CCNA Security 2.0 Study Material – Chapter 5: Implementing Intrusion Prevention
5.0 Introduction
5.0.1 Welcome
5.0.1.1 Chapter 5: Implementing Intrusion Prevention
Chapter 5: Ethernet
The OSI physical layer provides the means to transport the bits that make up a data link layer frame across the network media.
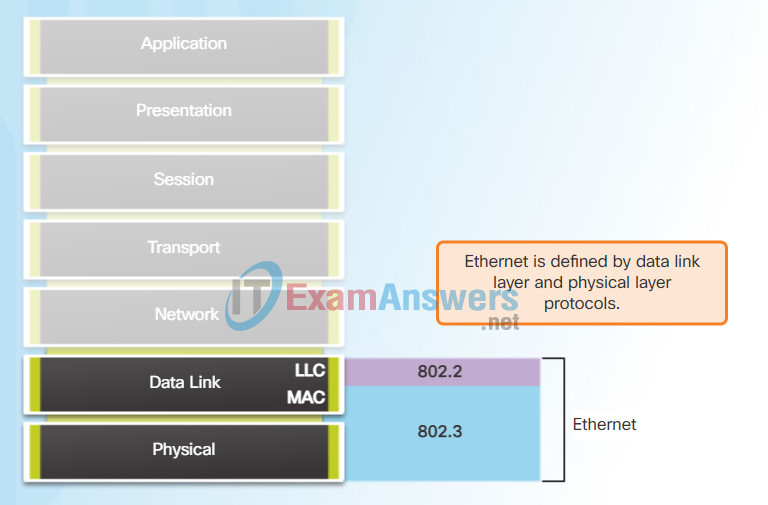
Ethernet is now the predominant LAN technology in the world. Ethernet operates in the data link layer and the physical layer. The Ethernet protocol standards define many aspects of network communication including frame format, frame size, timing, and encoding. When messages are sent between hosts on an Ethernet network, the hosts format the messages into the frame layout that is specified by the standards.
Because Ethernet is comprised of standards at these lower layers, it may best be understood in reference to the OSI model. The OSI model separates the data link layer functionalities of addressing, framing, and accessing the media from the physical layer standards of the media. Ethernet standards define both the Layer 2 protocols and the Layer 1 technologies. Although Ethernet specifications support different media, bandwidths, and other Layer 1 and 2 variations, the basic frame format and address scheme is the same for all varieties of Ethernet.
This chapter examines the characteristics and operation of Ethernet as it has evolved from a shared media, contention-based data communications technology to today’s high bandwidth, full-duplex technology.
5.1 IPS Technologies
5.1.1 IDS and IPS Characteristics
5.1.1.1 Zero-Day Attacks
Ethernet Encapsulation
Ethernet is the most widely used LAN technology today.
Ethernet operates in the data link layer and the physical layer. It is a family of networking technologies that are defined in the IEEE 802.2 and 802.3 standards. Ethernet supports data bandwidths of:
- 10 Mb/s
- 100 Mb/s
- 1000 Mb/s (1 Gb/s)
- 10,000 Mb/s (10 Gb/s)
- 40,000 Mb/s (40 Gb/s)
- 100,000 Mb/s (100 Gb/s)
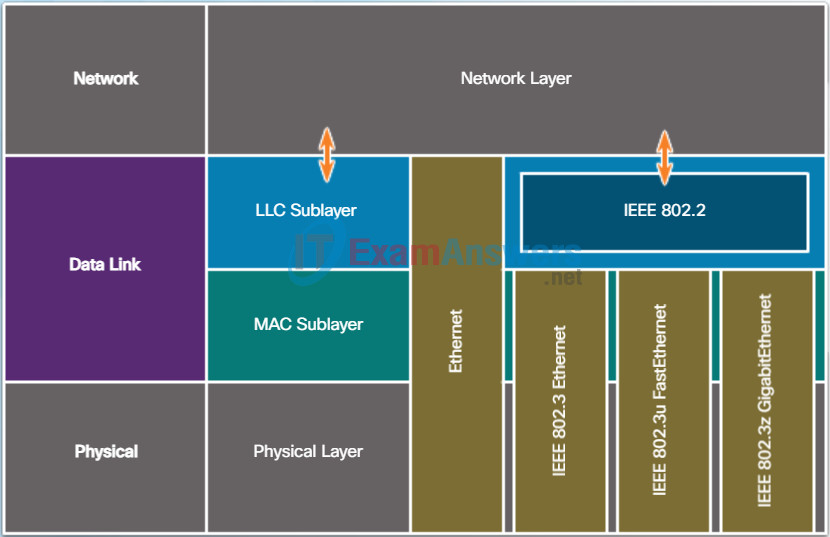
As shown in Figure 1, Ethernet standards define both the Layer 2 protocols and the Layer 1 technologies. For the Layer 2 protocols, as with all 802 IEEE standards, Ethernet relies on the two separate sublayers of the data link layer to operate, the Logical Link Control (LLC) and the MAC sublayers.
