Networking Basics Course Final Exam Answers
1. Which statement describes the use of powerline networking technology?
- A device connects to an existing home LAN using an adapter and an existing electrical outlet.
- New “smart” electrical cabling is used to extend an existing home LAN.
- Wireless access points use powerline adapters to distribute data through the home LAN.
- A home LAN is installed without the use of physical cabling.
2. Which wireless RF band do IEEE 802.11b/g devices use?
- 60 GHz
- 2.4 GHz
- 900 MHz
- 5 GHz
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which term correctly identifies the device type that is included in the area B?
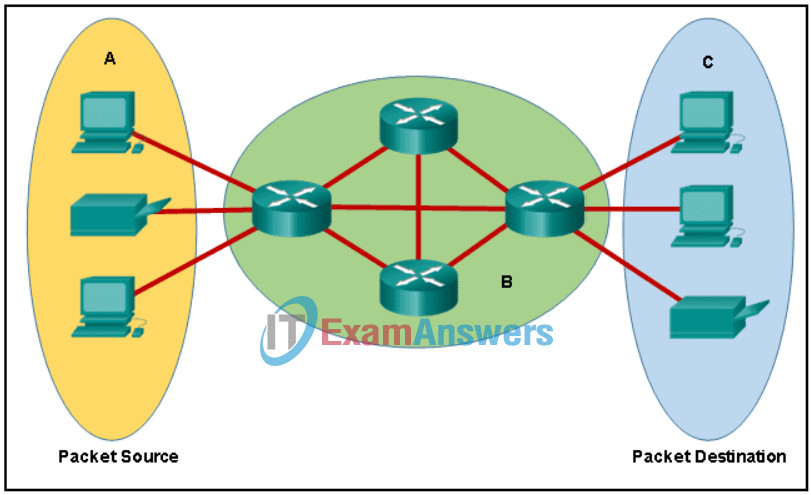
Networking Basics Course Final Exam 3
- end
- transfer
- source
- intermediary
4. What is a disadvantage of deploying a peer-to-peer network model?
- lack of centralized administration
- high cost
- difficulty of setup
- high degree of complexity
5. Which three steps must be completed to manually connect an Android or IOS device to a secured wireless network? (Choose three.)
- Change the MAC address.
- Set the IP address.
- Enter the network SSID.
- Activate the Bluetooth antenna.
- Input the authentication password.
- Choose the correct security type.
6. A company is contemplating whether to use a client/server or a peer-to-peer network. What are three characteristics of a peer-to-peer network? (Choose three.)
- better security
- scalable
- easy to create
- better device performance when acting as both client and server
- less cost to implement
- lacks centralized administration
7. Which type of device provides an Internet connection through the use of a phone jack?
- satellite modem
- Wi-Fi AP
- DSL modem
- cable modem
8. A traveling sales representative uses a cell phone to interact with the home office and customers, track samples, make sales calls, log mileage, and upload/download data while at a hotel. Which internet connectivity method would be a preferred method to use on the mobile device due to the low cost?
- cellular
- Wi-Fi
- DSL
- cable
9. A user is configuring a wireless access point and wants to prevent any neighbors from discovering the network. What action does the user need to take?
- Configure DMZ settings.
- Disable SSID broadcast.
- Configure a DNS server.
- Enable WPA encryption.
10. A tourist is traveling through the countryside and needs to connect to the internet from a laptop. However, the laptop only has Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections. The tourist has a smartphone with 3G/4G connectivity. What can the tourist do to allow the laptop to connect to the internet?
- Enable tethering and create a hotspot.
- Use the smartphone to access web pages and then pass the web pages to the laptop.
- Use the smartphone to access the internet through a satellite connection and then share that connection with the laptop.
- Use an Ethernet cable to connect the smartphone to the laptop.
11. What layer is responsible for routing messages through an internetwork in the TCP/IP model?
- network access
- session
- transport
- internet
12. What will a Cisco LAN switch do if it receives an incoming frame and the destination MAC address is not listed in the MAC address table?
- Send the frame to the default gateway address.
- Drop the frame.
- Forward the frame out all ports except the port where the frame is received.
- Use ARP to resolve the port that is related to the frame.
13. What process involves placing one message format inside of another message format?
- flow control
- encapsulation
- encoding
- segmentation
14. A cable installation company is trying to convince a customer to use fiber-optic cabling instead of copper cables for a particular job. What is one advantage of using fiber-optic cabling compared to copper cabling?
- The installation skills required for fiber-optic cabling are lower.
