The RFC 1518 is Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR). CIDR is a mechanism developed to help alleviate the problem of exhaustion of IP addresses and growth of routing tables. The problems were: + With the classful routing system, individual networks were either limited to 254 hosts (/24) or 65,534 hosts (/16). For many network enterprises, 254 hosts were not enough and 65,534 were too large to be used efficiently. + Routing information overload. The size and rate of growth of the routing tables in Internet routers is beyond the ability of current software (and people) to effectively manage. + Eventual exhaustion of IP network numbers. To solve these problem, CIDR was selected as the solution in 1992. In contrast to classful routing, which categorizes addresses into one of three blocks, CIDR allows for blocks of IP addresses to be allocated to Internet service providers. The blocks are then split up and assigned to the provider’s customers. According to the CIDR standard, the first part of an IP address is a prefix, which identifies the network. The prefix is followed by the host identifier so that information packets can be sent to particular computers within the network. A CIDR address includes the standard 32-bit IP address and also the network prefix. For example, a CIDR address of 200.1.45.2/26, the “/26” indicates the first 26 bits are used to identify the unique network, leaving the remaining bits to identify the specific hosts. Therefore, instead of assigning the whole block of a class B or C address, now smaller blocks of a class can be assigned. For example, instead of assigning a whole block of 200.1.45.0/24, a smaller block, like 200.1.45.0/27 or 200.1.45.32/27, can be assigned. -
Question 86 of 214
86. Question
1 pointsIn which two circumstances are private IPv4 addresses appropriate? (Choose two)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 87 of 214
87. Question
1 pointsWhich major IPv6 address type is supported in IPv4 but rarely used?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 88 of 214
88. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit, you determine that Computer A cannot ping Computer. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?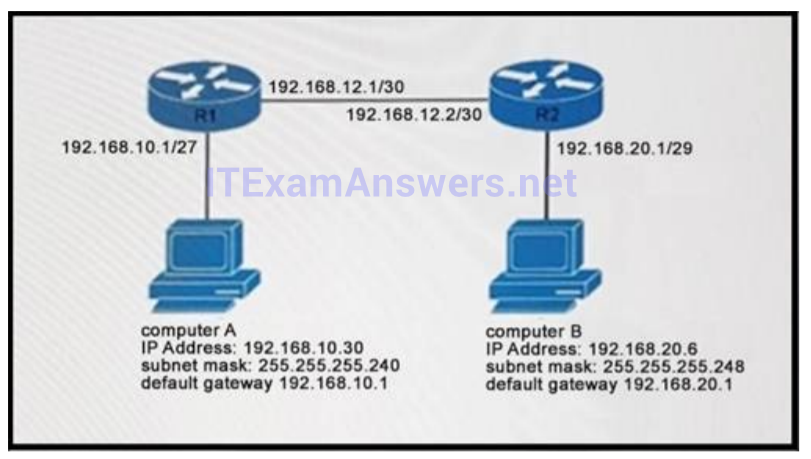 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
255.255.255.224 = /27 -
Question 89 of 214
89. Question
1 pointsWhich option is a valid IPv6 address?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 90 of 214
90. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. A new subnet with 60 hosts has been added to the network. Which subnet address should this network use to provide enough usable addresses while wasting the fewest addresses?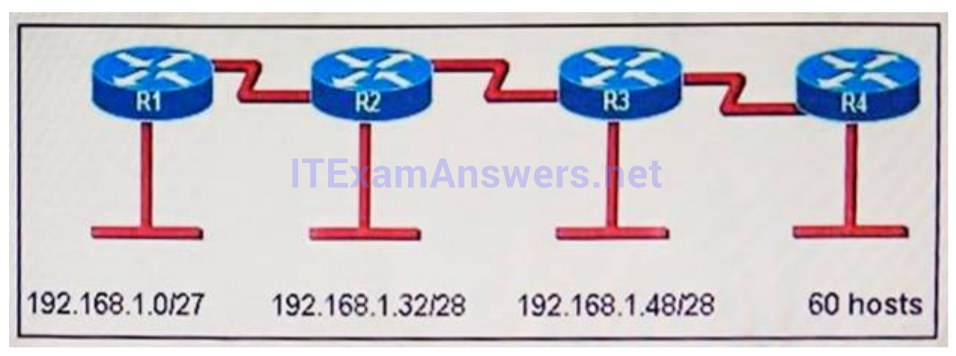 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 91 of 214
91. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Which subnet mask will place all hosts on Network B in the same subnet with the least amount of wasted addresses?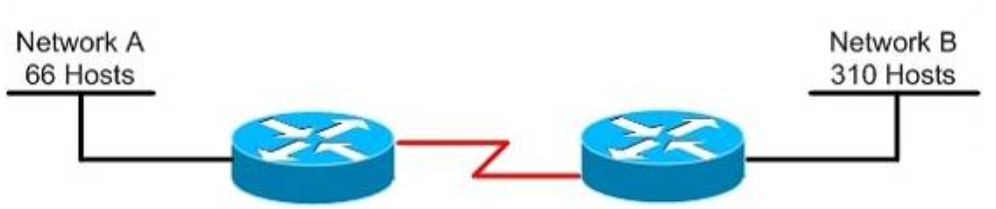 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
310 hosts < 512 = 29 -> We need a subnet mask of 9 bits 0 -> 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1110.0000 0000 -> 255.255.254.0 -
Question 92 of 214
92. Question
1 pointsWhich two are features of IPv6? (choose two)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
IPv6 addresses are classified by the primary addressing and routing methodologies common in networkinG. unicast addressing, anycast addressing, and multicast addressing. -
Question 93 of 214
93. Question
1 pointsGiven an IP address 172.16.28.252 with a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0, what is the correct network address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
For this example, the network range is 172.16.16.1 – 172.16.31.254, the network address is 172.16.16.0 and the broadcast IP address is 172.16.31.255. -
Question 94 of 214
94. Question
1 pointsWhich IPv6 address is the equivalent of the IPv4 interface loopback address 127.0.0.1?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In IPv6 the loopback address is written as, This is a 128bit number, with the first 127 bits being ‘0’ and the 128th bit being ‘1’. It’s just a single address, so could also be written as ::1/128. -
Question 95 of 214
95. Question
1 pointsYou are working in a data center environment and are assigned the address range 10.188.31.0/23. You are asked to develop an IP addressing plan to allow the maximum number of subnets with as many as 30 hosts each. Which IP address range meets these requirements?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Each subnet has 30 hosts < 32 = 25 so we need a subnet mask which has at least 5 bit 0s -> /27. Also the question requires the maximum number of subnets (which minimum the number of hosts- per-subnet) so /27 is the best choice -> . -
Question 96 of 214
96. Question
1 pointsA network administrator is verifying the configuration of a newly installed host by establishing an FTP connection to a remote server. What is the highest layer of the protocol stack that the network administrator is using for this operation?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
FTP belongs to Application layer and it is also the highest layer of the OSI model. -
Question 97 of 214
97. Question
1 pointsA receiving host computes the checksum on a frame and determines that the frame is damaged. The frame is then discarded. At which OSI layer did this happen?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Data Link layer provides the physical transmission of the data and handles error notification, network topology, and flow control. The Data Link layer formats the message into pieces, each called a data frame, and adds a customized header containing the hardware destination and source address. Protocols Data Unit (PDU) on Datalink layer is called frame. According to this question the frame is damaged and discarded which will happen at the Data Link layer. -
Question 98 of 214
98. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements correctly describe steps in the OSI data encapsulation process? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Application Layer (Layer 7) refers to communications services to applications and is the interface between the network and the application. Examples include. Telnet, HTTP, FTP, Internet browsers, NFS, SMTP gateways, SNMP, X.400 mail, and FTAM. The Presentation Layer (Layer 6) defining data formats, such as ASCII text, EBCDIC text, binary, BCD, and JPEG. Encryption also is defined as a presentation layer service. Examples include. JPEG, ASCII, EBCDIC, TIFF, GIF, PICT, encryption, MPEG, and MIDI. The Session Layer (Layer 5) defines how to start, control, and end communication sessions. This includes the control and management of multiple bidirectional messages so that the application can be notified if only some of a series of messages are completed. This allows the presentation layer to have a seamless view of an incoming stream of data. The presentation layer can be presented with data if all flows occur in some cases. Examples include. RPC, SQL, NFS, NetBios names, AppleTalk ASP, and DECnet SCP The Transport Layer (Layer 4) defines several functions, including the choice of protocols. The most important Layer 4 functions are error recovery and flow control. The transport layer may provide for retransmission, i.e., error recovery, and may use flow control to prevent unnecessary congestion by attempting to send data at a rate that the network can accommodate, or it might not, depending on the choice of protocols. Multiplexing of incoming data for different flows to applications on the same host is also performed. Reordering of the incoming data stream when packets arrive out of order is included. Examples include. TCP, UDP, and SPX. The Network Layer (Layer 3) defines end-to-end delivery of packets and defines logical addressing to accomplish this. It also defines how routing works and how routes are learned; and how to fragment a packet into smaller packets to accommodate media with smaller maximum transmission unit sizes. Examples include. IP, IPX, AppleTalk DDP, and ICMP. Both IP and IPX define logical addressing, routing, the learning of routing information, and end-to-end delivery rules. The IP and IPX protocols most closely match the OSI network layer (Layer 3) and are called Layer 3 protocols because their functions most closely match OSI’s Layer 3. The Data Link Layer (Layer 2) is concerned with getting data across one particular link or medium. The data link protocols define delivery across an individual link. These protocols are necessarily concerned with the type of media in use. Examples includE. IEEE 802.3/802.2, HDLC, Frame Relay, PPP, FDDI, ATM,and IEEE 802.5/802.2. -
Question 99 of 214
99. Question
1 pointsAt which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
RSTP and STP operate on switches and are based on the exchange of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) between switches. One of the most important fields in BPDUs is the Bridge Priority in which the MAC address is used to elect the Root Bridge -> RSTP operates at Layer 2 ?Data Link layer -> . -
Question 100 of 214
100. Question
1 pointsWhat does a Layer 2 switch use to decide where to forward a received frame?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
When a frame is received, the switch looks at the destination hardware address and finds the interface if it is in its MAC address table. If the address is unknown, the frame is broadcast on all interfaces except the one it was received on. -
Question 101 of 214
101. Question