LLC sublayer
The Ethernet LLC sublayer handles the communication between the upper layers and the lower layers. This is typically between the networking software and the device hardware. The LLC sublayer takes the network protocol data, which is typically an IPv4 packet, and adds control information to help deliver the packet to the destination node. The LLC is used to communicate with the upper layers of the application, and transition the packet to the lower layers for delivery.
LLC is implemented in software, and its implementation is independent of the hardware. In a computer, the LLC can be considered the driver software for the NIC. The NIC driver is a program that interacts directly with the hardware on the NIC to pass the data between the MAC sublayer and the physical media.
MAC sublayer
MAC constitutes the lower sublayer of the data link layer. MAC is implemented by hardware, typically in the computer NIC. The specifics are listed in the IEEE 802.3 standards. Figure 2 lists common IEEE Ethernet standards.
Ethernet
5.1.1.2 Monitor for Attacks
MAC Sublayer
As shown in the figure, the Ethernet MAC sublayer has two primary responsibilities:
- Data encapsulation
- Media access control
Data encapsulation
The data encapsulation process includes frame assembly before transmission, and frame disassembly upon reception of a frame. In forming the frame, the MAC layer adds a header and trailer to the network layer PDU.
Data encapsulation provides three primary functions:
- Frame delimiting – The framing process provides important delimiters that are used to identify a group of bits that make up a frame. These delimiting bits provide synchronization between the transmitting and receiving nodes.
- Addressing – The encapsulation process contains the Layer 3 PDU and also provides for data link layer addressing.
- Error detection – Each frame contains a trailer used to detect any errors in transmissions.
The use of frames aids in the transmission of bits as they are placed on the media and in the grouping of bits at the receiving node.
Media Access Control
The second responsibility of the MAC sublayer is media access control. Media access control is responsible for the placement of frames on the media and the removal of frames from the media. As its name implies, it controls access to the media. This sublayer communicates directly with the physical layer.
The underlying logical topology of Ethernet is a multi-access bus; therefore, all nodes (devices) on a single network segment share the medium. Ethernet is a contention-based method of networking. A contention-based method means that any device can try to transmit data across the shared medium whenever it has data to send. The Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) process is used in half-duplex Ethernet LANs to detect and resolve collisions. Today’s Ethernet LANs use full-duplex switches, which allow multiple devices to send and receive simultaneously with no collisions.
Data Encapsulation
- Frame delimiting
- Addressing
- Error detection
Media Access Control
- Control of frame placement on and off the media
- Media recovery
5.1.1.3 Detect and Stop Attacks
Ethernet Evolution
Since the creation of Ethernet in 1973, standards have evolved for specifying faster and more flexible versions of the technology. This ability for Ethernet to improve over time is one of the main reasons it has become so popular. Early versions of Ethernet were relatively slow at 10 Mbps. The latest versions of Ethernet operate at 10 Gigabits per second and faster. Scroll through the timeline in Figure 1 to view the various versions of Ethernet.
At the data link layer, the frame structure is nearly identical for all speeds of Ethernet. The Ethernet frame structure adds headers and trailers around the Layer 3 PDU to encapsulate the message being sent, as shown in Figure 2.
Ethernet II is the Ethernet frame format used in TCP/IP networks.
5.1.1.4 Similarities Between IDS and IPS
Ethernet Frame Fields
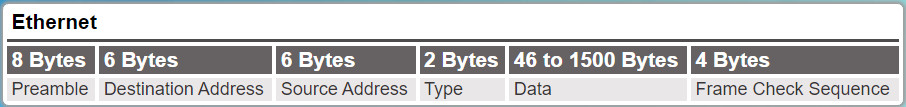
The minimum Ethernet frame size is 64 bytes and the maximum is 1518 bytes. This includes all bytes from the Destination MAC Address field through the Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. The Preamble field is not included when describing the size of a frame.
