6.8.1 Packet Tracer – Skills Integration Challenge-Planning Subnets and Configuring IP Addresses Answers
Topology Diagram:
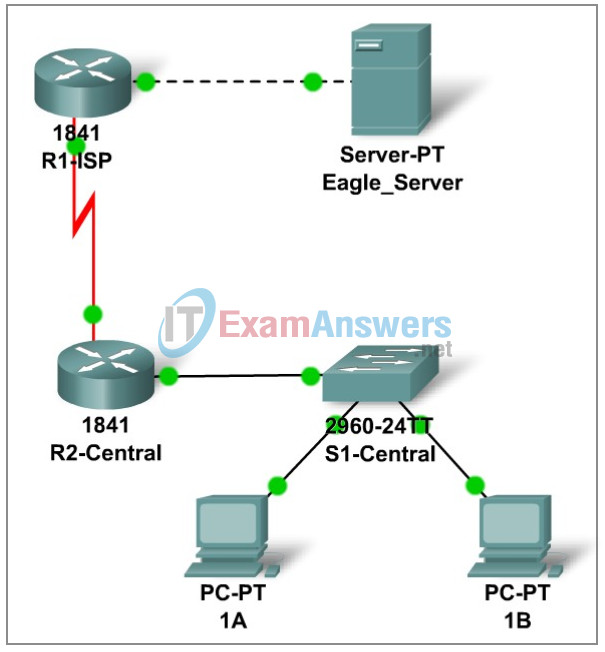
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1-ISP | Fa0/0 | 192.168.23.110 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.23.122 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R2-Central | Fa0/0 | 192.168.23.62 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.23.121 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| PC 1A | NIC | 192.168.23.1 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.23.62 |
| PC 1B | NIC | 192.168.23.2 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.23.62 |
| Eagle Server | NIC | 192.168.23.109 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.23.110 |
Learning Objectives:
- IP Subnet Planning
- Practice your subnetting skills
- Build the Network
- Connect devices with Ethernet and serial cables
- Configure the network
- Apply your subnetting scheme to server, PCs, and router interfaces; configure services and static routing
- Test the network
- Using ping, trace, web traffic, Inspect tool
Background:
You have been asked to implement the standard lab topology, but with a new IP addressing scheme. You will use many of the skills you have learned to this point in the course.
Task 1: IP Subnet Planning
You have been given an IP address block of 192.168.23.0 /24. You must provide for existing networks as well as future growth.
Subnet assignments are (assuming ip subnet-zero is enabled):
- 1st subnet, existing student LAN (off of router R2-Central), up to 60 hosts;
- 2nd subnet, future student LAN, up to 28 hosts;
- 3rd subnet, existing ISP LAN, up to 12 hosts;
- 4th subnet, future ISP LAN, up to 6 hosts;
- 5th subnet, existing WAN, point-to-point link;
- 6th subnet, future WAN, point-to-point link;
- 7th subnet, future WAN, point-to-point link.
| subnet | prefix | Mask | network | lowest host | highest host | broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st subnet, existing student LAN (off of router R2-Central), up to 60 hosts; | /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 192.168.23.0 | 192.168.23.1 | 192.168.23.62 | 192.168.23.63 |
| 2nd subnet, future student LAN, up to 28 hosts; | /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 192.168.23.64 | 192.168.23.65 | 192.168.23.94 | 192.168.23.95 |
| 3rd subnet, existing ISP LAN, up to 12 hosts; | /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.23.96 | 192.168.23.97 | 192.168.23.110 | 192.168.23.111 |
| 4th subnet, future ISP LAN, up to 6 hosts; | /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 192.168.23.112 | 192.168.23.113 | 192.168.23.118 | 192.168.23.119 |
| 5th subnet, existing WAN, point-topoint link; | /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 192.168.23.120 | 192.168.23.121 | 192.168.23.122 | 192.168.23.123 |
| 6th subnet, future WAN, point-topoint link; | /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 192.168.23.124 | 192.168.23.125 | 192.168.23.126 | 192.168.23.127 |
| 7th subnet, future WAN, point-topoint link. | /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 192.168.23.128 | 192.168.23.129 | 192.168.23.130 | 192.168.23.131 |
Interface IP addresses:
- For the server, configure the second highest usable IP address on the existing ISP LAN subnet.
- For R1-ISP’s Fa0/0 interface, configure the highest usable IP address on the existing ISP LAN subnet.
- For R1-ISP’s S0/0/0 interface, configure the highest usable address on the existing WAN subnet.
- For R2-Central’s S0/0/0 interface, use the lowest usable address on the existing WAN subnet.
- For R2-Central’s Fa0/0 interface, use the highest usable address on the existing student LAN subnet.
- For hosts 1A and 1B, use the first 2 IP addresses (two lowest usable addresses) on the existing student LAN subnet.
Additional configurations:
- For PCs 1A and 1B, in addition to IP and default gateway configuration, configure them to use DNS services.
- For the server, in addition to IP and default gateway configuration, enable DNS services, use the domain name eagle-server.example.com, and enable HTTP services.
- For R1-ISP router serial interface, you will need to set the clock rate (a timing mechanism required on the DCE end of serial links) to 64000.
- No clock rate is needed on the DTE side, in this case R2-Central’s serial interface.
Task 2: Finish building the network in Packet Tracer
Add cables where missing.
- Connect a serial DCE cable to R1-ISP S0/0/0, with the other end to R2-Central S0/0/0.
- Connect PC 1A to the first FastEthernet port on switch S1-Central.
- Connect PC 1B to the second FastEthernet port on switch S1-Central.
- Connect interface Fa0/0 on router R2-Central to the highest FastEthernet port on switch S1-Central.
- Connect interface Fa0/0 on router R1-ISP to Eagle-Server.
- For all devices, make sure the power is on to the device and the interfaces.
Task 3: Configure the Network
You will need to configure the server, both routers, and the two PCs. You will not need to configure the switch nor do you need the IOS CLI to configure the routers. Part of the router configuration has already been done for you: all you must do is configure the static routes and the interfaces via the GUI. The static route on R1-ISP should point to the existing student LAN subnet via R2-Central’s serial interface IP address; the static route on R2-Central should be a default static route which points via R1-ISP’s serial interface IP address. These procedures were explained in the Chapter 5 Skills Integration Challenge.
Task 4: Test the Network
Verify your work using feedback from the Check Results button and the Assessment Items tab. Use ping, trace, web traffic, and the Inspect tool to examine the network. Trace packet flow in the simulation mode, with HTTP, DNS, TCP, UDP, and ICMP viewable in the Event List Filters. Use the simulation to test your understanding of how the network is operating.
Reflection:
Reflect upon how much you have learned so far! Practicing IP subnetting skills and networking building, configuration and testing skills will serve you well throughout your networking courses.
