- Which network topology allows all traffic to flow through a central hub?
- A. bus
- B. star*
- C. mesh
- D. ring
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceStar topology is the most popular topology for the network which allows all traffic to flow through a central device.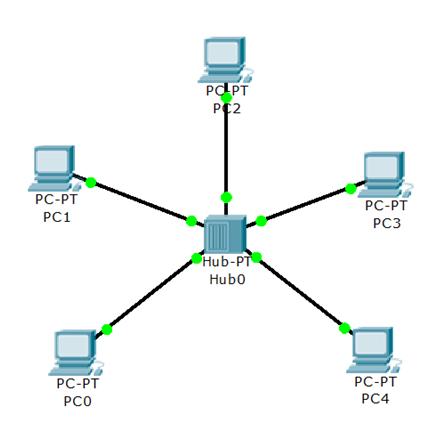
- What is true about Ethernet? (Choose two)
- A.802.2 Protocol
- B. 802.3 Protocol*
- C. 10BaseT half duplex
- D. CSMA/CD stops transmitting when congestion occurs*
- E. CSMA/CA stops transmitting when congestion occurs
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceCarrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is a media access control method used most notably in early Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) technology for local area networking. When collision detection (CD) observes a collision (excess current above what it is generating, i.e. > 24 mA for coaxial Ethernet), it stops transmission immediately and instead transmits a 32-bit jam sequence.Note: CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance) is a protocol for carrier transmission used in wireless networks. Unlike CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect) which deals with transmissions after a collision has occurred, CSMA/CA acts to prevent collisions before they happen.
- If a router has 3 hosts connected in one port and two other hosts connected in another port, how may broadcast domains are present on the router?
- A. 5
- B. 2*
- C. 3
- D. 4
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceEach port of a router is a broadcast domain. This router has 2 ports so it has 2 broadcast domains. - On which type of device is every port in the same collision domain?
- A. a router
- B. a Layer 2 switch
- C. a hub*
- Which MTU size can cause a baby giant error?
- A. 1500
- B. 9216
- C. 1600
- D. 1518*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceEthernet frame size refers to the whole Ethernet frame, including the header and the trailer while MTU size refers only to Ethernet payload. Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes, and jumbo frame refers to Ethernet frame size up to 9216 bytes (according to this link: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-4000-series-switches/29805-175.html)For example, standard Ethernet frame MTU is 1500 bytes. This does not include the Ethernet header and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) trailer, which is 18 bytes in length, to make the total Ethernet frame size of 1518.
So according to strict definition, MTU size of 1600 cannot be classified as baby giant frames as the whole Ethernet frames will surely larger than 1600 -> Answer C is not correct.
Answer D is a better choice as the MTU is 1518, so the whole Ethernet frame would be 1536 (1518 + 18 Ethernet header and CRC trailer). This satisfies the requirement of baby giant frames “Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes”.
- What are three characteristics of the TCP protocol? (Choose three)
- A. The connection is established before data is transmitted.*
- B. It uses a single SYN-ACK message to establish a connection.
- C. It ensures that all data is transmitted and received by the remote device.*
- D. It uses separate SYN and ACK messages to establish a connection.*
- E. It supports significantly higher transmission speeds than UDP.
- F. It requires applications to determine when data packets must be retransmitted.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceNote: Answer F is not correct because TCP does not require applications to determine the retranmission. TCP itself will determine if the data packets should be retransmitted or not.
- Which of the following statements describe the network shown in the graphic? (Choose two)
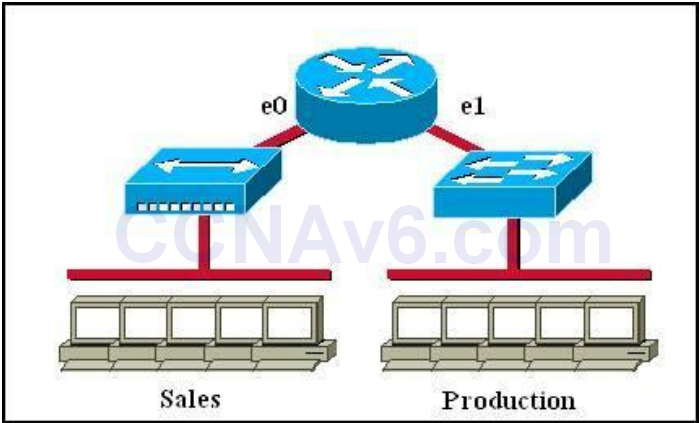
- A. There are two broadcast domains in the network.*
- B. There are four broadcast domains in the network.
- C. There are six broadcast domains in the network.
- D. There are four collision domains in the network.
- E. There are five collision domains in the network.
- F. There are seven collision domains in the network.*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceOnly router can break up broadcast domains so in the exhibit there are 2 broadcast domains: from e0 interface to the left is a broadcast domain and from e1 interface to the right is another broadcast domain -> A is correct.Both router and switch can break up collision domains so there is only 1 collision domain on the left of the router (because hub doesn’t break up collision domain) and there are 6 collision domains on the right of the router (1 collision domain from e1 interface to the switch + 5 collision domains for 5 PCs in Production) -> F is correct.
- A network interface port has collision detection and carrier sensing enabled on a shared twisted pair network. From this statement, what is known about the network interface port?
- A. This is a 10 Mb/s switch port.
- B. This is a 100 Mb/s switch port.
- C. This is an Ethernet port operating at half duplex.*
- D. This is an Ethernet port operating at full duplex.
- E. This is a port on a network interface card in a PC.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceModern Ethernet networks built with switches and full-duplex connections no longer utilize CSMA/CD. CSMA/CD is only used in obsolete shared media Ethernet (which uses repeater or hub). - If there are 3 hosts connected in one port of a switch and two other hosts connected in another port, how many collision domains are present on the router?
- A. 5
- B. 2*
- C. 3
- D. 4
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceEach port of a switch is a separate collision domain. This switch uses two ports (for 5 hosts) so there are two collision domains in total. - What are contained in Layer 2 Ethernet frame? (Choose three)
- A. Preamble*
- B. TTL
- C. Type/length*
- D. Frame check sequence*
- E. version
- F. others
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceAt the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur.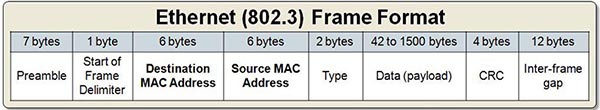
Preamble is used to indicate the start of the frame by arranging the first 62 bits as alternating “1/0s” and the last two bits as “1”s. Like so, 010101010101010………………………10101011. Therefore when the receiving end sees the “11” it knows where the actual Ethernet header starts. The alternating 1s and 0s will also allow the two endpoints to sync their internal clocks. In summary, preamble is used for synchronization.
The “Type/Length” field is used to indicate the “Type”of the payload (Layer 3 protocol) which is indicated as a Hexadecimal value.
Note: Ethernet II uses “Type” while the old Ethernet version use “Length”