Any frame less than 64 bytes in length is considered a “collision fragment” or “runt frame” and is automatically discarded by receiving stations. Frames with more than 1500 bytes of data are considered “jumbo” or “baby giant frames”.
If the size of a transmitted frame is less than the minimum or greater than the maximum, the receiving device drops the frame. Dropped frames are likely to be the result of collisions or other unwanted signals and are therefore considered invalid.
In the figure, click each field in the Ethernet frame to read more about its function.

Ethernet II Frame Fields
- Preamble and Start Frame Delimiter Fields: The Preamble (7 bytes) and Start Frame Delimiter (SFD), also called the Start of Frame (1 byte), fields are used for synchronization between the sending and receiving devices. These first eight bytes of the frame are used to get the attention of the receiving nodes. Essentially, the first few bytes tell the receivers to get ready to receive a new frame.
- Destination MAC Address Field: This 6-byte field is the identifier for the intended recipient. As you will recall, this address is used by Layer 2 to assist devices in determining if a frame is addressed to them. The address in the frame is compared to the MAC address in the device. If there is a match, the device accepts the frame. Can be a unicast, multicast or broadcast address.
- Source MAC Address Field: This 6-byte field identifies the frame’s originating NIC or interface. Must be a unicast address.
- EtherType Field: This 2-byte field identifies the upper layer protocol encapsulated in the Ethernet frame. Common values are, in hexadecimal, 0x800 for IPv4, 0x86DD for IPv6 and 0x806 for ARP.
- Data Field: This field (46 – 1500 bytes) contains the encapsulated data from a higher layer, which is a generic Layer 3 PDU, or more commonly, an IPv4 packet. All frames must be at least 64 bytes long. If a small packet is encapsulated, additional bits called a pad are used to increase the size of the frame to this minimum size.
- Frame Check Sequence Field: The Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field (4 bytes) is used to detect errors in a frame. It uses a cyclic redundancy check (CRC). The sending device includes the results of a CRC in the FCS field of the frame. The receiving device receives the frame and generates a CRC to look for errors. If the calculations match, no error occurred. Calculations that do not match are an indication that the data has changed; therefore, the frame is dropped. A change in the data could be the result of a disruption of the electrical signals that represent the bits.
5.1.1.5 Advantages and Disadvantages of IDS and IPS
Instructions
Descriptions of the MAC and LLC sublayers are provided in the table. Click in the MAC or LLC fields to match the descriptions to the correct sublayer.
| Hacker Characteristic | MAC | LLC |
|---|---|---|
| Controls the network interface card through software drivers. | V | |
| Works with the upper layers to add application information for deliveryof data to higher level protocols. | V | |
| Works with hardware to support bandwidth requirements and checks errors in the bits sent and received. | V | |
| Controls access to the media through signaling and physical mediastandards requirements. | V | |
| Supports Ethernet technology by using CSMA/CD or CSMA/CA. | V | |
| Remains relatively independent of physical equipment. | V |
5.1.2 Network-Based IPS Implementations
5.1.2.1 Host-Based IPS
MAC Address and Hexadecimal
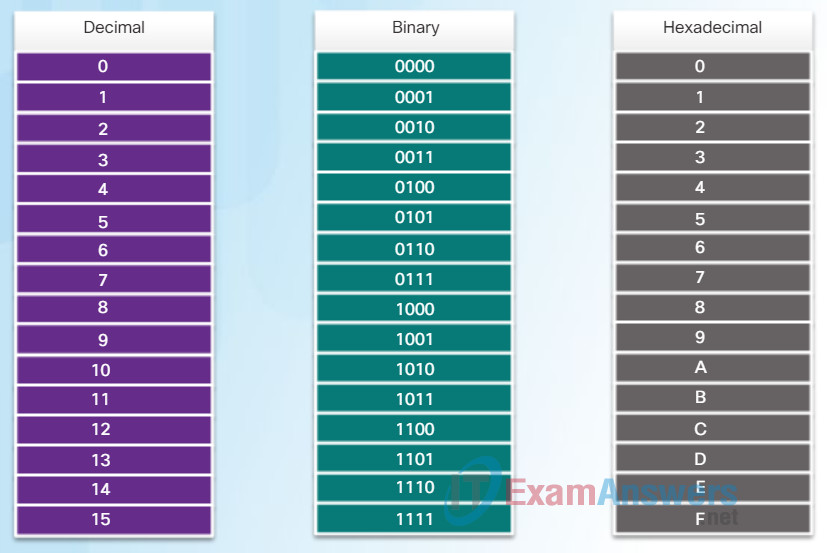
An Ethernet MAC address is a 48-bit binary value expressed as 12 hexadecimal digits (4 bits per hexadecimal digit).