- Fiber-optic cabling can transmit signals without attenuation.
- Fiber-optic cabling is completely immune to EMI and RFI.
- The cost of fiber-optic connectors is lower.
15. What data encoding technology is used in copper cables?
- electrical pulses
- modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves
- modulation of light rays
- pulses of light
16. What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
- destination IP address and incoming port number
- source MAC address and incoming port number
- source IP address and incoming port number
- destination MAC address and incoming port number
17. At which layer of the OSI model would a logical address be added during encapsulation?
- network layer
- physical layer
- transport layer
- data link layer
18. Which type of network model describes the functions that must be completed at a particular layer, but does not specify exactly how each protocol should work?
- reference model
- hierarchical design model
- protocol model
- TCP/IP model
19. Which two criteria are used to help select a network medium for a network? (Choose two.)
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
- the cost of the end devices that are used in the network
- the number of intermediate devices that are installed in the network
- the distance the selected medium can successfully carry a signal
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
20. Which scenario is suitable for deploying twisted-pair cables?
- to connect network devices in backbone networks
- to connect a TV set to the wall plug at home
- to connect data centers with high bandwidth requirements over long distances
- to connect PC workstations in an office
21. Refer to the exhibit. How many bits are represented by each group of four hexadecimal values contained between the colons in an IPv6 address?

- 16
- 64
- 4
- 32
- 8
22. Which network design has the fewest broadcast domains?
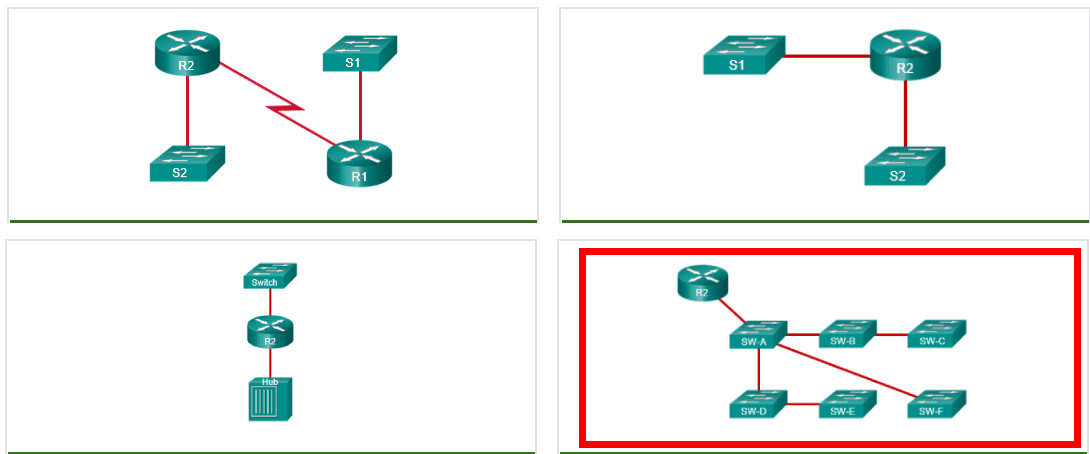
23. A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
24. What are two characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose two.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
25. Which three types of nodes should be assigned static IP addresses on a network? (Choose three.)
- desktop PCs
- printers
- mobile laptops
- gateways
- tablets
- servers
26. What benefit does DHCP provide to a network?
- DHCP allows users to refer to locations by a name rather than an IP address.
- Hosts always have the same IP address and are therefore always reachable.
- Hosts can connect to the network and get an IP address without manual configuration.
- Duplicate addresses cannot occur on a network that issues dynamic addresses using DHCP and has static assignments.
27. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 10.15.250.5
- 64.104.78.227
- 192.168.1.245
28. Which number grouping is a valid IPv6 address?
- 1234:1230::1238::1299:1000::
- 1b10::1100::2001::2900::ab11::1102::0000::2900
- 2001:0db8:3c55:0015:1010:0000:abcd:ff13
- 12aa::1298:1200::129b
29. Refer to the exhibit. A newly purchased client laptop has just connected to the local area network. The local area network is using a wireless router that is providing dynamic addressing as shown. Which IP address does the laptop use as a destination address when requesting a dynamically assigned address?