1 pointsBased on the network shown in the graphic. Which option contains both the potential networking problem and the protocol or setting that should be used to prevent the problem?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) prevents loops from being formed when switches or bridges are interconnected via multiple paths. Spanning-Tree Protocol implements the 802.1D IEEE algorithm by exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, and then removes the loop by shutting down selected bridge interfaces. This algorithm guarantees that there is one and only one active path between two network devices. -
Question 102 of 214
102. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. However, host A is unavailable. The administrator’s attempt to telnet to the switch from host fails, but pings to the other two hosts are successful. What is the issue?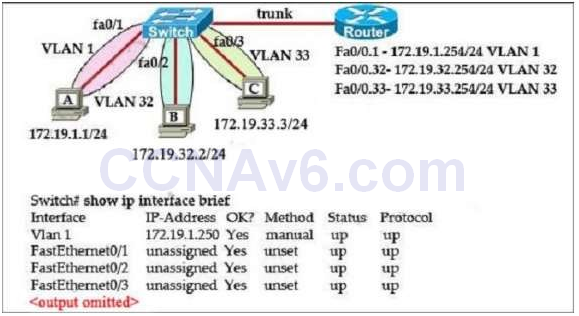 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A. But host B (172.19.32.2) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are not in the same subnet. Therefore packets from host B must reach the router Fa0/0.32 interface before forwarding to the switch. But when the switch replies, it does not know how to send packets so an appropriate default gateway must be assigned on the switch (to Fa0/0.32 – 172.19.32.254). Answer A is not correct because even when host B & the switch are in the same subnet, they cannot communicate because of different VLANs. Answer C is not correct as host B can ping other two hosts. Answer D is not correct because host B always belongs to VLAN 32 so assigning an IP address in VLAN 1 does not solve the problem. -
Question 103 of 214
103. Question
1 pointsWhat is the alternative notation for the IPv6 address B514:82C3:0000:0000:0029:EC7A:0000:EC72?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
There are two ways that an IPv6 address can be additionally compressed: compressing leading zeros and substituting a group of consecutive zeros with a single double colon (::). Both of these can be used in any number of combinations to notate the same address. It is important to note that the double colon (::) can only be used once within a single IPv6 address notation. So, the extra 0’s can only be compressed once. -
Question 104 of 214
104. Question
1 pointsRefer to the diagram. All hosts have connectivity with one another. Which statements describe the addressing scheme that is in use in the network? (Choose three.)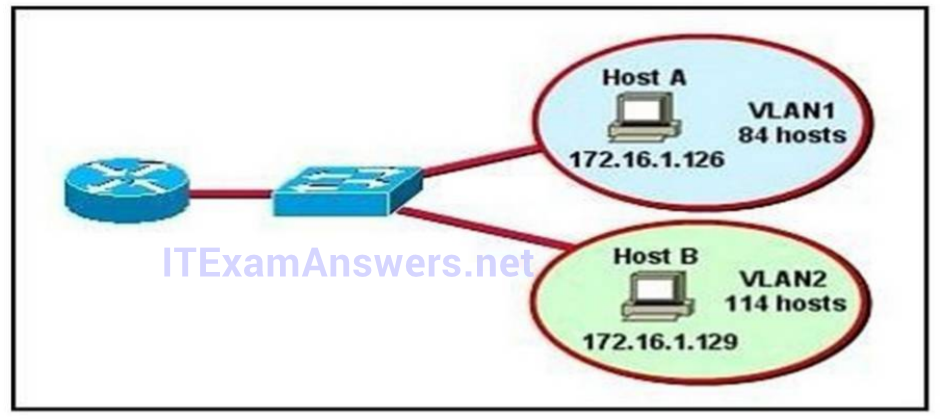 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The subnet mask in use is 255.255.255.128: This is subnet mask will support up to 126 hosts, which is needed. The IP address 172.16.1.25 can be assigned to hosts in VLAN1: The usable host range in this subnet is 172.16.1.1-172.16.1.126 The LAN interface of the router is configured with multiple IP addresses: The router will need 2 subinterfaces for the single physical interface, one with an IP address that belongs in each VLAN. -
Question 105 of 214
105. Question
1 pointsThe network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
IPv6 does not use broadcasts, and autoconfiguration is a feature of IPV6 that allows for hosts to automatically obtain an IPv6 address. -
Question 106 of 214
106. Question
1 pointsAn administrator must assign static IP addresses to the servers in a network. For network 192.168.20.24/29, the router is assigned the first usable host address while the sales server is given the last usable host address. Which of the following should be entered into the IP properties box for the sales server?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
For the 192.168.20.24/29 network, the usable hosts are 192.168.24.25 (router) ?192.168.24.30 (used for the sales server). -
Question 107 of 214
107. Question
1 pointsWhich subnet mask would be appropriate for a network address range to be subnetted for up to eight LANs, with each LAN containing 5 to 26 hosts?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
For a class C network, a mask of 255.255.255.224 will allow for up to 8 networks with 32 IP addresses each (30 usable). -
Question 108 of 214
108. Question
1 pointsHow many bits are contained in each field of an IPv6 address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits (two octets). The groups are separated by colons (:). An example of an IPv6 address is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. -
Question 109 of 214
109. Question
1 pointsWhat are three approaches that are used when migrating from an IPv4 addressing scheme to an IPv6 scheme. (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Several methods are used terms of migration including tunneling, translators, and dual stack. Tunnels are used to carry one protocol inside another, while translators simply translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets. Dual stack uses a combination of both native IPv4 and IPv6. With dual stack, devices are able to run IPv4 and IPv6 together and if IPv6 communication is possible that is the preferred protocol. Hosts can simultaneously reach IPv4 and IPv6 content. -
Question 110 of 214
110. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. In this VLSM addressing scheme, what summary address would be sent from router A?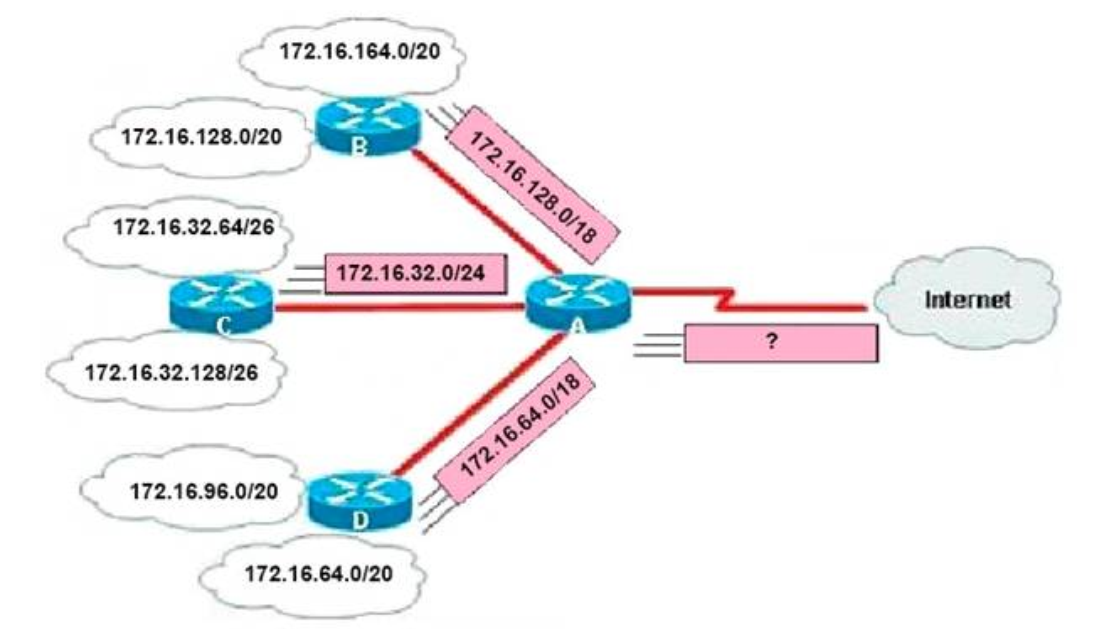 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Router A receives 3 subnets: 172.16.64.0/18, 172.16.32.0/24 and 172.16.128.0/18. All these 3 subnets have the same form of 172.16.x.x so our summarized subnet must be also in that form -> Only A, B or. The smallest subnet mask of these 3 subnets is /18 so our summarized subnet must also have its subnet mask equal or smaller than /18. -> Only answer A has these 2 conditions -> -
Question 111 of 214
111. Question
1 pointsHow is an EUI-64 format interface ID created from a 48-bit MAC address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The modified EUI-64 format interface identifier is derived from the 48-bit link-layer (MAC) address by inserting the hexadecimal number FFFE between the upper three bytes (OUI field) and the lower three bytes (serial number) of the link layer address. -
Question 112 of 214
112. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. What is the most efficient summarization that R1 can use to advertise its networks to R2?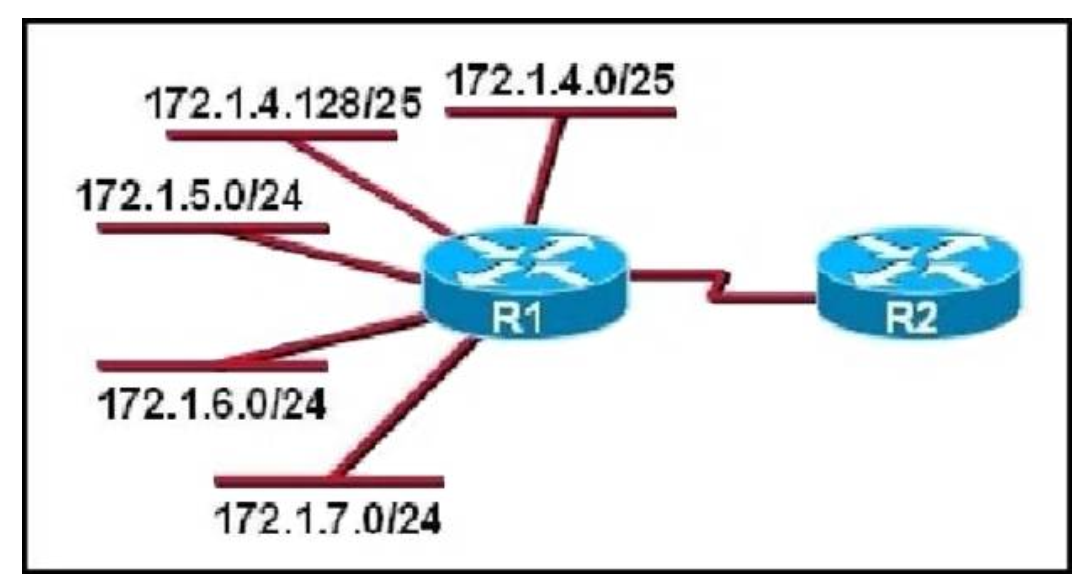 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The 172.1.4.0/22 subnet encompasses all routes from the IP range 172.1.4.0 ?172.1.7.255. -
Question 113 of 214
113. Question
1 pointsWhich three are characteristics of an IPv6 anycast address? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
A new address type made specifically for IPv6 is called the Anycast Address. These IPv6 addresses are global addresses, these addresses can be assigned to more than one interface unlike an IPv6 unicast address. Anycast is designed to send a packet to the nearest interface that is a part of that anycast group. The sender creates a packet and forwards the packet to the anycast address as the destination address which goes to the nearest router. The nearest router or interface is found by using the metric of a routing protocol currently running on the network. However, in a LAN setting the nearest interface is found depending on the order the neighbors were learned. The anycast packet in a LAN setting forwards the packet to the neighbor it learned about first. -
Question 114 of 214
114. Question
1 pointsA national retail chain needs to design an IP addressing scheme to support a nationwide network. The company needs a minimum of 300 sub-networks and a maximum of 50 host addresses per subnet. Working with only one Class B address, which of the following subnet masks will support an appropriate addressing scheme? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Subnetting is used to break the network into smaller more efficient subnets to prevent excessive rates of Ethernet packet collision in a large network. Such subnets can be arranged hierarchically, with the organization’s network address space (see also Autonomous System) partitioned into a tree-like structure. Routers are used to manage traffic and constitute borders between subnets. A routing prefix is the sequence of leading bits of an IP address that precede the portion of the address used as host identifier. In IPv4 networks, the routing prefix is often expressed as a “subnet mask”, which is a bit mask covering the number of bits used in the prefix. An IPv4 subnet mask is frequently expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation, e.g., 255.255.255.0 is the subnet mask for the 192.168.1.0 network with a 24-bit routing prefix (192.168.1.0/24). -
Question 115 of 214
115. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator is adding two new hosts to Switch A . Which three values could be used for the configuration of these hosts? (Choose three.)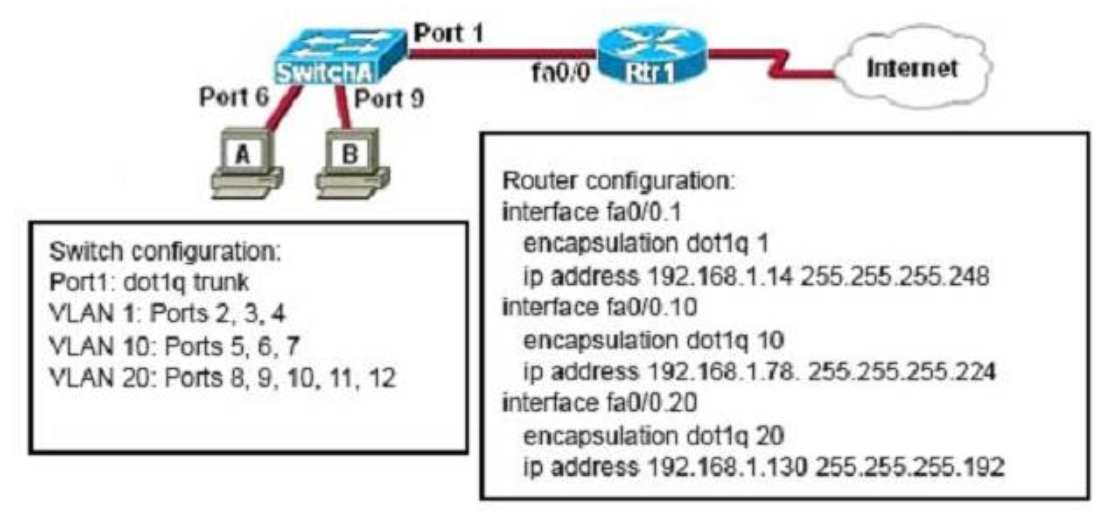 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 116 of 214
116. Question
1 pointsWhich IPv6 address is the all-router multicast group?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Well-known IPv6 multicast addresses: Address Description ff02::1 All nodes on the local network segment ff02::2 All routers on the local network segment -
Question 117 of 214
117. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Which address range efficiently summarizes the routing table of the addresses for router Main?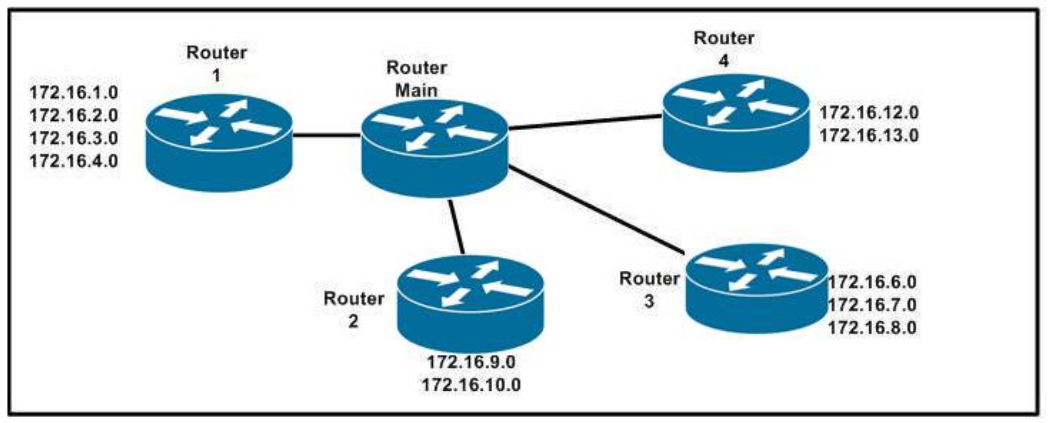 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The 172.16.0.0./20 network is the best option as it includes all networks from 172.16.0.0 – 172.16.16.0 anddoes it more efficiently than the /16 and /18 subnets. The /21 subnet will not include all the other subnets in this one single summarized address. -
Question 118 of 214
118. Question
1 pointsWhich IPv6 address is valid?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