Just as decimal is a base ten number system, hexadecimal is a base sixteen system. The base sixteen number system uses the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. Figure 1 shows the equivalent decimal and hexadecimal values for binary 0000 to 1111. It is easier to express a value as a single hexadecimal digit than as four binary bits.
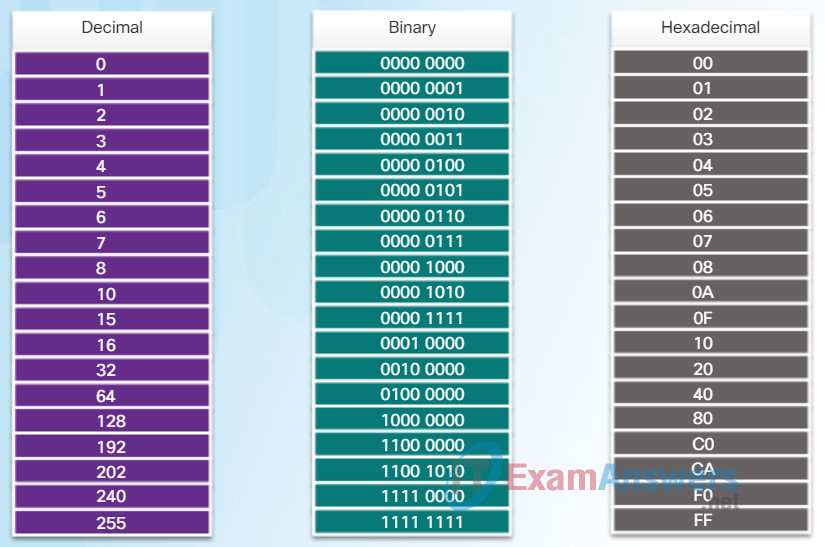
Given that 8 bits (one byte) is a common binary grouping, binary 00000000 to 11111111 can be represented in hexadecimal as the range 00 to FF, as shown in Figure 2. Leading zeroes are always displayed to complete the 8-bit representation. For example, the binary value 0000 1010 is shown in hexadecimal as 0A.
Note: It is important to distinguish hexadecimal values from decimal values regarding the characters 0 to 9, as shown in the figure.
Representing Hexadecimal Values
Hexadecimal is usually represented in text by the value preceded by 0x (for example 0x73) or a subscript 16. Less commonly, it may be followed by an H(for example 73H). However, because subscript text is not recognized in command line or programming environments, the technical representation of hexadecimal is preceded with “0x” (zero X). Therefore, the examples above would be shown as 0x0A and 0x73 respectively.
Hexadecimal is used to represent Ethernet MAC addresses and IP Version 6 addresses.
Hexadecimal Conversions
Number conversions between decimal and hexadecimal values are straightforward, but quickly dividing or multiplying by 16 is not always convenient. If such conversions are required, it is usually easier to convert the decimal or hexadecimal value to binary, and then to convert the binary value to either decimal or hexadecimal as appropriate.
Hexadecimal Numbering
Decimal and Binary equivalents of 0 to F Hexadecimal
Selected Decimal, Binary, and Hexadecimal equivalents
5.1.2.2 Network-Based IPS Sensors
MAC Address: Ethernet Identity
In Ethernet, every network device is connected to the same, shared media. Ethernet was once predominantly a half-duplex topology using a multi-access bus or later Ethernet hubs. This meant that all nodes would receive every frame transmitted. To prevent the excessive overhead involved in the processing of every frame, MAC addresses were created to identify the actual source and destination. MAC addressing provides a method for device identification at the lower level of the OSI model. Although Ethernet has now transitioned to full-duplex NICs and switches, it is still possible that a device that is not the intended destination will receive an Ethernet frame.