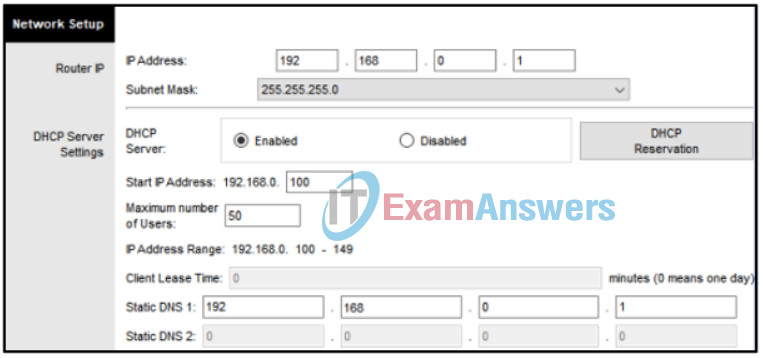
- 192.168.0.100
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.0.255
- 255.255.255.0
- 192.168.0.1
30. Refer to the exhibit. A technician is attempting to configure the IPv6 address 2001:db8::1111::0200 on a device. Why does the device return an error message that indicates the address is not valid?
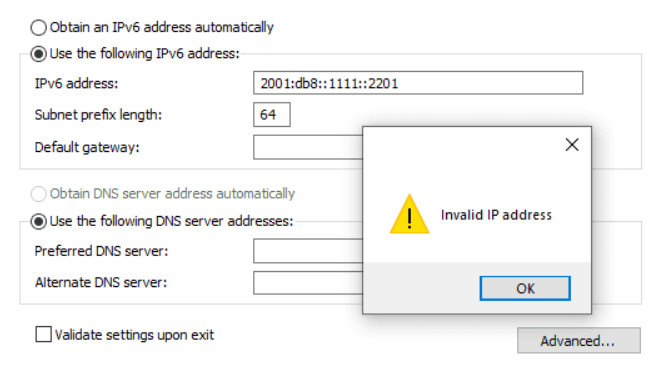
Networking Basics Course Final Exam 30
- The IPv6 address notation is incorrect.
- IPv6 is not implemented on this network.
- The device already is configured with an IPv4 address.
- The address is already in use on the network.
31. What type of route is indicated by the code C in an IPv4 routing table on a Cisco router?
- directly connected route
- default route
- dynamic route learned from another router
- static route
32. A small accounting office is setting up a wireless network to connect end devices and to provide internet access. In which two scenarios does a wireless router perform Network Address Translation (NAT)? (Choose two.)
- when a host is sending packets to the ISP in order to request a speed increase for Internet services
- when a host is sending packets to a local server in order to update the network media settings and music playlists
- when a host is sending packets to a remote site owned by the manufacturer of the wireless router in order to request a digital copy of the device manual
- when a host is sending a print job to a network printer on the LAN
- when a host is sending HTTP packets to the wireless router in order to update the network addressing of the LAN
33. Refer to the exhibit. A switch with a default configuration connects four hosts. The ARP table for host A is shown. What happens when host A wants to send an IP packet to host D?
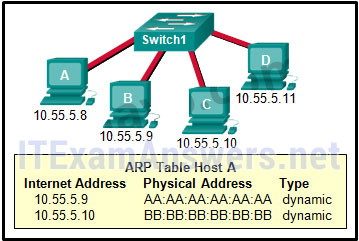
- Host A sends out the packet to the switch. The switch sends the packet only to the host D, which in turn responds.
- Host D sends an ARP request to host A.
- Host A sends an ARP request to the MAC address of host D.
- Host A sends out a broadcast of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Every other host connected to the switch receives the broadcast and host D responds with its MAC address.