An IPv6 address is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits (two octets). The groups are separated by colons (:). An example of an IPv6 address is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. The leading 0’s in a group can be collapsed using ::, but this can only be done once in an IP address. -
Question 119 of 214
119. Question
1 pointsWhich command can you use to manually assign a static IPv6 address to a router interface?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
To assign an IPv6 address to an interface, use the “ipv6 address” command and specify the IP address you wish to use. -
Question 120 of 214
120. Question
1 pointsWhich of these represents an IPv6 link-local address?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), the address block fe80::/10 has been reserved for link- local unicast addressing. The actual link local addresses are assigned with the prefix fe80::/64. They may be assigned byautomatic (stateless) or stateful (e.g. manual) mechanisms. -
Question 121 of 214
121. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the output MTU 1500 bytes? Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet (in bytes) that the layer can pass onwards. -
Question 122 of 214
122. Question
1 pointsOn a corporate network, hosts on the same VLAN can communicate with each other, but they are unable to communicate with hosts on different VLANs. What is needed to allow communication between the VLANs?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Different VLANs can’t communicate with each other, they can communicate with the help of Layer3 router. Hence, it is needed to connect a router to a switch, then make the sub-interface on the router to connect to the switch, establishing Trunking links to achieve communications of devices which belong to different VLANs. When using VLANs in networks that have multiple interconnected switches, you need to use VLAN trunking between the switches. With VLAN trunking, the switches tag each frame sent between switches so that the receiving switch knows to what VLAN the frame belongs. End user devices connect to switch ports that provide simple connectivity to a single VLAN each. The attached devices are unaware of any VLAN structure. By default, only hosts that are members of the same VLAN can communicate. To change this and allow interVLAN communication, you need a router or a layer 3 switch. Here is the example of configuring the router for inter-vlan communication RouterA(config)#int f0/0.1 RouterA(config-subif)#encapsulation ? dot1Q IEEE 802.1Q Virtual LAN RouterA(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q or isl VLAN ID RouterA(config-subif)# ip address x.x.x.x y.y.y.y -
Question 123 of 214
123. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Users on the 172.17.22.0 network cannot reach the server located on the 172.31.5.0 network. The network administrator connected to router Coffee via the console port, issued the show ip route command, and was able to ping the server. Based on the output of the show ip route command and the topology shown in the graphic, what is the cause of the failure?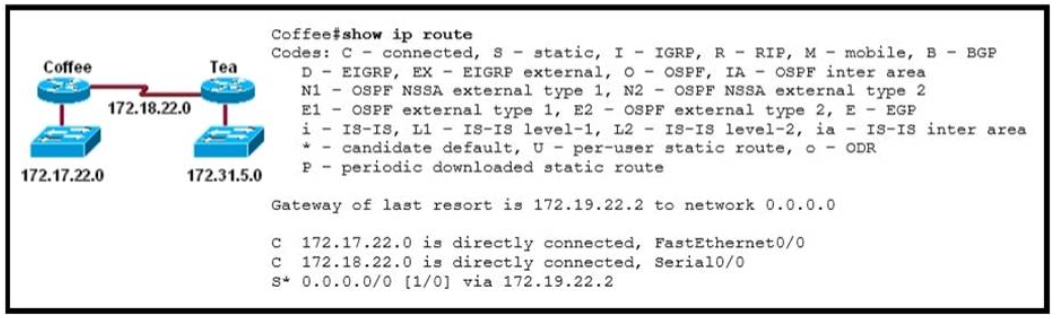 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The default route or the static route was configured with incorrect next-hop ip address 172.19.22.2 The correct ip address will be 172.18.22.2 to reach server located on 172.31.5.0 network. Ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.18.22.2 -
Question 124 of 214
124. Question
1 pointsHost 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Router C will send ICMP packets to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached. -
Question 125 of 214
125. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. A network technician is asked to design a small network with redundancy. The exhibit represents this design, with all hosts configured in the same VLAN. What conclusions can be made about this design?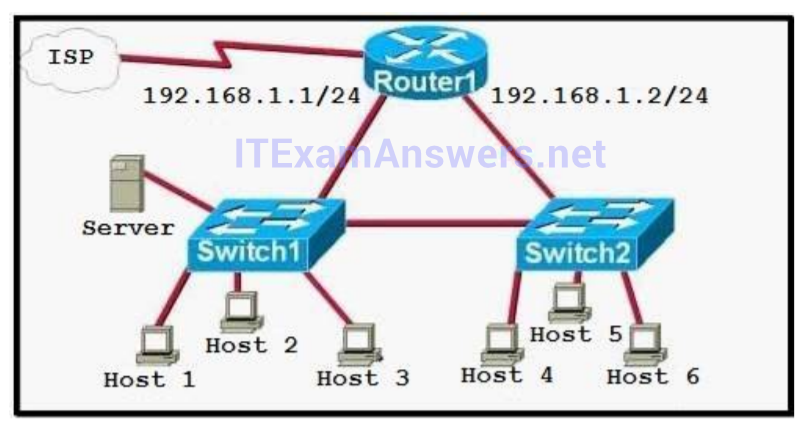 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Each interface on a router must be in a different network. If two interfaces are in the same network, the router will not accept it and show error when the administrator assigns it. -
Question 126 of 214
126. Question
1 pointsIn which circumstance are multiple copies of the same unicast frame likely to be transmitted in a switched LAN?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
If we connect two switches via 2 or more links and do not enable STP on these switches then a loop (which creates multiple copies of the same unicast frame) will occur. It is an example of an improperly implemented redundant topology. -
Question 127 of 214
127. Question
1 pointsThe network shown in the diagram is experiencing connectivity problems. Which of the following will correct the problems? (Choose two.)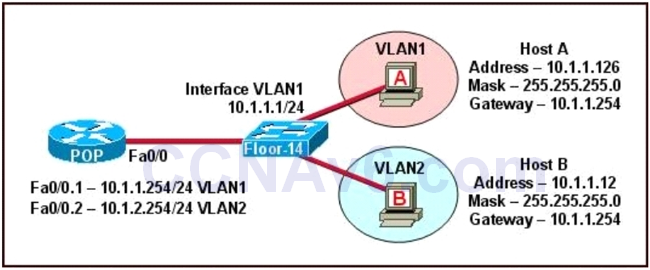 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The switch 1 is configured with two VLANs: VLAN1 and VLAN2. The IP information of member Host A in VLAN1 is as follows: Address : 10.1.1.126 Mask : 255.255.255.0 Gateway : 10.1.1.254 The IP information of member Host B in VLAN2 is as follows: Address : 10.1.1.12 Mask : 255.255.255.0 Gateway : 10.1.1.254 The configuration of sub-interface on router 2 is as follows: Fa0/0.1 — 10.1.1.254/24 VLAN1 Fa0/0.2 — 10.1.2.254/24 VLAN2 It is obvious that the configurations of the gateways of members in VLAN2 and the associated network segments are wrong. The layer3 addressing information of Host B should be modified as follows: Address : 10.1.2.X Mask : 255.255.255.0 -
Question 128 of 214
128. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. HostA cannot ping HostB. Assuming routing is properly configured, what is the cause of this problem?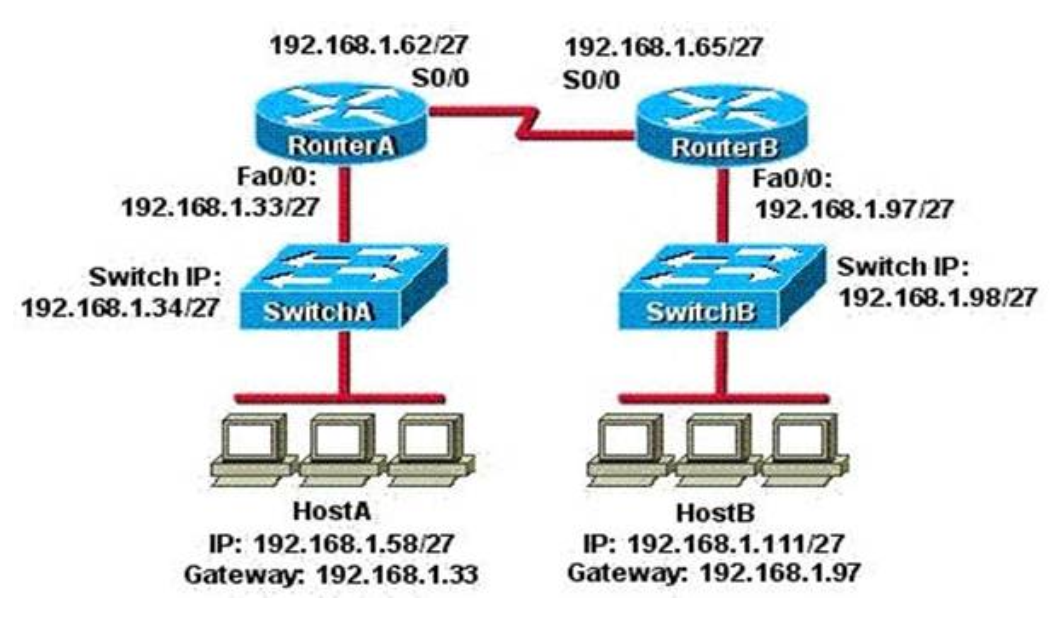 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Now let’s find out the range of the networks on serial link: For the network 192.168.1.62/27: Increment: 32 Network address: 192.168.1.32 Broadcast address: 192.168.1.63 For the network 192.168.1.65/27: Increment: 32 Network address: 192.168.1.64 Broadcast address: 192.168.1.95 -> These two IP addresses don’t belong to the same network and they can’t see each other -
Question 129 of 214
129. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three.)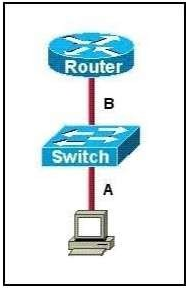 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in. -
Question 130 of 214
130. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. A network administrator attempts to ping Host2 from Host1 and receives the results that are shown. What is the problem?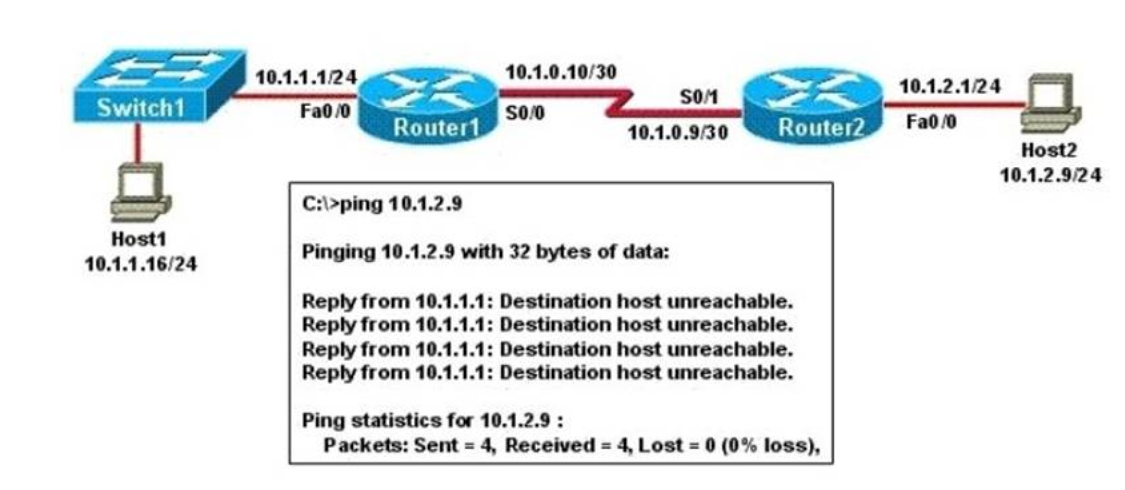 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Host1 tries to communicate with Host2. The message destination host unreachable from Router1 indicates that the problem occurs when the data is forwarded from Host1 to Host2. According to the topology, we can infer that The link between Router1 and Router2 is down. -
Question 131 of 214
131. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Hosts in network 192.168.2.0 are unable to reach hosts in network 192.168.3.0. Based on the output from RouterA, what are two possible reasons for the failure? (Choose two.)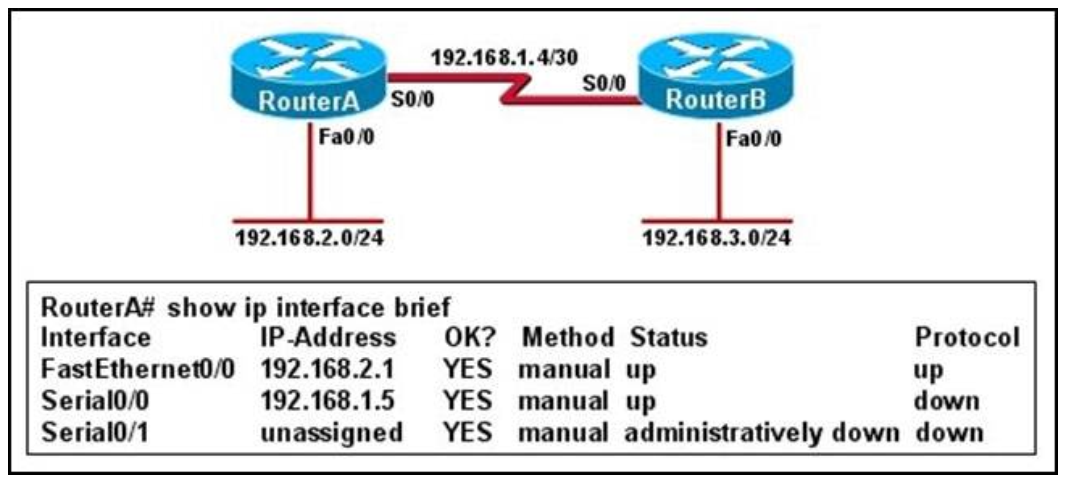 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
From the output we can see that there is a problem with the Serial 0/0 interface. It is enabled, but the line protocol is down. The could be a result of mismatched encapsulation or the interface not receiving a clock signal from the CSU/ DSU. -
Question 132 of 214
132. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. An administrator pings the default gateway at 10.10.10.1 and sees the output as shown. At which OSI layer is the problem? Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The command ping uses ICMP protocol, which is a network layer protocol used to propagate control message between host and router. The command ping is often used to verify the network connectivity, so it works at the network layer. -
Question 133 of 214
133. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. What will Router1 do when it receives the data frame shown? (Choose three.) Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Remember, the source and destination MAC changes as each router hop along with the TTL being decremented but the source and destination IP address remain the same from source to destination. -
Question 134 of 214
134. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Host A pings interface S0/0 on router 3. What is the TTL value for that ping?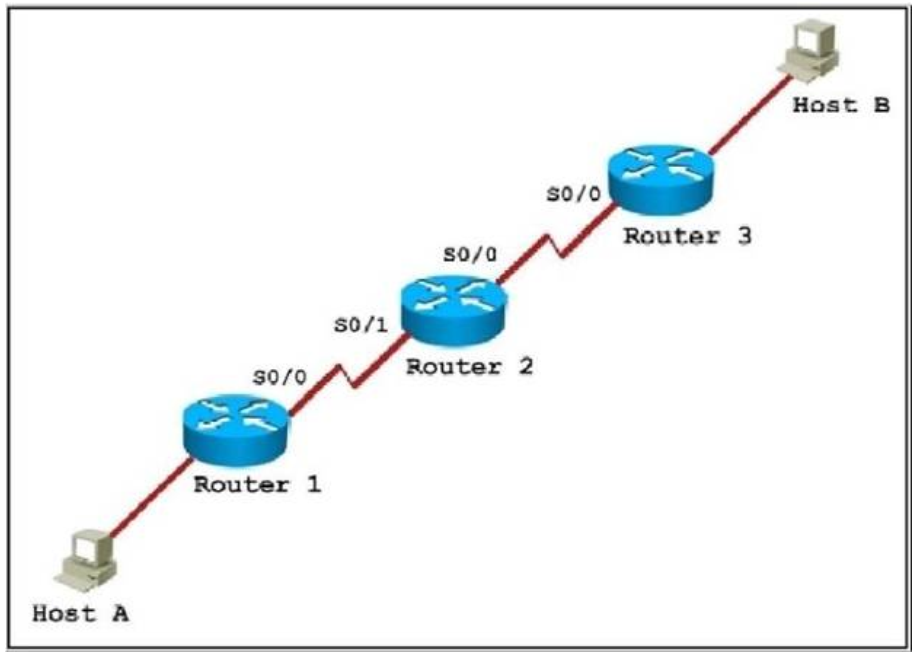 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
From the CCNA ICND2 Exam book: “Routers decrement the TTL by 1 every time they forward a packet; if a router decrements the TTL to 0, it throws away the packet. This prevents packets from rotating forever.” I want to make it clear that before the router forwards a packet, the TTL is still remain the same. For example, in the topology above, pings to S0/1 and S0/0 of Router 2 have the same TTL. -
Question 135 of 214
135. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following describes the roles of devices in a WAN? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The idea behind a WAN is to be able to connect two DTE networks together through a DCE network. The network’s DCE device (includes CSU/DSU) provides clocking to the DTE-connected interface (the router’s serial interface). A modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair telephone line and demodulates the incoming analog signal and converts it to a digital signal for the digital device. A CSU/DSU is used between two digital lines -> A & D are correct but B & C are not correct.