MAC Address Structure
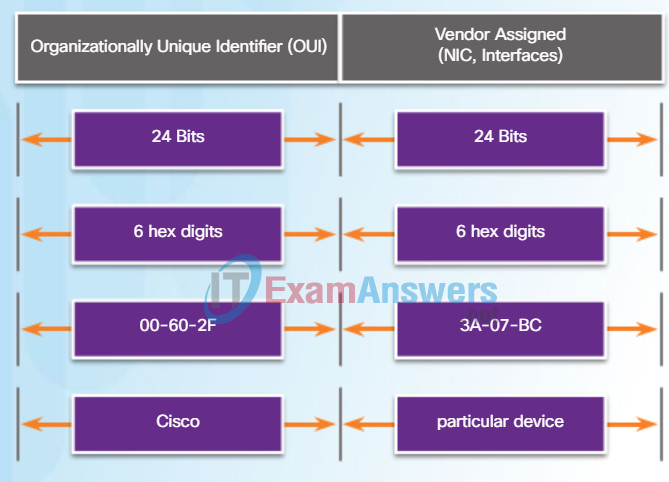
The MAC address value is a direct result of IEEE-enforced rules for vendors to ensure globally unique addresses for each Ethernet device. The rules established by IEEE require any vendor that sells Ethernet devices to register with IEEE. The IEEE assigns the vendor a 3-byte (24-bit) code, called the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI).
IEEE requires a vendor to follow two simple rules, as shown in the figure:
- All MAC addresses assigned to a NIC or other Ethernet device must use that vendor’s assigned OUI as the first 3 bytes.
- All MAC addresses with the same OUI must be assigned a unique value in the last 3 bytes.
Note: It is possible for duplicate MAC addresses to exist due to mistakes during manufacturing or in some virtual machine implementation methods. In either case, it will be necessary to modify the MAC address with a new NIC or in software.
The Ethernet MAC Address Structure
5.1.2.3 Cisco’s Modular and Appliance-Based IPS Solutions
Frame Processing
The MAC address is often referred to as a burned-in address (BIA) because, historically, this address is burned into ROM (Read-Only Memory) on the NIC. This means that the address is encoded into the ROM chip permanently.
Note: On modern PC operating systems and NICs, it is possible to change the MAC address in software. This is useful when attempting to gain access to a network that filters based on BIA. Consequently, filtering or controlling traffic based on the MAC address is no longer as secure.
When the computer starts up, the first thing the NIC does is copy the MAC address from ROM into RAM. When a device is forwarding a message to an Ethernet network, it attaches header information to the frame. The header information contains the source and destination MAC address.
Click Play in the animation to view the frame forwarding process. When a NIC receives an Ethernet frame, it examines the destination MAC address to see if it matches the device’s physical MAC address stored in RAM. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, it passes the frame up the OSI layers, where the de-encapsulation process takes place.
Note: Ethernet NICs will also accept frames if the destination MAC address is a broadcast or a multicast group of which the host is a member.
Any device that can be the source or destination of an Ethernet frame must be assigned a MAC address. This includes workstations, servers, printers, mobile devices, and routers.
Frame Forwarding
5.1.2.4 Cisco’s Modular and Appliance-Based IPS Solutions (Cont.)
MAC Address Representations
On a Windows host, the ipconfig /all command can be used to identify the MAC address of an Ethernet adapter. In Figure 1, notice the display indicates the Physical Address (MAC) of the computer to be 00-18-DE-DD-A7-B2. If you have access, you may wish to try this on your own computer. On a MAC or Linux host, the ifconfig command is used.
Depending on the device and the operating system, you will see various representations of MAC addresses, as displayed in Figure 2. Cisco routers and switches use the form XXXX.XXXX.XXXX where X is a hexadecimal character.