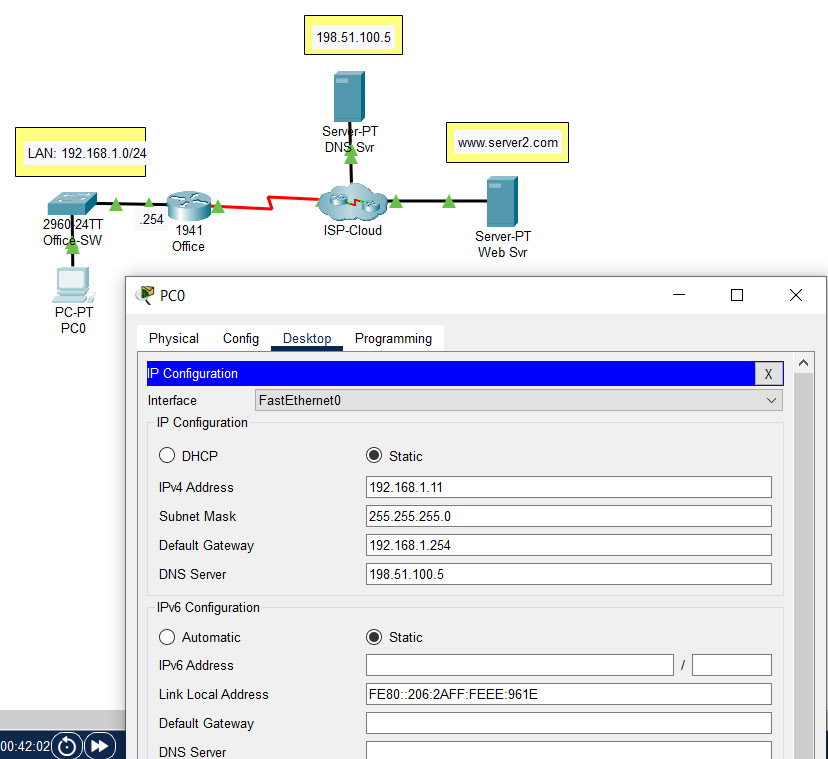
34. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which IP address should be used as the default gateway address on PC0?
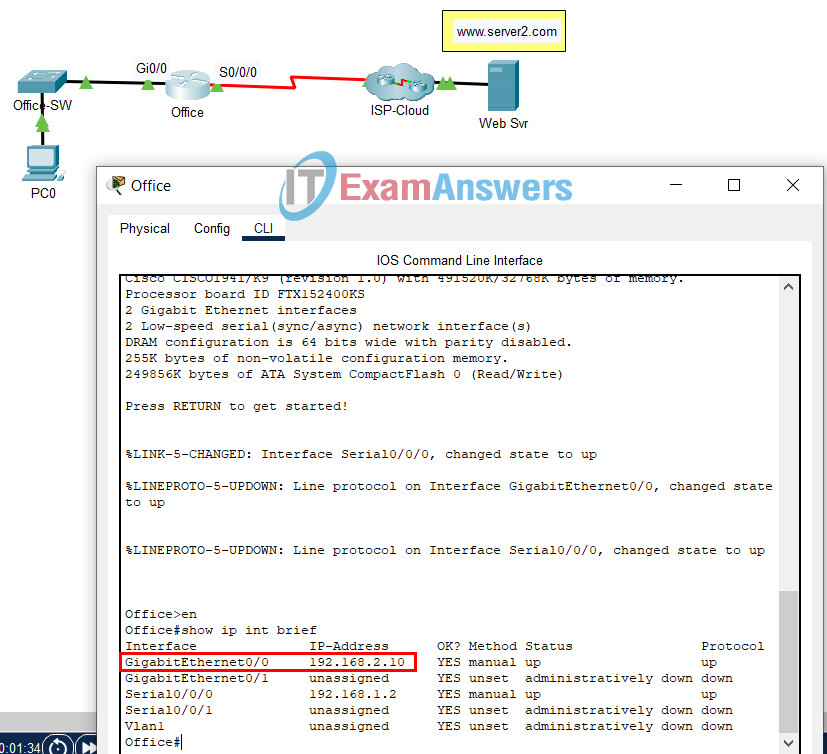
Networking Basics Course Final Exam
- 192.168.2.10
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.2.5
- 192.168.1.2
35. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
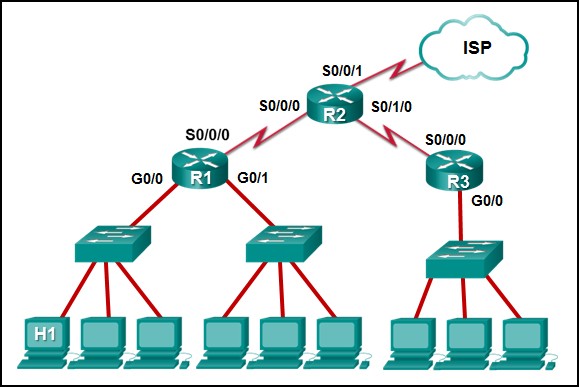
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: S0/0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
36. A network administrator has a multi-floor LAN to monitor and maintain. Through careful monitoring, the administrator has noticed a large amount of broadcast traffic slowing the network. Which device would you use to best solve this problem?
- switch
- router
- host
- server
37. An employee is having connectivity issues. Why might a network technician try to ping the default gateway from the employee laptop?
- to verify connectivity with the device that provides access to remote networks
- to verify that an IP address was provided by the DHCP server
- to determine if the laptop address is included in the DNS server
- to verify that the SVI interface on the switch is configured correctly
38. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC3. In this scenario, what will happen next?