For more explanation of answer D, in telephony the local loop (also referred to as a subscriber line) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider’s network. Therefore a modem terminates an analog local loop is correct.
A modem modulates outgoing digital signals from a computer or other digital device to analog signals for a conventional copper twisted pair telephone line and demodulates the incoming analog signal and converts it to a digital signal for the digital device. A CSU/DSU is used between two digital lines -> A & D are correct but B & C are not correct.
For more explanation of answer D, in telephony the local loop (also referred to as a subscriber line) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point of the customer premises to the edge of the carrier or telecommunications service provider’s network. Therefore a modem terminates an analog local loop is correct.
-
Question 136 of 214
136. Question
1 pointsThe network administrator is asked to configure 113 point-to-point links. Which IP addressing scheme defines the address range and subnet mask that meet the requirement and waste the fewest subnet and host addresses?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
We need 113 point-to-point links which equal to 113 sub-networks < 128 so we need to borrow 7 bits (because 2^7 = 128). The network used for point-to-point connection should be /30. So our initial network should be 30 ?7 = 23. So 10.10.0.0/23 is the correct answer. You can understand it more clearly when writing it in binary form: /23 = 1111 1111.1111 1110.0000 0000 /30 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1100 (borrow 7 bits) -
Question 137 of 214
137. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following IP addresses fall into the CIDR block of 115.64.4.0/22? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 138 of 214
138. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following are types of flow control? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 139 of 214
139. Question
1 pointsWhich additional configuration step is necessary in order to connect to an access point that has SSID broadcasting disabled?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 140 of 214
140. Question
1 pointsWhat is one reason that WPA encryption is preferred over WEP?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 141 of 214
141. Question
1 pointsAs a CCNA candidate, you must have a firm understanding of the IPv6 address structure. Refer to IPv6 address, could you tell me how many bits are included in each filed?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 142 of 214
142. Question
1 pointsWhile troubleshooting a connectivity issue from a PC you obtain the following information: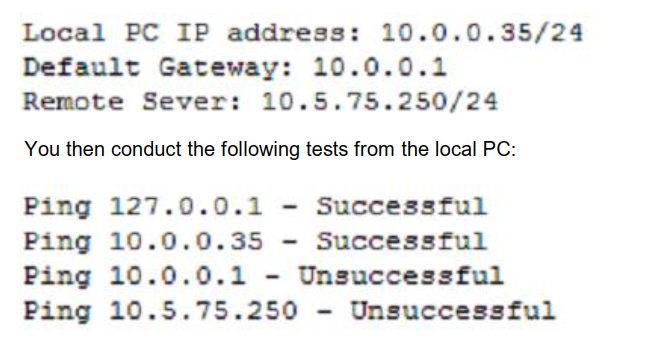
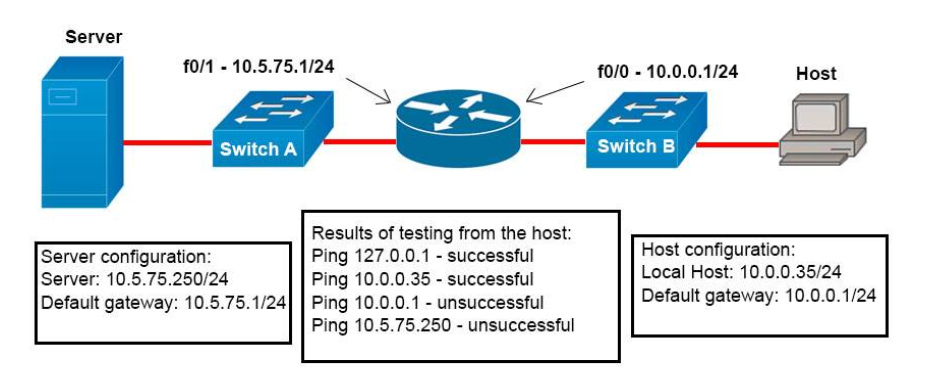 What is the underlying cause of this problem?
Correct
What is the underlying cause of this problem?
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 143 of 214
143. Question
1 pointsWhich name describes an IPV6 host-enable tunneling technique that uses IPV4 UDP,does not require dedicated gateway tunnels,and can pass through existing IPV4 NAT gateways?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 144 of 214
144. Question
1 pointsWhat are two advantages of Layer 2 Ethernet switches over hubs? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 145 of 214
145. Question
1 pointsWhat are two security appliances that can be installed in a network? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 146 of 214
146. Question
1 pointsA network administrator is planning a network installation for a large organization. The design requires 100 separate subnetworks, so the company has acquired a Class B network address. What subnet mask will provide the 100 subnetworks required, if 500 usable host addresses are required per subnet?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 147 of 214
147. Question
1 pointsWhich of the following services use UDP? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 148 of 214
148. Question
1 pointsWhich technology allows a large number of private IP addresses to be represented by a smaller number of public IP addresses?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 149 of 214
149. Question
1 pointsWhat are three broadband wireless technologies? (Choose three)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
WiMAX is short for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. WiMAX is a family of wireless communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards. Satellite Internet provides Internet access via satellite. It is a form of wireless broadband technology. But it is usually slower than DSL and cable modem. Municipal wireless network is a city-wide wireless network. This is usually done by providing municipal broadband via Wi-Fi to large parts or all of a municipal area by deploying a wireless mesh network. The typical deployment design uses hundreds of wireless access points deployed outdoors, often on poles. DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer) is a network device, usually at a telephone company central office, that receives signals from multiple customer Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) connections and puts the signals on a high-speed backbone line using multiplexing techniques. It is a cable technology, not a wireless technology. Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS) is a piece of equipment, typically located in a cable company’s headend or hubsite, which is used to provide high speed data services, such as cable Internet or Voice over Internet Protocol, to cable subscribers. It is a cable technology, not a wireless technology. -
Question 150 of 214
150. Question
1 pointsIn which three ways is an IPv6 header simpler than an IPv4 header? (Choose three)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The IPv4 and IPv6 headers are shown below for your comparison: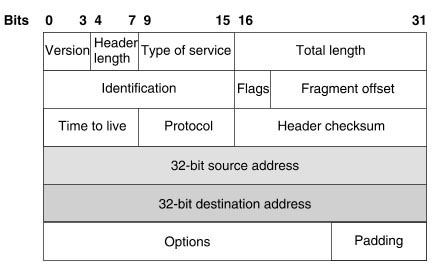
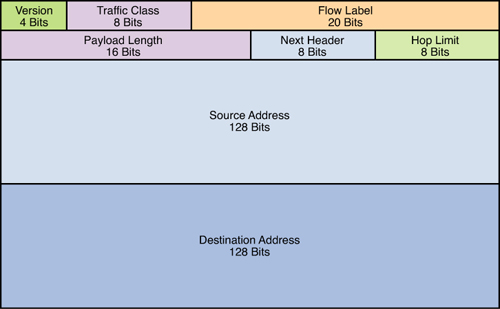 IPv6 eliminates the Header Checksum field, which handles error checking in IPv4. IPv6 depends on reliable transmission in the data link protocols and on error checking in upper-layer protocols instead -> Answer C is correct.
While IPv4 header’s total length comprises a minimum of 20 octets (8 bits per octet), IPv6 header has only 8 fields with a fixed length of 40 octets -> Answer A is correct.
IPv4 header does not have a fixed length because of the Options fields. This field is used to convey additional information on the packet or on the way it should be processed. Routers, unless instructed otherwise, must process the Options in the IPv4 header. The processing of most header options pushes the packet into the slow path leading to a forwarding performance hit.
IPv4 Options perform a very important role in the IP protocol operation therefore the capability had to be preserved in IPv6. However, the impact of IPv4 Options on performance was taken into consideration in the development of IPv6. The functionality of Options is removed from the main header and implemented through a set of additional headers called extension headers. The “Next Header” field in IPv6 can be used to point to the extension headers.
IPv6 eliminates the Header Checksum field, which handles error checking in IPv4. IPv6 depends on reliable transmission in the data link protocols and on error checking in upper-layer protocols instead -> Answer C is correct.
While IPv4 header’s total length comprises a minimum of 20 octets (8 bits per octet), IPv6 header has only 8 fields with a fixed length of 40 octets -> Answer A is correct.
IPv4 header does not have a fixed length because of the Options fields. This field is used to convey additional information on the packet or on the way it should be processed. Routers, unless instructed otherwise, must process the Options in the IPv4 header. The processing of most header options pushes the packet into the slow path leading to a forwarding performance hit.
IPv4 Options perform a very important role in the IP protocol operation therefore the capability had to be preserved in IPv6. However, the impact of IPv4 Options on performance was taken into consideration in the development of IPv6. The functionality of Options is removed from the main header and implemented through a set of additional headers called extension headers. The “Next Header” field in IPv6 can be used to point to the extension headers.
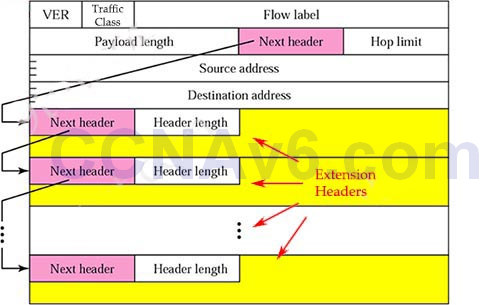 Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk648/tk872/technologies_white_paper0900aecd8054d37d.html
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk648/tk872/technologies_white_paper0900aecd8054d37d.html
-
Question 151 of 214
151. Question
1 pointsWhich type of address is the public IP address of a NAT device?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
NAT use four types of addresses: * Inside local address – The IP address assigned to a host on the inside network. The address is usually not an IP address assigned by the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC) or service provider. This address is likely to be an RFC 1918 private address. * Inside global address – A legitimate IP address assigned by the InterNIC or service provider that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world. * Outside local address – The IP address of an outside host as it is known to the hosts on the inside network. * Outside global address – The IP address assigned to a host on the outside network. The owner of the host assigns this address.