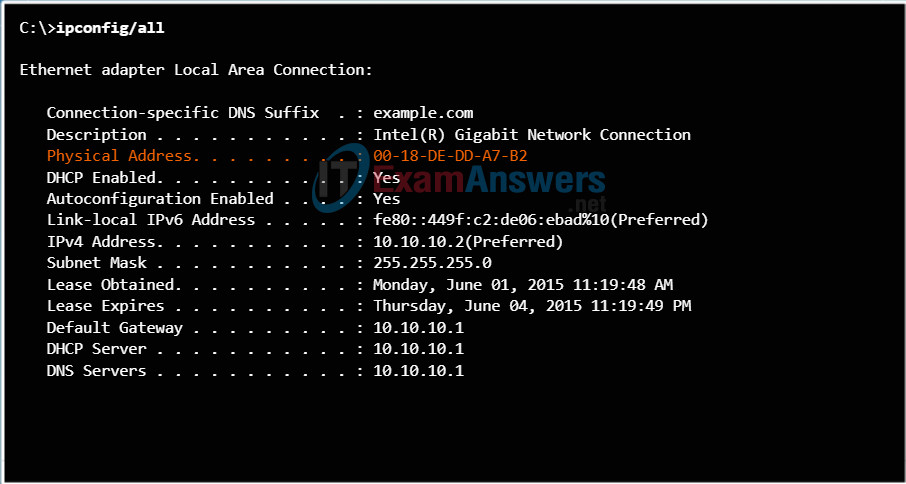
Physical Address of a Host
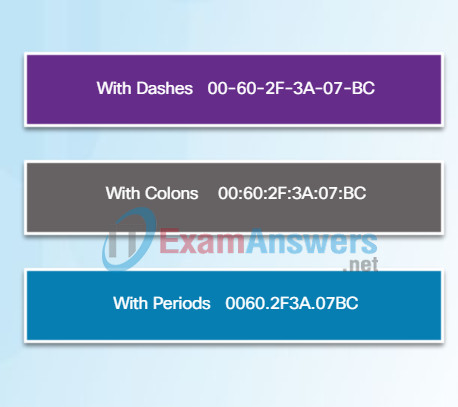
Different Representations of MAC Addresses
5.1.2.5 Choose an IPS Solution
Unicast MAC Address
In Ethernet, different MAC addresses are used for Layer 2 unicast, broadcast, and multicast communications.
A unicast MAC address is the unique address used when a frame is sent from a single transmitting device to a single destination device.
In the example shown in the animation, a host with IPv4 address 192.168.1.5 (source) requests a web page from the server at IPv4 unicast address 192.168.1.200. For a unicast packet to be sent and received, a destination IP address must be in the IP packet header. A