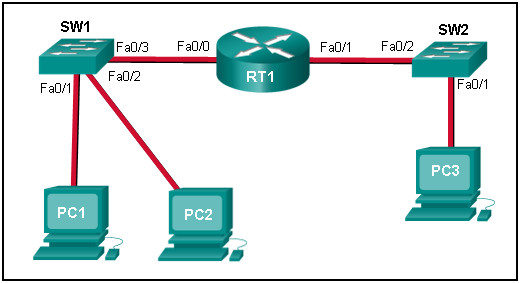
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/0 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC3 MAC address.
- RT1 will forward the ARP request to PC3.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its own Fa0/1 MAC address.
39. Refer to the exhibit. Host H2 sends a unicast message to host H6. Which destination IP address is contained in the header of the packet when it reaches host H6?
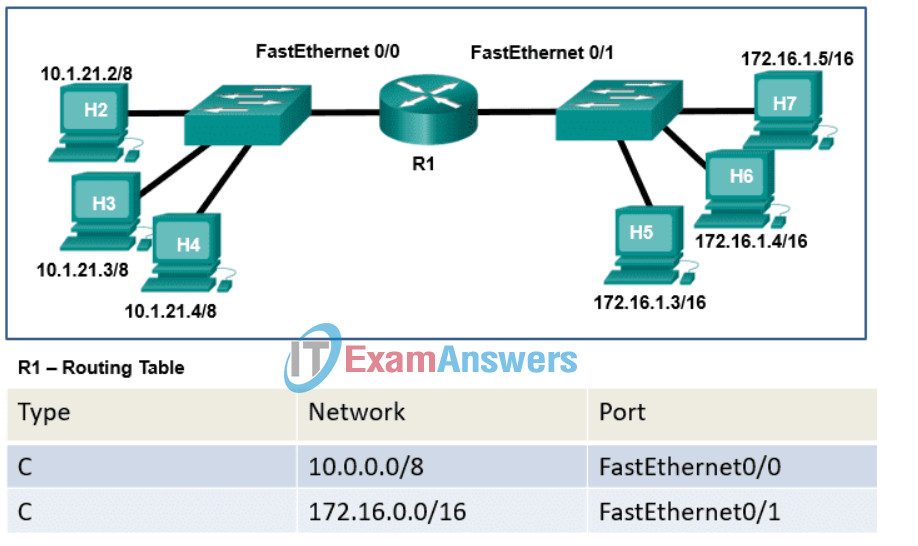
- the IP address assigned to the network adapter on host H2
- the IP address assigned to the network adapter on host H6
- the IP address of the FastEthernet0/1 interface on router R1
- the IP address of the FastEthernet0/0 interface on router R1
40. Refer to the exhibit. Host A sends a data packet to host B. What will be the addressing information of the data packet when it reaches host B?
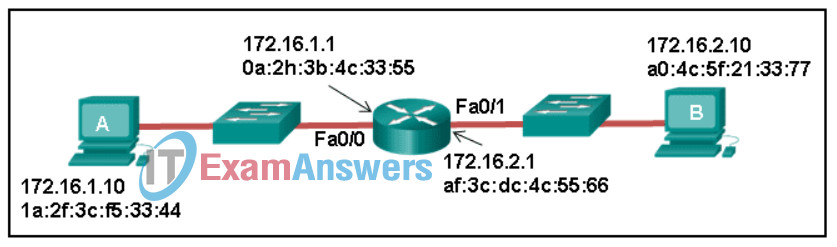
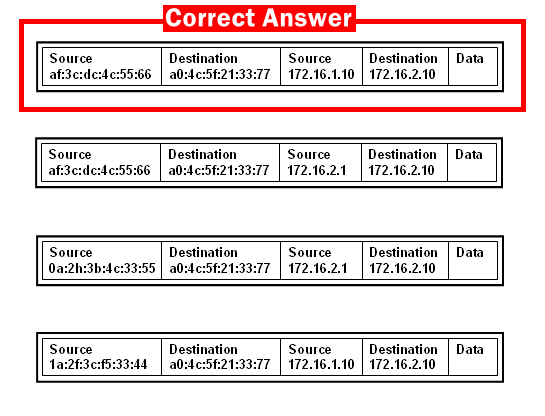
41. Which command would a technician use to display network connections on a host computer?
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- tracert
- netstat
42. How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
43. Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
- The default gateway is not operational.
- The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
- Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.
