CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0
1.1 Globally Connected
Networking Today

Network has no boundary and supports the way we:
- Learn
- Communicate
- Work
- Play
Providing Resources in a Network
- Small Home / Office Networks
- Medium to Large Networks
- World Wide Network
- ormation
- Servers provide information to other devices on the network
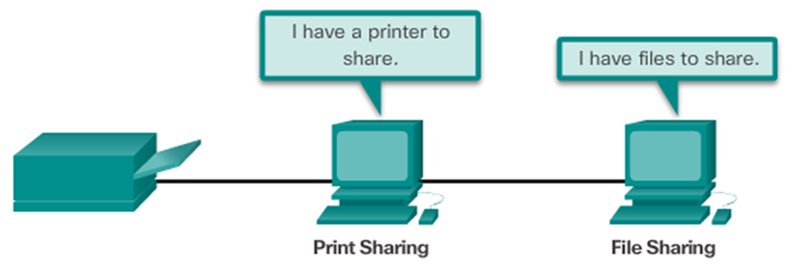
- Peer-to-Peer
- Computers can be both server and client at the same time.
- What are the advantages?
- What are the disadvantages?
1.2 LANs, WANs, and the Internet
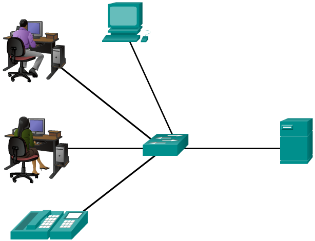
LANs, WANs, and the Internet Network Components

- End Devices
- Either the source or destination of a message
- Name some end devices
- Intermediary Network Devices
- Connect multiple individual networks to form an internetwork
- Connect the individual end devices to the network
- Ensure data flows across the network
- Provide connectivity
- Network Media
- Provide the pathway for data transmission
- Interconnect devices
- Name the three types of media
LANs, WANs, and the Internet Network Components
-
- Network Representations
What do the symbols represent?
- Topology Diagrams
- Physical
- Logical
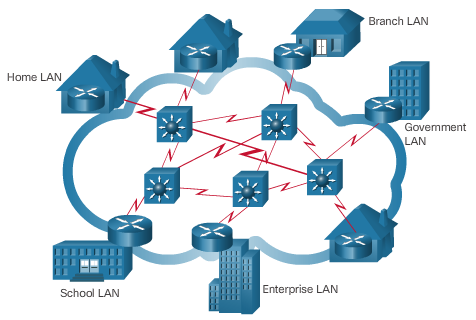
LANs, WANs, and the Internet LANs and WANs
-
- Local Area Networks
Spans across small geographical area
Interconnects end devices
Administrated by a single organization
Provide high speed bandwidth to internal devices
-
- WAN Area Networks
Interconnects LAN
Administrated by multiple service providers
Provide slower speed links between LANS
- Can you name more network types?
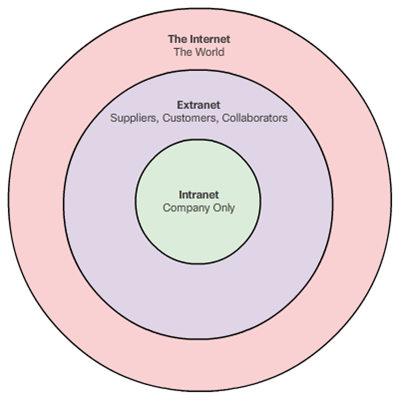
LANs, WANs, and the Internet The Internet, Intranets, and Extranets
- The Internet
- Worldwide collection of interconnected networks
- Not owned by any individual or group
- Intranets and Extranets
LANs, WANs, and the Internet Internet Connections
- Internet Access Technologies
- Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- Broadband cable
- Broadband Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
- Wireless WANs
- Mobile Services
- Business DSL
- Leased Lines
- Metro Ethernet
- Types of Internet Connections
- Home and Small Office
- Business
1.3 The Network as a Platform 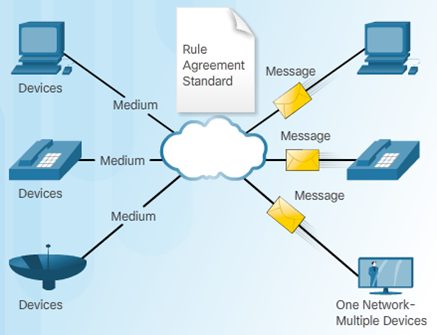
The Network as a Platform Converged Networks
-
- Traditional Separate Networks
Each network with its own rules and
-
- The Converging Network
Capable of delivering data, voice, and video over the same network infrastructure
The Network as a Platform Reliable Network
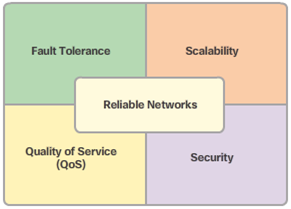
Four Basic Characteristics of Network Architecture
- Fault Tolerance
- Scalability
- Quality of Service (QoS)
- Security
1.4 The Changing Network Environment
The Changing Network Environment Network Trends
Picture9.png
Top trends include:
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOB)
- Online Collaboration
- Video Communications
- Cloud Computing
The Changing Network Environment Networking Technologies for the Home
-
- Technology Trends in the Home