-
Question 152 of 214
152. Question
1 pointsWhich command can you enter to display the hits counter for NAT traffic?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
An example of the output of the “show ip nat statistics” is shown below. As we can see, the “Hits” counter is displayed.
-
Question 153 of 214
153. Question
1 pointsWhat is the first step in the NAT configuration process?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In NAT configuration we should specify the inside and outside interfaces first with the command “ip nat inside” and “ip nat outside” under interface mode. -
Question 154 of 214
154. Question
1 pointsWhat is the best way to verify that a host has a path to other hosts in different networks?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Ping is a tool that helps to verify IP-level connectivity; PathPing is a tool that detects packet loss over multiple-hop trips. When troubleshooting, the ping command is used to send an ICMP Echo Request to a target host name or IP address. Use Ping whenever you want to verify that a host computer can send IP packets to a destination host. You can also use the Ping tool to isolate network hardware problems and incompatible configurations. If you call ipconfig /all and receive a response, there is no need to ping the loopback address and your own IP address — Ipconfig has already done so in order to generate the report. It is best to verify that a route exists between the local computer and a network host by first using ping and the IP address of the network host to which you want to connect. The command syntax is: ping < IP address > Perform the following steps when using Ping: Ping the loopback address to verify that TCP/IP is installed and configured correctly on the local computer. ping 127.0.0.1 If the loopback step fails, the IP stack is not responding. This might be because the TCP drivers are corrupted, the network adapter might not be working, or another service is interfering with IP. Ping the IP address of the local computer to verify that it was added to the network correctly. Note that if the routing table is correct, this simply forwards the packet to the loopback address of 127.0.0.1. ping < IP address of local host > Ping the IP address of the default gateway to verify that the default gateway is functioning and that you can communicate with a local host on the local network. ping < IP address of default gateway > Ping the IP address of a remote host to verify that you can communicate through a router. ping < IP address of remote host > Ping the host name of a remote host to verify that you can resolve a remote host name. ping < Host name of remote host > Run a PathPing analysis to a remote host to verify that the routers on the way to the destination are operating correctly. pathping < IP address of remote host > -
Question 155 of 214
155. Question
1 pointsIf host Z needs to send data through router R1 to a storage server, which destination MAC address does host Z use to transmit packets?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Host Z will use ARP to get the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to it and use this MAC as the destination MAC address. It use the IP address of the storage server as the destination IP address. For example in the topology below, host A will use the MAC address of E0 interface of the router as its destination MAC address to reach the Email Server.
-
Question 156 of 214
156. Question
1 pointsWhile you were troubleshooting a connection issue, a ping from one VLAN to another VLAN on the same switch failed. Which command verifies that IP routing is enabled on interfaces and the local VLANs are up?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The “show ip nat statistics” only gives us information about NAT translation. We cannot know if IP routing is enabled or the VLANs are up not not. The “show ip statistics” command does not exist. In the Troubleshoot part of “How to configure InterVLAN Routing on Layer 3 switches” (http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/inter-vlan-routing/41860-howto-L3-intervlanrouting.html) Cisco recommends to use the “show ip interface brief” command as follows: Also verify the interface VLAN status by issuing the show ip interface brief command. + If the interface status is administratively down, enter the no shutdown command in the VLAN interface configuration mode. + If the interface status is down/down, verify the VTP configuration and that the VLANs have been added to the VLAN database. Check to see if a port is assigned to the VLAN and whether it is in the Spanning Tree forwarding state. Initiate a ping from an end device in one VLAN to the interface VLAN on another VLAN in order to verify that the switch routes between VLANs. In this example, ping from VLAN 2 (10.1.2.1) to Interface VLAN 3 (10.1.3.1) or Interface VLAN 10 (10.1.10.1). If the ping fails, verify that IP routing is enabled and that the VLAN interfaces status is up with the show ip interface brief command. Also in the above link Cisco only mentions about the “show ip route” in the “Verify” part, not “Troubleshooting” part so “show ip interface brief” is a better answer. -
Question 157 of 214
157. Question
1 pointsUnder which circumstance should a network administrator implement one-way NAT?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
NAT operation is typically transparent to both the internal and external hosts. Typically, the internal host is aware of the true IP address and TCP or UDP port of the external host. Typically, the NAT device may function as the default gateway for the internal host. However, the external host is only aware of the public IP address for the NAT device and the particular port being used to communicate on behalf of a specific internal host. NAT and TCP/UDP “Pure NAT”, operating on IP alone, may or may not correctly parse protocols that are totally concerned with IP information, such as ICMP, depending on whether the payload is interpreted by a host on the “inside” or “outside” of translation. As soon as the protocol stack is traversed, even with such basic protocols as TCP and UDP, the protocols will break unless NAT takes action beyond the network layer. IP packets have a checksum in each packet header, which provides error detection only for the header. IP datagrams may become fragmented and it is necessary for a NAT to reassemble these fragments to allow correct recalculation of higher-level checksums and correct tracking of which packets belong to which connection. The major transport layer protocols, TCP and UDP, have a checksum that covers all the data they carry, as well as the TCP/UDP header, plus a “pseudo-header” that contains the source and destination IP addresses of the packet carrying the TCP/UDP header. For an originating NAT to pass TCP or UDP successfully, it must recompute the TCP/ UDP header checksum based on the translated IP addresses, not the original ones, and put that checksum into the TCP/UDP header of the first packet of the fragmented set of packets. The receiving NAT must recompute the IP checksum on every packet it passes to the destination host, and also recognize and recompute the TCP/UDP header using the retranslated addresses and pseudo-header. This is not a completely solved problem. One solution is for the receiving NAT to reassemble the entire segment and then recompute a checksum calculated across all packets. The originating host may perform Maximum transmission unit (MTU) path discovery to determine the packet size that can be transmitted without fragmentation, and then set the don’t fragment (DF) bit in the appropriate packet header field. Of course, this is only a one-way solution, because the responding host can send packets of any size, which may be fragmented before reaching the NAT. -
Question 158 of 214
158. Question
1 pointsWhen a router makes a routing decision for a packet that is received from one network and destined to another, which portion of the packet does if replace?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The Layer 2 information (source and destination MAC) would be changed when passing through each router. The Layer 3 information (source and destination IP addresses) remains unchanged. -
Question 159 of 214
159. Question
1 pointsOn which type of device is every port in the same collision domain?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Collision domain A collision domain is, as the name implies, a part of a network where packet collisions can occur. A collision occurs when two devices send a packet at the same time on the shared network segment. The packets collide and both devices must send the packets again, which reduces network efficiency. Collisions are often in a hub environment, because each port on a hub is in the same collision domain. By contrast, each port on a bridge, a switch or a router is in a separate collision domain. -
Question 160 of 214
160. Question
1 pointsWhat is one requirement for interfaces to run IPv6?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
To run IPv6 on an interface we have to configure an IPv6 on that interface somehow -> A is correct. IPv6 must be enabled first but with the “ipv6 unicast-routing”, not “ipv6 enable” command -> D is not correct. -
Question 161 of 214
161. Question
1 pointsWhich destination IP address can a host use to send one message to multiple devices across different subnets?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
In order to send traffic to multiple devices (not all) across different subnets we need to use multicast addresses, which are in the range 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255 -> D is correct. -
Question 162 of 214
162. Question
1 pointsWhich MTU size can cause a baby giant error?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Ethernet frame size refers to the whole Ethernet frame, including the header and the trailer while MTU size refers only to Ethernet payload. Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes, and jumbo frame refers to Ethernet frame size up to 9216 bytes (according to this link: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-4000-series-switches/29805-175.html) For example, standard Ethernet frame MTU is 1500 bytes. This does not include the Ethernet header and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) trailer, which is 18 bytes in length, to make the total Ethernet frame size of 1518. So according to strict definition, MTU size of 1600 cannot be classified as baby giant frames as the whole Ethernet frames will surely larger than 1600 -> Answer C is not correct. Answer D is a better choice as the MTU is 1518, so the whole Ethernet frame would be 1536 (1518 + 18 Ethernet header and CRC trailer). This satisfies the requirement of baby giant frames “Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes”. -
Question 163 of 214
163. Question
1 pointsWhich type of broadcast barely used in IPv4 which also exist in IPv6 like?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 164 of 214
164. Question
1 pointsWhich type of cable must you use to connect to device with mdi interfaces?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 165 of 214
165. Question
1 pointsWhich two of these statements are true of IPv6 address representation? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Leading zeros in IPv6 are optional do that 05C7 equals 5C7 and 0000 equals 0 -> D is not correct. -
Question 166 of 214
166. Question
1 pointsWhat is the first 24 bits in a MAC address called?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
An Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) is a 24-bit number that uniquely identifies a vendor, manufacturer, or other organization globally or worldwide. They are used as the first 24 nits of the MAC address to uniquely identify a particular piece of equipment. -
Question 167 of 214
167. Question
1 pointsWhat is the difference between a CSU/DSU and a modem?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
CSU/DSU is used to convert digital signals from a router to a network circuit such as a T1, while a modem is used to convert digital signals over a regular POTS line. -
Question 168 of 214
168. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about EUI-64 addressing are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Extended Unique Identifier (EUI) allows a host to assign itself a unique 64-Bit IPv6 interface identifier (EUI-64). This feature is a key benefit over IPv4 as it eliminates the need of manual configuration or DHCP as in the world of IPv4. The IPv6 EUI-64 format address is obtained through the 48-bit MAC address. The MAC address is first separated into two 24-bits, with one being OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) and the other being NIC specific. The 16-bit 0xFFFE is then inserted between these two 24-bits for the 64-bit EUI address. IEEE has chosen FFFE as a reserved value which can only appear in EUI-64 generated from the an EUI-48 MAC address. For example, suppose we have the MAC address of C601.420F.0007. It would be divided into two 24-bit parts, which are “C60142” (OUI) and “0F0007” (NIC). Then “FFFE” is inserted in the middle. Therefore we have the address: C601.42FF.FE0F.0007. Then, according to the RFC 3513 we need to invert the Universal/Local bit (“U/L” bit) in the 7th position of the first octet. The “u” bit is set to 1 to indicate Universal, and it is set to zero (0) to indicate local scope. Therefore with the subnet of 2001:DB8:0:1::/64, the full IPv6 address is 2001:DB8:0:1:C601:42FF:FE0F:7/64 -
Question 169 of 214
169. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about IPv4 multicast traffic are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
http://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en_us/about/ciscoitatwork/downloads/ciscoitatwork/pdf/cisco_it_case_study_multicast.pdf Cisco IOS IP Multicast in the Cisco Network “IP Multicast as defined in RFC1112, the standard for IP Multicast across networks and the Internet, supports one-to-many content needs by delivering application-source traffic to multiple users without burdening the source or the network, using a minimum amount of network bandwidth. At the point where paths diverge, Cisco routers replace IP Multicast packets in the network, resulting in the most efficient delivery of data to multiple receivers.” Even low-bandwidth applications can benefit fro IP Multicast when there are thousands of receivers. High-bandwidth applications, such as MPEG video, may need a large portion of the available network bandwidth for a single stream. In these applications, IP Multicast is the only way to efficiently send the same content to more than one receiver simultaneously, because it makes sure that only one copy of the data stream is sent across any one network link. It relies on each router in the stream to intelligently copy the data stream whenever it needs to deliver it to multiple receivers. -
Question 170 of 214
170. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about IPv6 router advertisement messages are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
IPv6 router advertisement message is one type of the ICMPv6 packets with Type field value of 134. It lists many facts, including the link-local IPv6 address of the router. Normally, it is sent to the all-IPv6-hosts local-scope multicast address of FF02::1. When sent in response to router solicitation messages (ICMPv6 Type 133), it flows back to either the unicast address of the host that sent the RS or to the all-IPv6-hosts address FF02::1. The advertised IPv6 prefix length must be 64 bits for the stateless address autoconfiguration to be operational. -
Question 171 of 214
171. Question
1 pointsWhich three technical services support cloud computing?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Four technical services are essential to supporting the high level of flexibility, resource availability, and transparent resource connectivity required for cloud computing: + The Layer 3 network offers the traditional routed interconnection between remote sites and provides end-user access to cloud services. + The extended LAN between two or more sites offers transparent transport and supports application and operating system mobility. + Extended SAN services support data access and accurate data replication. + IP Localization improves northbound and southbound traffic as well as server-to-server workflows. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/ios-xr-software/white_paper_c11-694882.html -
Question 172 of 214
172. Question
1 pointsWhich component of the Cisco SDN solution serves as the centralized management system?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/data-center-virtualization/application-centric-infrastructure/index.html Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) Provides single-click access to all Cisco ACI fabric information, enabling network automation, programmability, and centralized management. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/cloud-systems-management/application-policy-infrastructure-controller-apic/index.html The Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (Cisco APIC) is the unifying point of automation and management for the Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) fabric. The Cisco APIC provides centralized access to all fabric information, optimizes the application lifecycle for scale and performance, and supports flexible application provisioning across physical and virtual resources. The Cisco APIC provides centralized access to all fabric information, optimizes the application lifecycle for scale and performance, and supports flexible application provisioning across physical and virtual resources. Centralized application-level policy engine for physical, virtual, and cloud infrastructures Designed for automation, programmability, and centralized management, the Cisco APIC itself exposes northbound APIs through XML and JSON. It provides both a command-line interface (CLI) and GUI which utilize the APIs to manage the fabric holistically. Cisco APIC provides: A single pane of glass for application-centric network policies Fabric image management and inventory Application, tenant, and topology monitoring Troubleshooting -
Question 173 of 214
173. Question
1 pointsWhat are the three major components of cisco network virtualization? (Choose Three)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Network virtualization architecture has three main components: + Network access control and segmentation of classes of users: Users are authenticated and either allowed or denied into a logical partition. Users a re segmented into employees, contractors and consultants, and guests, with respective access to IT assets. This component identifies users who are authorized to access the network and then places them into the appropriate logical partition. + Path isolation: Network isolation is preserved across the entire enterprise: from the edge to the campus to the WAN and back again. This component maintains traffic partitioned over a routed infrastructure and transports traffic over and between isolated partitions. The function of mapping isolated paths to VLANs and to virtual services is also performed in component. + Network Services virtualization: This component provides access to shared or dedicated network services such as security, quality of service (QoS), and address management (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol [DHCP] and Domain Name System [DNS]). It also applies policy per partition and isolates application environments, if required. Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/catalyst-6500-series switches/white_paper_c11-531522.pdf
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/catalyst-6500-series switches/white_paper_c11-531522.pdf -
Question 174 of 214
174. Question
1 pointsWhich IPV6 function serves the same purpose as ARP entry verification on an IPv4 network?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Neighbor Discovery Protocol is an umbrella that defines these mechanisms: + Subsitute of ARP – Since ARP has been removed in IPv6, IPv6 follows a newer way to find the link-layer addresses of nodes on the local link. This new mechanism uses a mix of ICMPv6 messages and multicast addresses Reference: https://supportforums.cisco.com/document/77521/ipv6-neighbor-discovery-protocol-ndp -
Question 175 of 214
175. Question
1 pointsWhen you troubleshoot an IPv4 connectivity issue on a router, which three router configuration checks you must perform?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 176 of 214
176. Question
1 pointsWhich Type of ipv6 unicast ip address is reachable across the internet?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 177 of 214
177. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about IPv6 address 2002:ab10:beef::/48 are true?(choose two)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Any IPv6 address that begins with the 2002::/16 prefix is known as a 6to4 address. A 6to4 gateway adds its IPv4 address to this 2002::/16, creating a unique /48 prefix (because an IPv4 consists of 32 bits). For example: In the IPv6 address 2002:ab10:beef::/48, “ab10:beef” is equivalent to 171.16.190.239 (convert “ab” in hexadecimal to “171” in decimal; “10” in hexadecimal to “16” in decimal…). Therefore the corresponding IPv4 address can be globally routed. -
Question 178 of 214
178. Question
1 pointsWhich three functions are major components of a network virtualization architecture? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 179 of 214
179. Question
1 pointsWhich two benefits are provided by using a hierarchical addressing network addressing scheme? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Here are some of the benefits of hierarchical addressing: Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=174107 -
Question 180 of 214
180. Question
1 pointsRefer to the exhibit. Both switches are using a default configuration. Which two destination addresses will host 4 use to send data to host 1? (Choose two.) Correct
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 181 of 214
181. Question
1 pointsWhich technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
DHCPv6 Technology Overview IPv6 Internet Address Assignment Overview IPv6 has been developed with Internet Address assignment dynamics in mind. Being aware that IPv6 Internet addresses are 128 bits in length and written in hexadecimals makes automation of address- assignment an important aspect within network design. These attributes make it inconvenient for a user to manually assign IPv6 addresses, as the format is not naturally intuitive to the human eye. To facilitate address assignment with little or no human intervention, several methods and technologies have been developed to automate the process of address and configuration parameter assignment to IPv6 hosts. The various IPv6 address assignment methods are as follows: 1. Manual Assignment An IPv6 address can be statically configured by a human operator. However, manual assignment is quite open to errors and operational overhead due to the 128 bit length and hexadecimal attributes of the addresses, although for router interfaces and static network elements and resources this can be an appropriate solution. 2. Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (RFC2462) Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) is one of the most convenient methods to assign Internet addresses to IPv6 nodes. This method does not require any human intervention at all from an IPv6 user. If one wants to use IPv6 SLAAC on an IPv6 node, it is important that this IPv6 node is connected to a network with at least one IPv6 router connected. This router is configured by the network administrator and sends out Router Advertisement announcements onto the link. These announcements can allow the on-link connected IPv6 nodes to configure themselves with IPv6 address and routing parameters, as specified in RFC2462, without further human intervention. 3. Stateful DHCPv6 The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6) has been standardized by the IETF through RFC3315. DHCPv6 enables DHCP servers to pass configuration parameters, such as IPv6 network addresses, to IPv6 nodes. It offers the capability of automatic allocation of reusable network addresses and additional configuration flexibility. This protocol is a stateful counterpart to “IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration” (RFC 2462), and can be used separately, or in addition to the stateless autoconfiguration to obtain configuration parameters. 4. DHCPv6-PD DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation (DHCPv6-PD) is an extension to DHCPv6, and is specified in RFC3633. Classical DHCPv6 is typically focused upon parameter assignment from a DHCPv6 server to an IPv6 host running a DHCPv6 protocol stack. A practical example would be the stateful address assignment of “2001:db8::1” from a DHCPv6 server to a DHCPv6 client. DHCPv6-PD however is aimed at assigning complete subnets and other network and interface parameters from a DHCPv6-PD server to a DHCPv6-PD client. This means that instead of a single address assignment, DHCPv6-PD will assign a set of IPv6 “subnets”. An example could be the assignment of “2001:db8::/60” from a DHCPv6-PD server to a DHCPv6-PD client. This will allow the DHCPv6-PD client (often a CPE device) to segment the received address IPv6 address space, and assign it dynamically to its IPv6 enabled interfaces. 5. Stateless DHCPv6 Stateless DHCPv6 is a combination of “stateless Address Autoconfiguration” and “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6” and is specified by RFC3736. When using stateless-DHCPv6, a device will use Stateless Address Auto-Configuration (SLAAC) to assign one or more IPv6 addresses to an interface, while it utilizes DHCPv6 to receive “additional parameters” which may not be available through SLAAC. For example, additional parameters could include information such as DNS or NTP server addresses, and are provided in a stateless manner by DHCPv6. Using stateless DHCPv6 means that the DHCPv6 server does not need to keep track of any state of assigned IPv6 addresses, and there is no need for state refreshment as result. On network media supporting a large number of hosts associated to a single DHCPv6 server, this could mean a significant reduction in DHCPv6 messages due to the reduced need for address state refreshments. From Cisco IOS 12.4(15)T onwards the client can also receive timing information, in addition to the “additional parameters” through DHCPv6. This timing information provides an indication to a host when it should refresh its DHCPv6 configuration data. This behavior (RFC4242) is particularly useful in unstable environments where changes are likely to occur. -