- The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
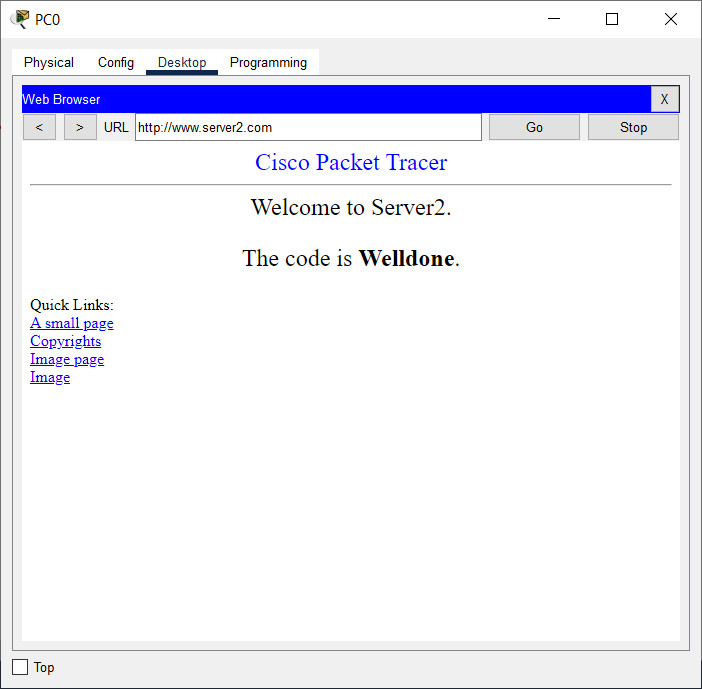
44. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. What is the code displayed on the web page?
- Success
- Correct
- Welldone
- Configured Right
45. A technician is troubleshooting a network connectivity problem. Pings to the local wireless router are successful but pings to a server on the Internet are unsuccessful. Which CLI command could assist the technician to find the location of the networking problem?
- msconfig
- ipconfig/renew
- tracert
- ipconfig
46. Which two TCP header fields are used to confirm receipt of data? (Choose two.)
- FCS
- acknowledgment number
- sequence number
- preamble
- checksum
47. When analog voice signals are converted for use on a computer network, in what format are they encapsulated?
- IP packets
- segments
- frames
- bits
48. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to troubleshoot connectivity between PC1 and PC2 and uses the tracert command from PC1 to do it. Based on the displayed output, where should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
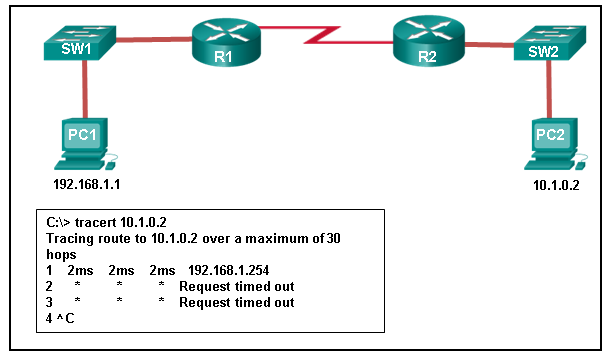
- SW1
- R1
- SW2
- PC2
- R2
49. A network technician attempts to ping www.example.net from a customer computer, but the ping fails. Access to mapped network drives and a shared printer are working correctly. What are two potential causes for this problem? (Choose two.)
- The Windows domain or workgroup name that is configured on the computer is incorrect.
- The computer has been assigned a static IP address.
- The target web server is down.
- DNS service is unavailable on the customer network.
- The HTTP protocol is not working properly on the target server.