- Technology Trends in the Home
Smart home
-
- Powerline Networking
Uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices
- Wireless Broadband
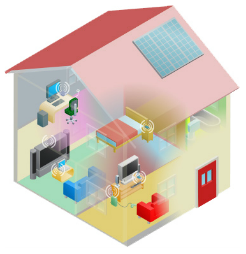
- Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP)
- Wireless Broadband Service using cellular technology
The Changing Network Environment Network Security
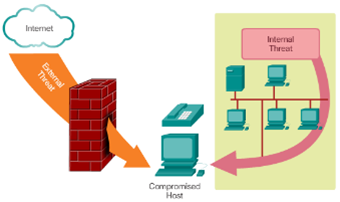
- Security Threats
- Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses
- Spyware and adware
- Zero-day attacks, also called zero-hour attacks
- Hacker attacks
- Denial of service attacks
- Data interception and theft
- Identity theft
- Security Solutions
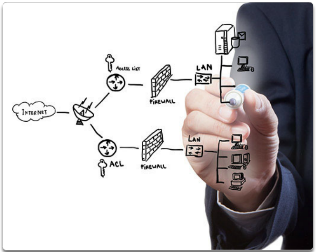
- Antivirus and antispyware
- Firewall filtering
- Dedicated firewall systems
- Access control lists (ACL)
- Intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
The Changing Network Environment Network Architecture
-
- Cisco Network Architecture
- Support technologies and applications
- Ensure connectivity across any combination of networks
- CCNA
- Cisco Network Architecture
A first step to a networking career

1.5 Chapter Summary
Chapter Summary Summary
- Explain how multiple networks are used in everyday life.
- Describe the topologies and devices used in a small to medium-sized business network.
- Explain the basic characteristics of a network that supports communication in a small to medium-sized business.
- Explain trends in networking that will affect the use of networks in small to medium-sized businesses.
Section 1.1 New Terms and Commands
- client
- collaborative learning spaces
- global communities
- human network
- network collaboration services
- network of networks
- peer-to-peer network
- server
Section 1.2 New Terms and Commands
- broadband DSL
- business DSL
- cable
- cellular
- dedicated leased line
- dial-up telephone
- DSL
- end devices
- extranet
- hardware
- intermediary devices
- internetworking devices
- Internet Service Provider (ISP)
- Intranet
- leased lines
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- logical topology diagrams
- medium
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- metro Ethernet
- network access devices
- network interface card (NIC)
- network media
- physical port, interface
- physical topology diagrams
- satellite
- security devices
- service provider (SP)
- software
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
- TelePresence endpoint
- teleworkers
- topology diagram
- VoIP phones
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Wireless LAN (WLAN)
Section 1.3 New Terms and Commands
- availability
- circuit switched networks
- content security
- converged network
- data confidentiality
- data integrity
- delay
- Denial of Service (DoS)
- encrypting data
- fault tolerance
- hierarchical layered structure
- intelligent information network
- network architecture
- network bandwidth
- network congestion
- network infrastructure security
- packet loss
- packet switched networks
- packets
- Quality of Service (QoS)
- queue
- redundancy
- routing function
- scalability
- user authentication
Section 1.4 New Terms and Commands
- access control lists (ACL)
- adware
- Bring Your Own Deice (BYOD)
- cloud computing
- data centers
- data interception and theft
- hacker attacks
- identity theft
- intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- multiple layers of security
- multitasking
- online collaboration
- person-to-person video calling
- powerline networking
- server clusters
- server farms
- smart home technology
- spyware
- Trojan horses
- video conferencing
- virtual private networks (VPNs)
- virtualization
- viruses
- wireless broadband service
- wireless internet service provider (WISP)
- wireless local area networks (WLAN)
- worms
- zero-day attacks
