8.1.3.3 Packet Tracer – Configuring DHCP Using Cisco IOS (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
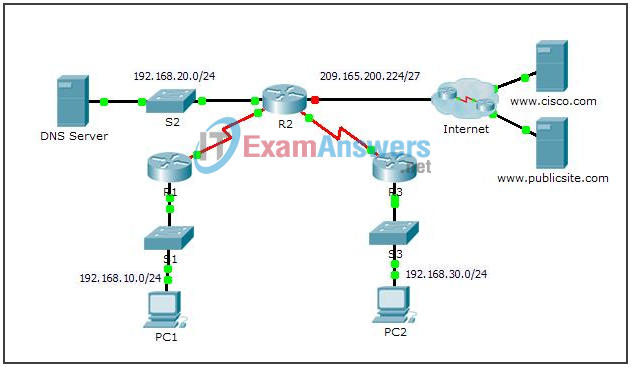
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv4 Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/1 | DHCP Assigned | DHCP Assigned | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 10.2.2.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/1 | 10.2.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | DHCP Assigned | DHCP Assigned | DHCP Assigned |
| PC2 | NIC | DHCP Assigned | DHCP Assigned | DHCP Assigned |
| DNS Server | NIC | 192.168.20.254 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Configure a Router as a DHCP Server
- Part 2: Configure DHCP Relay
- Part 3: Configure a Router as a DHCP Client
- Part 4: Verify DHCP and Connectivity
Scenario
A dedicated DHCP server is scalable and relatively easy to manage, but can be costly to have one at every location in a network. However, a Cisco router can be configured to provide DHCP services without the need for a dedicated server. As the network technician for your company, you are tasked with configuring a Cisco router as a DHCP server to provide dynamic allocation of addresses to clients on the network. You are also required to configure the edge router as a DHCP client so that it receives an IP address from the ISP network.
Part 1: Configure a Router as a DHCP Server
Step 1: Configure the excluded IPv4 addresses.
Configure R2 to exclude the first 10 addresses from the R1 and R3 LANs. All other addresses should be available in the DHCP address pool.
R2(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.10.1 192.168.10.10 R2(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.30.1 192.168.30.10
Step 2: Create a DHCP pool on R2 for the R1 LAN.
a. Create a DHCP pool named R1-LAN (case-sensitive).
R2(config)# ip dhcp pool R1-LAN
b. Configure the DHCP pool to include the network address, the default gateway, and the IP address of the DNS server.
R2(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 R2(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.10.1 R2(dhcp-config)# dns-server 192.168.20.254
Step 3: Create a DHCP pool on R2 for the R3 LAN.
a. Create a DHCP pool named R3-LAN (case-sensitive).
R2(config)# ip dh pool R3-LAN
b. Configure the DHCP pool to include the network address, the default gateway, and the IP address of the DNS server.
R2(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.30.0 255.255.255.0 R2(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.30.1 R2(dhcp-config)# dns-server 192.168.20.254
Part 2: Configure DHCP Relay
Step 1: Configure R1 and R3 as a DHCP relay agent.
!R1 R1(config)# interface g0/0 R1(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.1.1.2 !R3 R3(config)# interface g0/0 R3(config-if)# ip helper-address 10.2.2.2
Step 2: Set PC1 and PC2 to receive IP addressing information from DHCP.
Part 3: Configure R2 as a DHCP Client
a. Configure the Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 interface on R2 to receive IP addressing from DHCP and activate the interface.
R2(config)# interface g0/1 R2(config-if)# ip address dhcp R2(config-if)# no shutdown
Note: Use Packet Tracer’s Fast Forward Time feature to speed up the process or wait until R2 forms an EIGRP adjacency with the ISP router.
b. Use the show ip interface brief command to verify that R2 received an IP address from DHCP.
Part 4: Verify DHCP and Connectivity
Step 1: Verify DHCP bindings.
R2# show ip dhcp binding
IP address Client-ID/ Lease expiration Type
Hardware address
192.168.10.11 0002.4AA5.1470 -- Automatic
192.168.30.11 0004.9A97.2535 -- Automatic
Step 2: Verify configurations.
Verify that PC1 and PC2 can now ping each other and all other devices.