50. Open the PT activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. What is the IP address of this server?
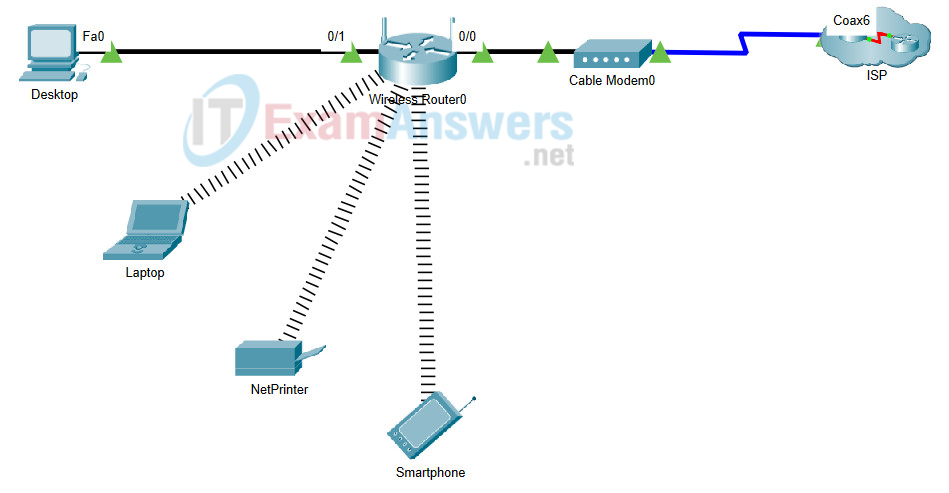
- 209.165.201.4
- 192.168.10.100
- 209.165.201.3
- 192.168.10.1
51. Which wireless technology allows a customer to connect to a payment terminal in the store with a smartphone?
- Wi-Fi
- GPS
- NFC
- Bluetooth
52. What are two methods typically used on a mobile device to provide internet connectivity? (Choose two.)
- Bluetooth
- cellular
- NFC
- GPS
- Wi-Fi
53. What information does an Ethernet switch examine and use to build its address table?
- destination IP address
- destination MAC address
- source IP address
- source MAC address
54. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- transport
- network
- data link
- session
- physical
55. What is the shortest valid representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:1470:0000:0000:0000:0200?
- 2001:DB8::1470::200
- 2001:0DB8:0:147::02
- 2001:0DB8::1470:0:0:0:2
- 2001:DB8:0:1470::200
56. A college has five campuses. Each campus has IP phones installed. Each campus has an assigned IP address range. For example, one campus has IP addresses that start with 10.1.x.x. On another campus the address range is 10.2.x.x. The college has standardized that IP phones are assigned IP addresses that have the number 4X in the third octet. For example, at one campus the address ranges used with phones include 10.1.40.x, 10.1.41.x, 10.1.42.x, etc. Which two groupings were used to create this IP addressing scheme? (Choose two.)
- personnel type
- device type
- geographic location
- department
- support model
57. Refer to the exhibit. If all devices are using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, which laptop would have an IP address with the same network number as the server?
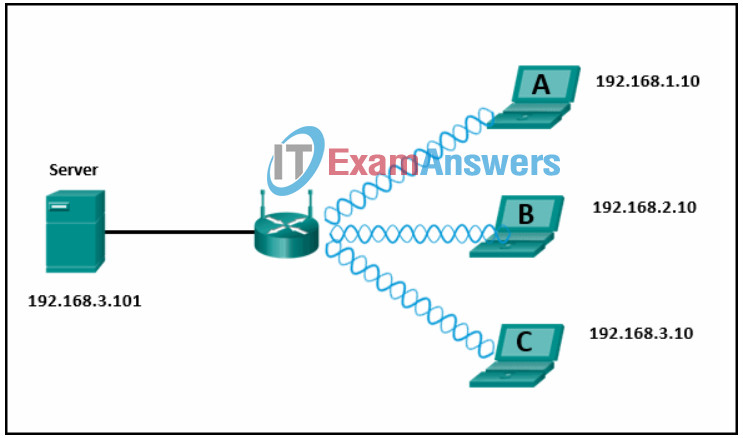
- B
- A
- C
58. For what purpose are IPv4 addresses utilized?
- An IPv4 address is burned into the network card to uniquely identify a device.
- An IPv4 address is used to identify the number of IP networks available.
- An IPv4 address is used to uniquely identify a device on an IP network.
- An IPv4 address is used to uniquely identify the application that requested the information from a remote device.
59. A user is setting up a home wireless network. A global address is to be used in NAT translations for traffic flowing through the wireless router. How is this global address assigned?
- The wireless router will act as a DHCP client in order to receive global addressing from the ISP.
- The default gateway IP address of the LAN device is used as the global address for NAT translations through the wireless router.
- The network administrator will choose an available IP address from the LAN and configure the global addressing of the wireless router.
- The host devices will select an unused IP address on the LAN for performing NAT through the wireless router.