Question 182 of 214
182. Question
1 pointsWhich command can you enter to verify that a 128-bit address is live and responding?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 183 of 214
183. Question
1 pointsWhich device allows users to connect to the network using a single or double radio?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Many Cisco access points offer single or double (dual) radio (2.4 and 5.0 GHz). Note: The wireless controller automates wireless configuration and management functions. It does not connect directly to users. -
Question 184 of 214
184. Question
1 pointsA switch is configured with all ports assigned to VLAN 2 with full duplex FastEthernet to segment existing departmental traffic. What is the effect of adding switch ports to a new VLAN on the switch?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 185 of 214
185. Question
1 pointsWhen troubleshooting Ethernet connectivity issues, how can you verify that an IP address is known to a router?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
If the IP address exists in the routing table then we can say the local router knew the way to reach that destination. But this question wants to ask if the destination has communicated to the local router or not (“an IP address is known to a router”). Maybe it is a tricky question. -
Question 186 of 214
186. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about the tunnel mode ipv6ip command are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
Hint
The “tunnel mode ipv6ip” command specifies IPv6 as the passenger protocol and IPv4 as both the encapsulation and transport protocol for the manual IPv6 tunnel. Notice that the tunnel source and destination are configured with IPv4 addressing and the tunnel interface is configured with IPv6. An example of configuring using this command is shown below:
An example of configuring using this command is shown below:
R1(config)#int tunnel 1 R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 1cde:7ea:348:1::3/127 R1(config-if)#tunnel source 10.1.1.1 R1(config-if)#tunnel destination 10.1.1.2 R1(config-if)#tunnel mode ipv6ip
-
Question 187 of 214
187. Question
1 pointsWhich configuration can you apply to enable encapsulation on a subinterface?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
To enabe encapsulation on a subinterface we have type the “encapsulation” command under that subinterface, not the main interface. An example of configuring encapsulation on subinterface of Fa0/1 is shown below:Router(config)#interface f0/0 Router(config-if)#no shutdown (Note: The main interface f0/0 doesn’t need an IP address but it must be turned on) Router(config)#interface f0/0.0 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-subif)#interface f0/0.1 Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 20 Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Note: In the “encapsulation dot1q 10”, number 10 is the VLAN applied to that subinterface. Or you can understand that the subinterface belongs to that VLAN. -
Question 188 of 214
188. Question
1 pointsWhat happens when an 802.11a node broadcasts within the range of an 802.11g access point?Correct
Incorrect
Hint
802.11g is only compatible with 802.11b, not 802.11a so when 802.11a node broadcast, 802.11g access point cannot receive it. -
Question 189 of 214
189. Question
1 pointsA network administrator receives an error message while trying to configure the Ethernet interface of a router with IP address 10.24.24.24/29. Which statement explains the reason for this issue?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 190 of 214
190. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about 1000BASE-T UTP cable are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 191 of 214
191. Question
1 pointsWhich two statements about IPv6 multicast addresses are true? (Choose two.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 192 of 214
192. Question
1 pointsWhich command can you enter on a Cisco IOS device to enable a scheduled algorithm that directs lookup calls to multiple DNS hosts?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 193 of 214
193. Question
1 pointsWhich three elements are field in a basic Ethernet data frame? (Choose three.)Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 194 of 214
194. Question
1 pointsWhich prompt does a Cisco switch display when it is running in privileged exec mode?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 195 of 214
195. Question
1 pointsWhich benefit of implementing a dual-homed WAN connection instead of a single-homed connection is true?Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 196 of 214
196. Question
1 pointsRefer to the graphic. Host A is communicating with the server. What will be the source MAC address of the frames received by Host A from the server?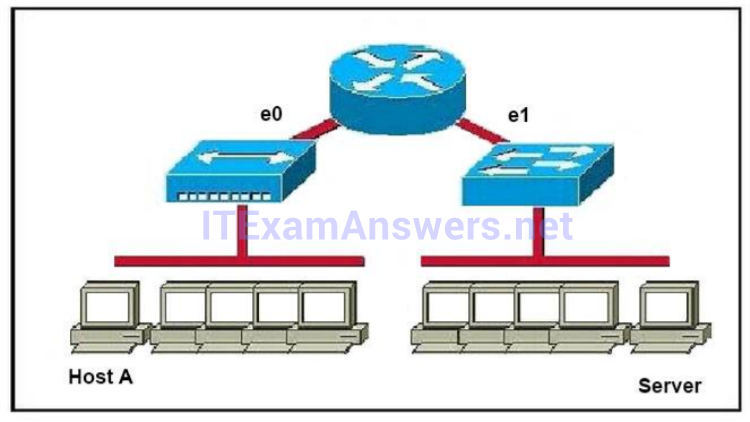 Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
Whereas switches can only examine and forward packets based on the contents of the MAC header, routers can look further into the packet to discover the network for which a packet is destined. Routers make forwarding decisions based on the packet’s network-layer header (such as an IPX header or IP header). These network-layer headers contain source and destination network addresses. Local devices address packets to the router’s MAC address in the MAC header. After receiving the packets, the router must perform the following steps: 1. Check the incoming packet for corruption, and remove the MAC header. The router checks the packet for MAC-layer errors. The router then strips off the MAC header and examines the network- layer header to determine what to do with the packet. 2. Examine the age of the packet. The router must ensure that the packet has not come too far to be forwarded. For example, IPX headers contain a hop count. By default, 15 hops is the maximum number of hops (or routers) that a packet can cross. If a packet has a hop count of 15, the router discards the packet. IP headers contain a Time to Live (TTL) value. Unlike the IPX hop count, which increments as the packet is forwarded through each router, the IP TTL value decrements as the IP packet is forwarded through each router. If an IP packet has a TTL value of 1, the router discards the packet. A router cannot decrement the TTL value to 1 and then forward the packet. 3. Determine the route to the destination. Routers maintain a routing table that lists available networks, thedirection to the desired network (the outgoing interface number), and the distance to those networks. After determining which direction to forward the packet, the router must build a new header. (If you want to read the IP routing tables on a Windows 95/98 workstation, type ROUTE PRINT in the DOS box.) 4. Build the new MAC header and forward the packet. Finally, the router builds a new MAC header for the packet. The MAC header includes the router’s MAC address and the final destination’s MAC address or the MAC address of the next router in the path. -
Question 197 of 214
197. Question
1 pointsRefer to exhibit: Which destination addresses will be used by Host A to send data to Host C? (Choose two.) Correct
Correct
Incorrect
Hint
While transferring data through many different networks, the source and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case Host A will use the IP address of Host C and the MAC address of E0 interface to send data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC address with it own E1 interface’s MAC address and replaces the destination MAC address with Host C’s MAC address before sending to Host C. -
Question 198 of 214
198. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the Ethernet terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right. Select and Place:
Sort elements
Correct
Incorrect
-
-
Question 199 of 214
199. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Refer to the exhibit. Select and Place:
Sort elements
Correct
Incorrect
-
-
Question 200 of 214
200. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag the cable type on the left to the purpose for which is the best suited on the right. Not all options are used. Select and Place: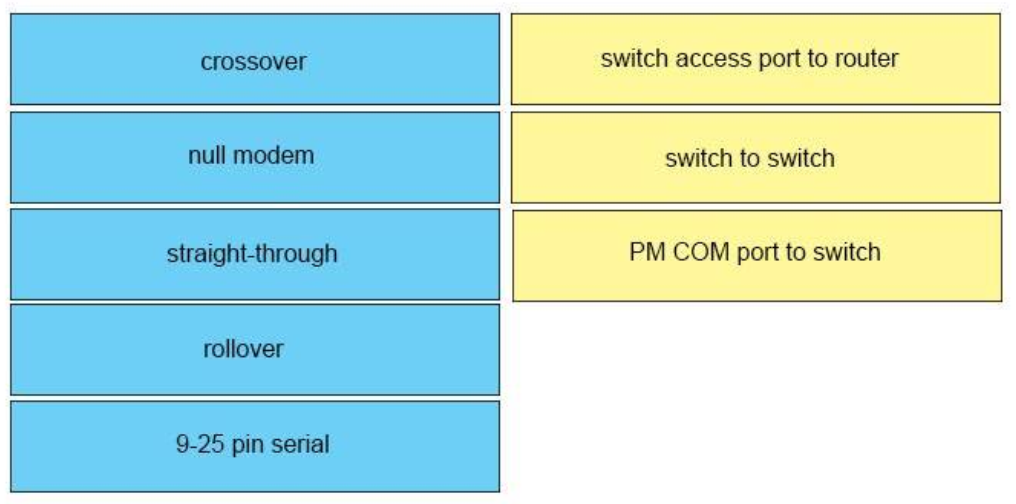
Sort elements
- crossover
- straight-through
- rollover
- 9-25 pin-serial
- null modem
-
switch to switch
-
switch access port to router
-
PM COM port to switch
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 201 of 214
201. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag the IPv6 multicast address type on the left to their purpose on the right.. Select and Place: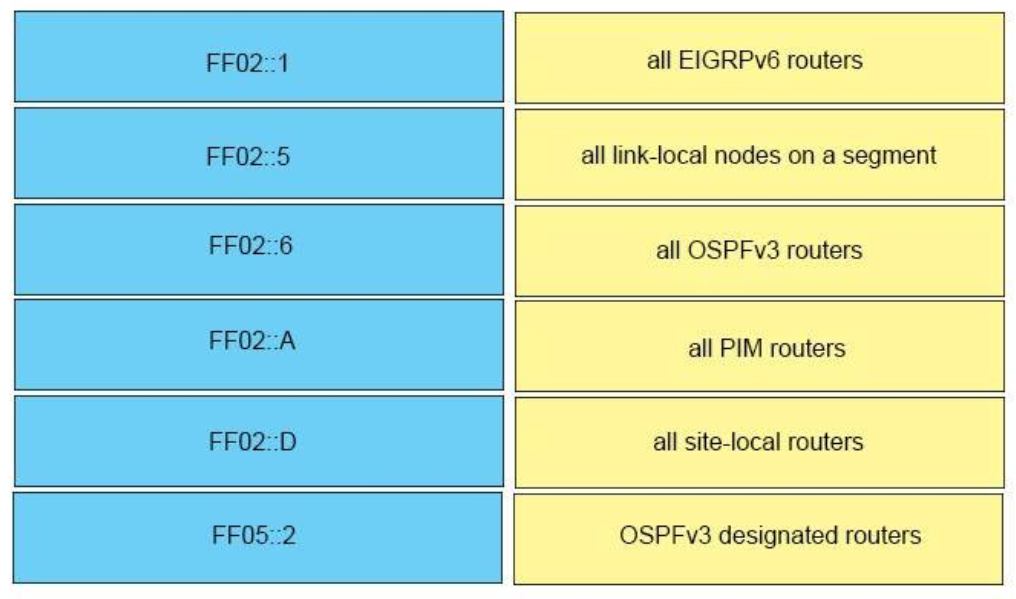
Sort elements
Correct
Incorrect
-
-
Question 202 of 214
202. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the IPv6 IP addresses from the left onto the correct IPv6 address types on the right. Select and Place: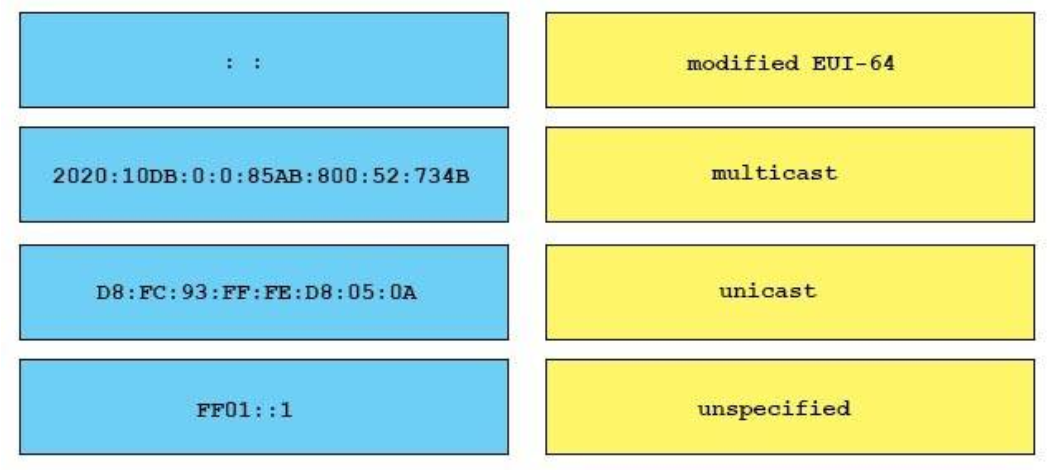
Sort elements
- unspecified
- unicast
- modified EUI-64
- multicast
-
: :
-
2010 : 10DB : 0 : 0 : 85AB : 800 : 52 : 734B
-
D8 : FC : 93 : FF : FE : D8 : 05 : 0A
-
FF01 : : 11
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 203 of 214
203. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the application protocols from the left onto the transport protocols that is uses on the right. Select and Place:
Sort elements
- FTP
- SMTP
- SSH
- DHCP
- SNMP
- TFTP
-
TCP (1)
-
TCP (2)
-
TCP (3)
-
UDP (1)
-
UDP (2)
-
UDP (3)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 204 of 214
204. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the IEEE standard cable names from the left onto the correct cable types on the right. Select and Place: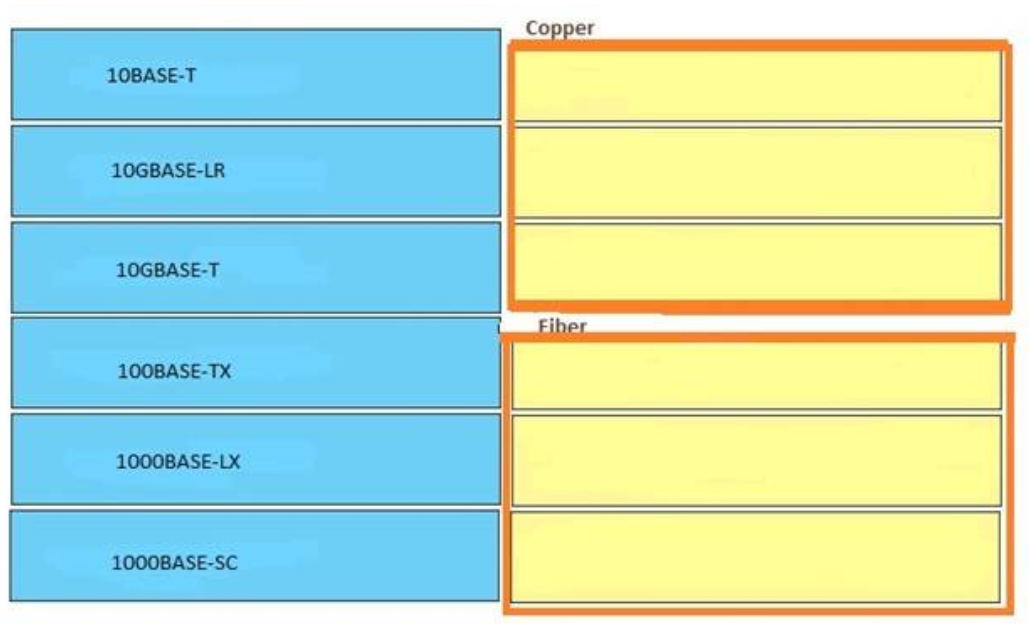
Sort elements
- 10BASE-T
- 10GBASE-T
- 100BASE-TX
- 10GBASE-LR
- 1000BASE-LX
- 1000BASE-SC
-
Copper (1)
-
Copper (2)
-
Copper (3)
-
Fiber (1)
-
Fiber (2)
-
Fiber (3)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 205 of 214
205. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. A user is unable to connect to the Internet. Based on the layered approach to troubleshooting and beginning with the lowest layer, drag each procedure on the left to its proper category on the right. Select and Place:
Sort elements
- verify Ethernet cable connection
- verify NIC operation
- verify IP configuration
- verify URL
-
Step 1
-
Step 2
-
Step 3
-
Step 4
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 206 of 214
206. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag the terms on the left onto the appropriate OSI layer on the right. (Not all options are used.) Select and Place: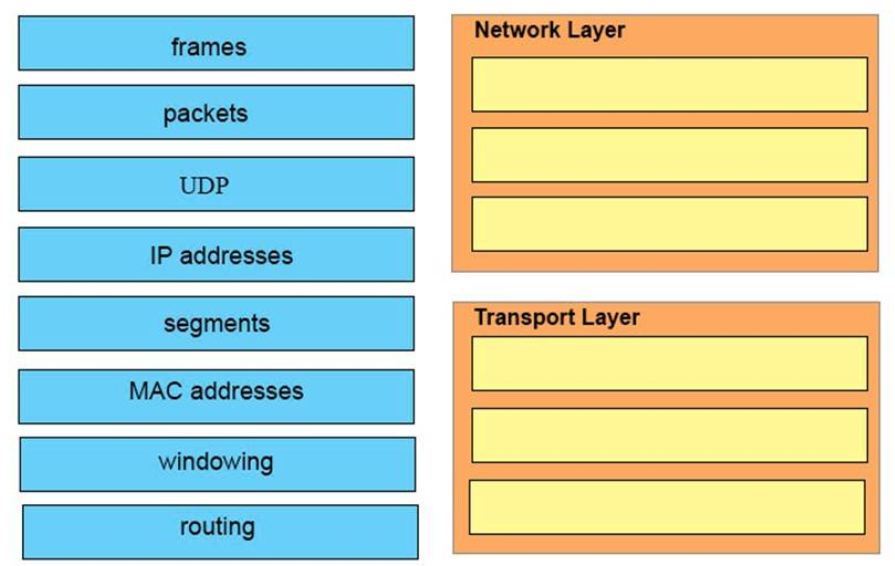
Sort elements
- packets
- IP addresses
- routing
- UDP
- segments
- windowing
- frames
- MAC addresses
-
Network Layer (1)
-
Network Layer (2)
-
Network Layer (3)
-
Transport Layer (1)
-
Transport Layer (2)
-
Transport Layer (3)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 207 of 214
207. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Refer to the exhibit.
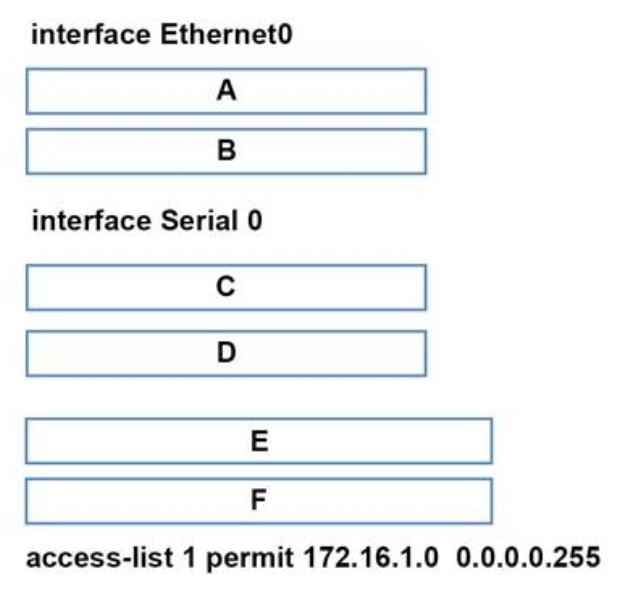 You are configuring the router to provide Static NAT for the web server.
Drag and drop the configuration commands from left onto the letters that correspond to its position in the
configuration on the right.
Select and Place:
You are configuring the router to provide Static NAT for the web server.
Drag and drop the configuration commands from left onto the letters that correspond to its position in the
configuration on the right.