corresponding destination MAC address must also be present in the Ethernet frame header. The IP address and MAC address combine to deliver data to one specific destination host.
The process that a source host uses to determine the destination MAC address is known as Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP is discussed later in this chapter.
Although the destination MAC address can be a unicast, broadcast, or multicast address, the source MAC address must always be a unicast.
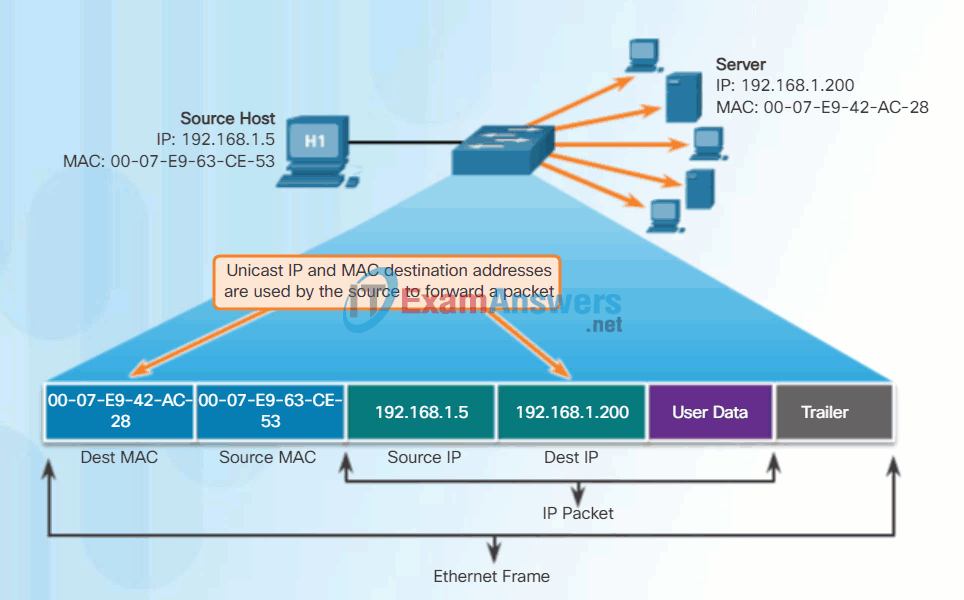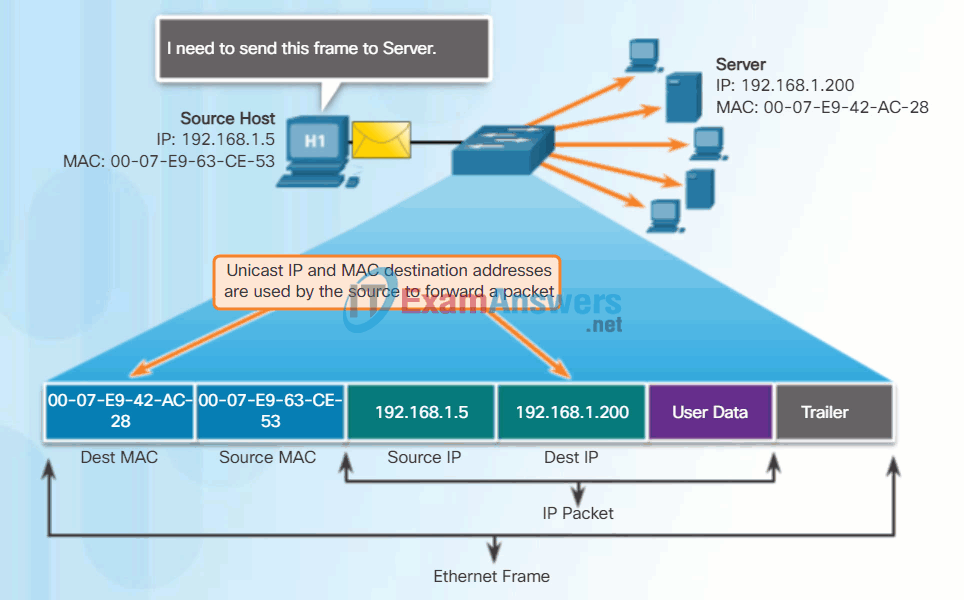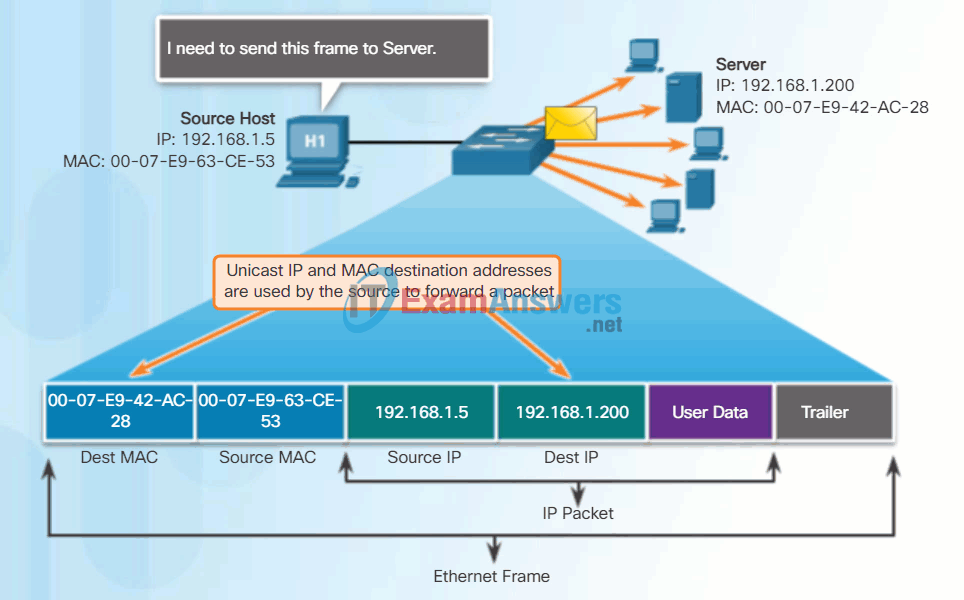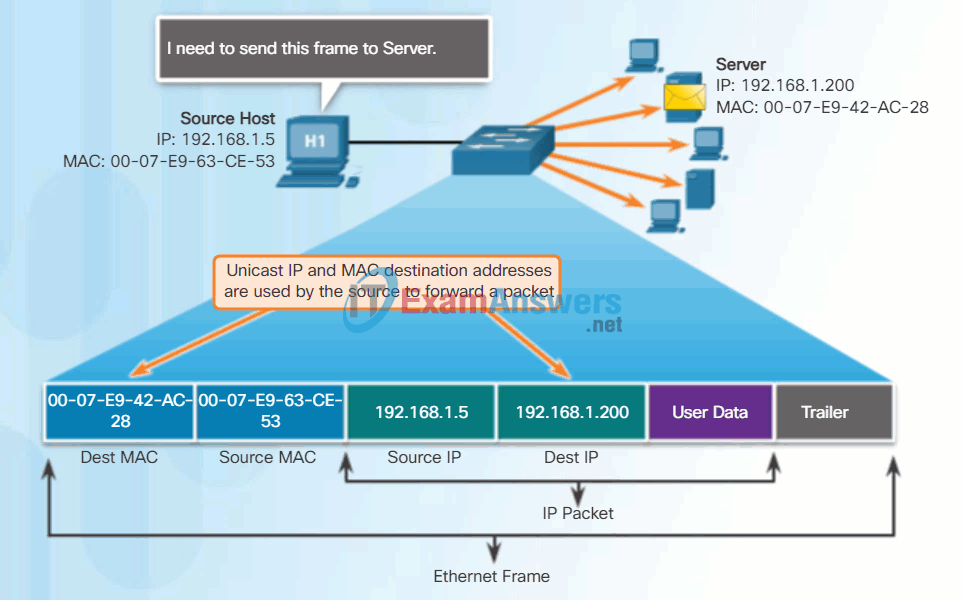
Unicast
5.1.2.6 Network-Based IPS
Broadcast MAC Address