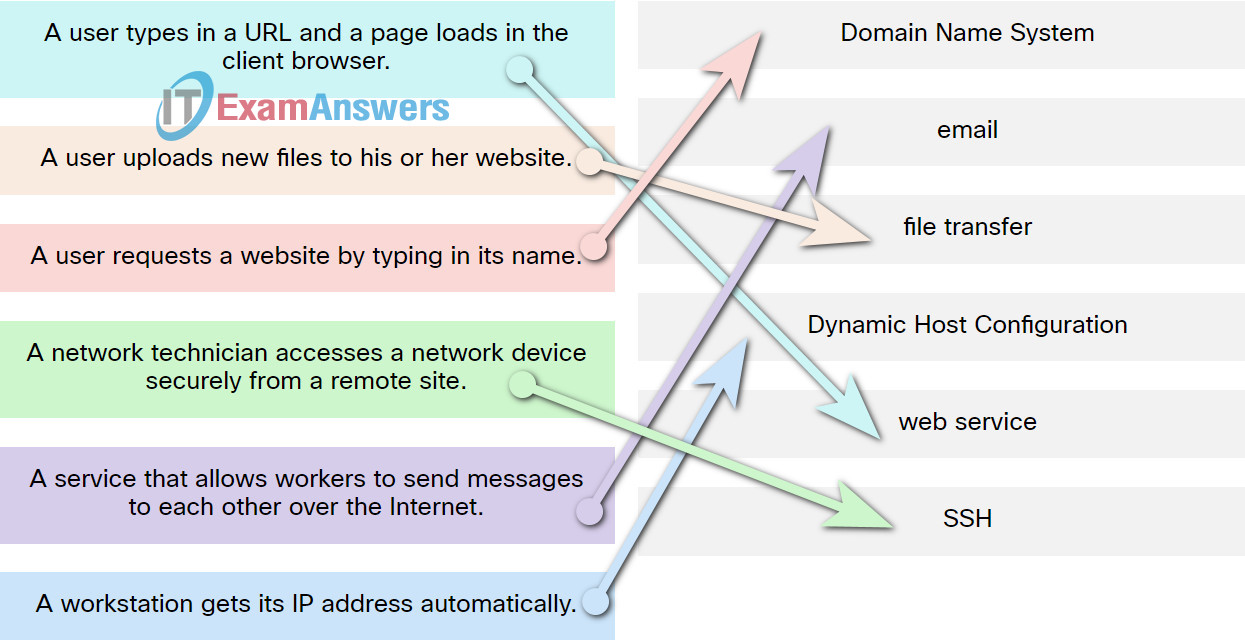
60. Match the protocol function to the description while taking into consideration that a network client is visiting a web site.
61. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 needs to resolve the host name of the web server into an IP address by using DNS. What destination IP address and destination port number will PC1 assign to the DNS query packet?
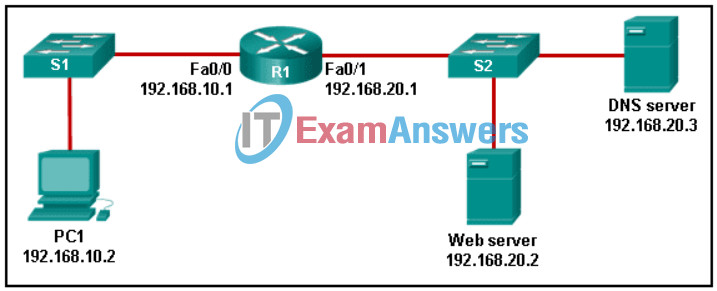
Networking Basics: Course Completion Assessment & Survey Q61
- 192.168.20.3 port 53
- 192.168.10.1 port 53
- 192.168.20.3 port 80
- 192.168.20.2 port 80
- 192.168.20.2 port 53
62. How many bits are in an IPv4 address?
- 32
- 256
- 128
- 64
63. When a host sends a packet, how does it determine if the destination of the packet is on the same local network or on a remote network?
- It compares the source and destination MAC addresses.
- It queries the DNS server with the destination IP address.
- It checks to see if the default gateway is configured.
- It uses the subnet mask to compare the source and destination IP address.
64. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?
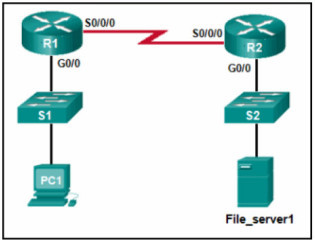
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of File_server1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1

The question that ends with “Which IP address should be used as the default gateway address on PC0?” WAS NOT taught during this course on the website Skillsforall. Unfair question.
I ALWAYS CHOOSE ADDIS ABABA UNIVERSITY FINAL EXAM QUESTION:BECAUSE IT GUIDE /SHOW ME I UNDERSTAND THE COURSE MORE IN DETAILS. THANKS
How do you get access to that? please help me or share the link here :)