Select and Place:
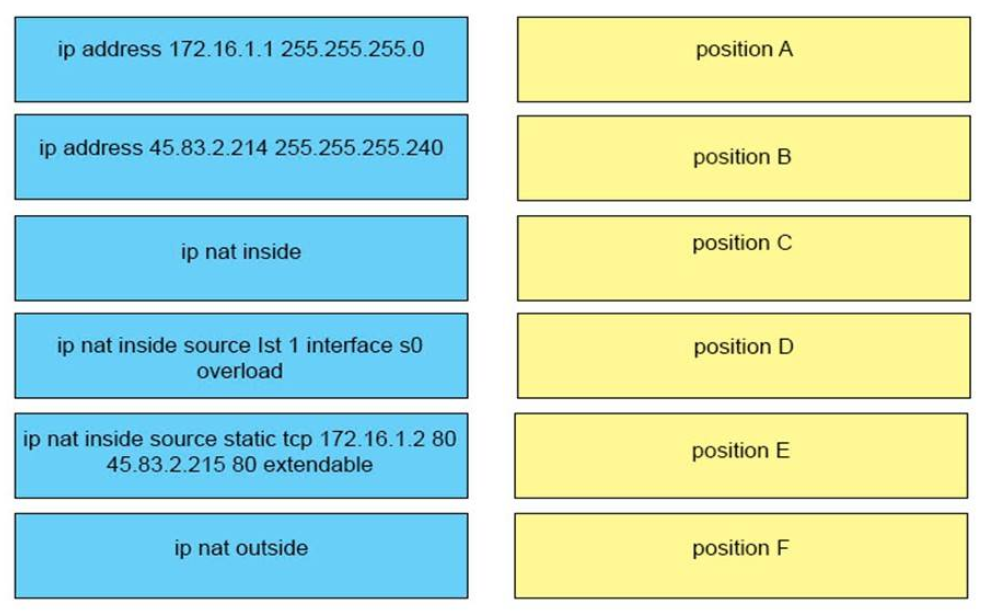
Sort elements
- ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
- ip nat inside
- ip address 45.83.2.214 255.255.255.240
- ip nat outside
- ip nat inside source static tcp 172.168.1.2 80.45.83.2.215 80 extendable
- ip nat inside source lst 1 interface s0 overload
-
position A
-
position B
-
position C
-
position D
-
position E
-
position F
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 208 of 214
208. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop each cable type from the left onto the type of connection for which it is best suited on the right. Select and Place: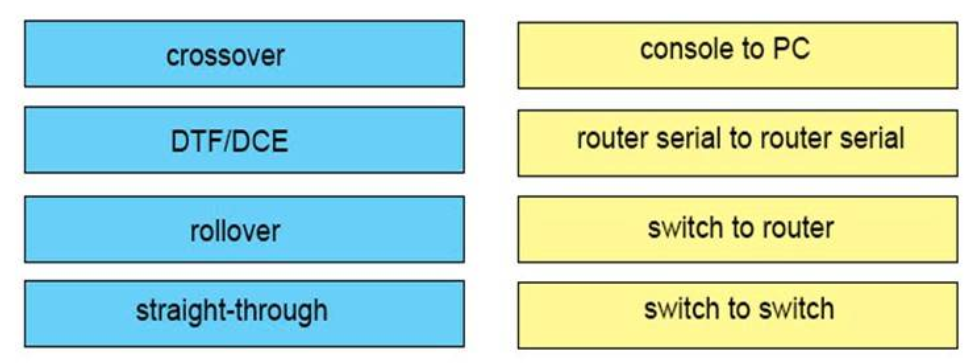
Sort elements
- rollover
- DTF/DCE
- straight-through
- crossover
-
console to PC
-
router serial to router serial
-
switch to router
-
switch to switch
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 209 of 214
209. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the characteristics of a cloud environment from the left onto the correct examples on the right Select and Place: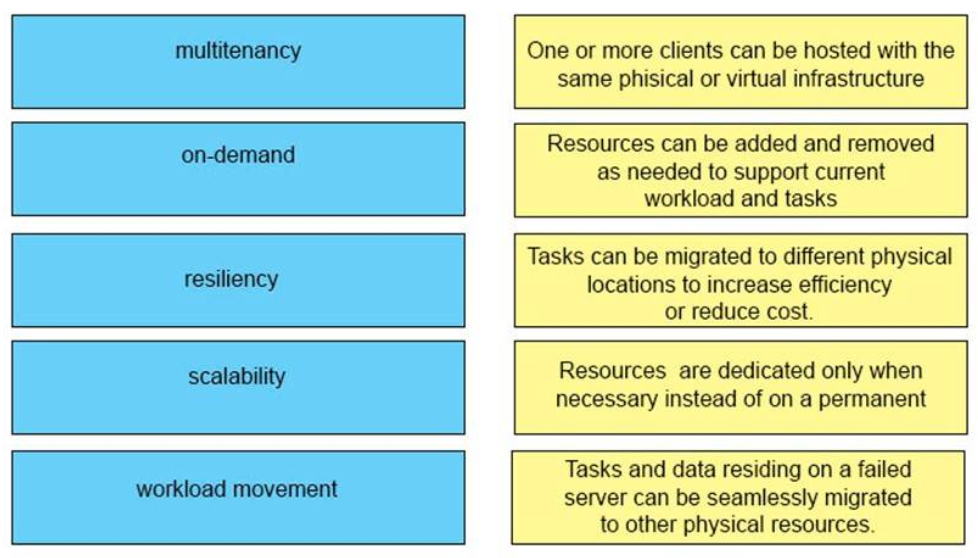
Sort elements
- One or more clients can be hosted with the same phisical or vitual infrastructure
- Resources are dedicated only when nesessary instead of on a permanent
- Tasks and data residing on a failed server can be seamlessly migrated to other physical resources
- Resources can be added and removed as needed to support current workload and tasks
- Tasks can be migrated to different physical locations to increases efficiency or reduce cost.
-
multitenancy
-
on-demand
-
resciliency
-
scalability
-
workload moverment
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 210 of 214
210. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop each broadcast IP address on the left to the Broadcast Address column on the right. Not alloptions are used. Select and Place:
Sort elements
- 10.63.255.255/10
- 172.16.255.39/29
- 172.20.55.255/16
- 192.168.255.127/25
- 10.1.255.254.24
- 192.168.1.10/24
-
A
-
B
-
C
-
D
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 211 of 214
211. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and Drop the descriptions of IP protocol transmissions from the left onto the correct IP traffic types on the right. Select and Place: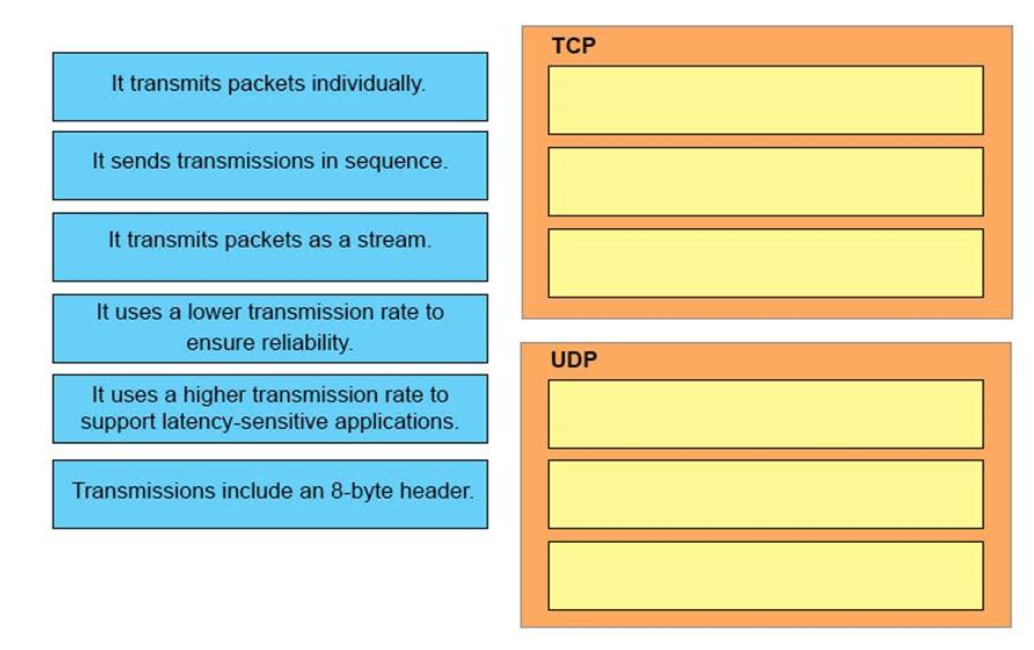
Sort elements
- it sends transmissions in sequence.
- It transmits packets as a stream
- It uses a lower transmissions rate to ensure reliability
- It transmits packets individually
- It use a higher transmission rate to support latency-sensitive applications.
- Transmissions include an 8-byte header.
-
TCP (1)
-
TCP (2)
-
TCP (3)
-
UDP (1)
-
UDP (2)
-
UDP (3)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 212 of 214
212. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag each category on the left to its corresponding router output line on the right. Each router output line is in the result of a show ip interface command. Not all categories are used. Select and Place:Sort elements
- port operational
- layer 2 problem
- layer 1 problem
- port disabled
- layer 3 problem
-
Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up
-
Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
-
Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
-
Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 213 of 214
213. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. Drag and drop the networking features of functions from the left onto the planes on which they operate on the right. Select and Place:
Sort elements
- filtering
- routing state exchange
- device access
- data encapsulation
- establishes Telnet sessions
- Qos
-
Control plane (1)
-
Control plane (2)
-
Control plane (3)
-
Data plane (1)
-
Data plane (2)
-
Data plane (3)
Correct
Incorrect
-
Question 214 of 214
214. Question
1 pointsDRAG DROP. You are connecting a variety of devices on your network. Drag and drop the combinations of devices from the left onto the correct cable types on the right. Select and Place: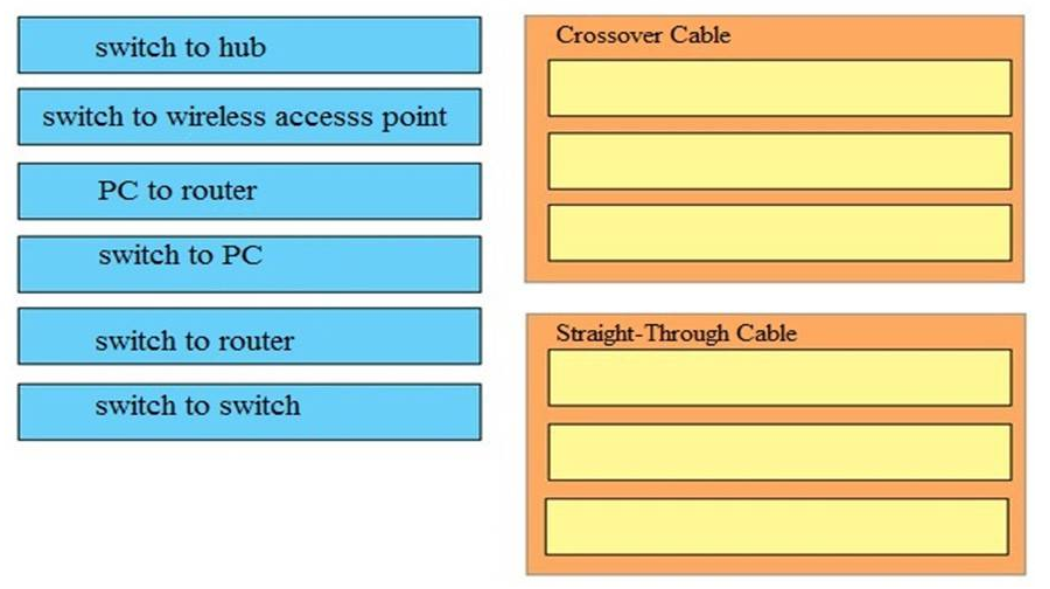
Sort elements
- switch to wireless access point
- switch to hub
- switch to switch
- switch to PC
- switch to router
- PC to router
-
Crossover Cable (1)
-
Crossover Cable (2)
-
Crossover Cable (3)
-
Straight - Through Cable (1)
-
Straight - Through Cable (2)
-
Straight - Through Cable (3)
Correct
Incorrect















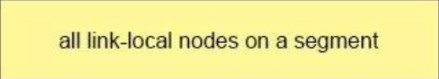









101. Question
Based on the network shown in the graphic…
there is no graphic in question 101 , Section I: Network Fundamentals – Test Online
Q64: Which RFC was created to alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses?
….Is it 1518 because it relates to moving to a classless system which makes more use of IP addressing and therefore not allowing public IPs to be depleted so quickly? And not 1918 because it just refers to what ranges are reserved for private and what are for public and not actually helping with conserving IPs?
Q80: Which protocol does ipv6 use to discover other ipv6 nodes on the same segment?
….Wouldn’t this be NDP as it replaced ARP for ipv6
Thanks,
Robin Hatton
We are asked to choose two answers for question 1 but only one choice can be made.
Fixed! Thanks you
yes guys , why do you offer a lot of questions like this? the ccna composite exam has 60-70 questions , but you offer more than 800 questions
for me i found it to be a lot . can you provide the dumps for icnd1 and 2 separatly please?
sorry, we don’t have dumps for icnd exam, you should study all 800 questions to get the maximum score