A broadcast packet contains a destination IPv4 address that has all ones (1s) in the host portion. This numbering in the address means that all hosts on that local network (broadcast domain) will receive and process the packet. Many network protocols, such as DHCP and ARP, use broadcasts.
As shown in the animation, the source host sends an IPv4 broadcast packet to all devices on its network. The IPv4 destination address is a broadcast address, 192.168.1.255. When the IPv4 broadcast packet is encapsulated in the Ethernet frame, the destination MAC address is the broadcast MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF in hexadecimal (48 ones in binary).
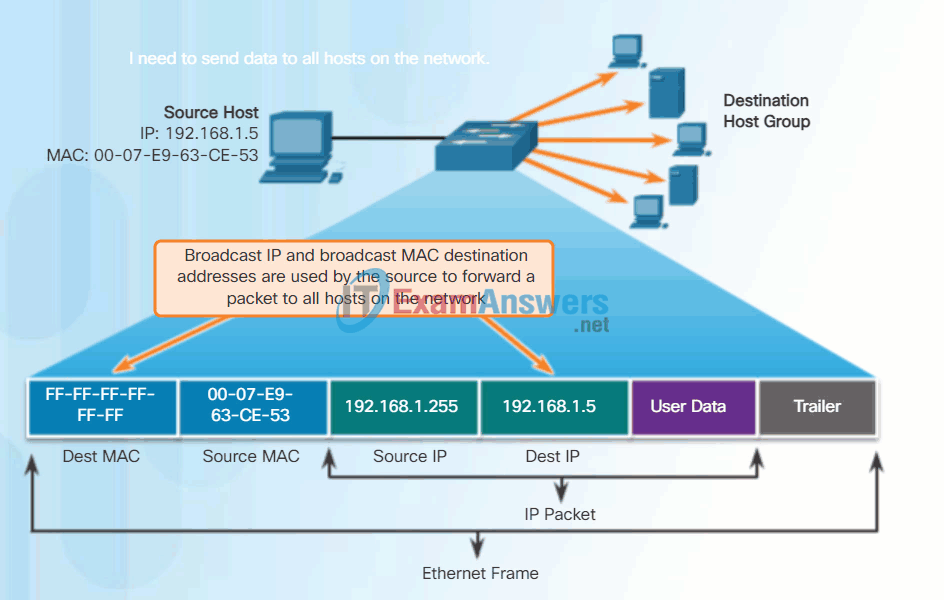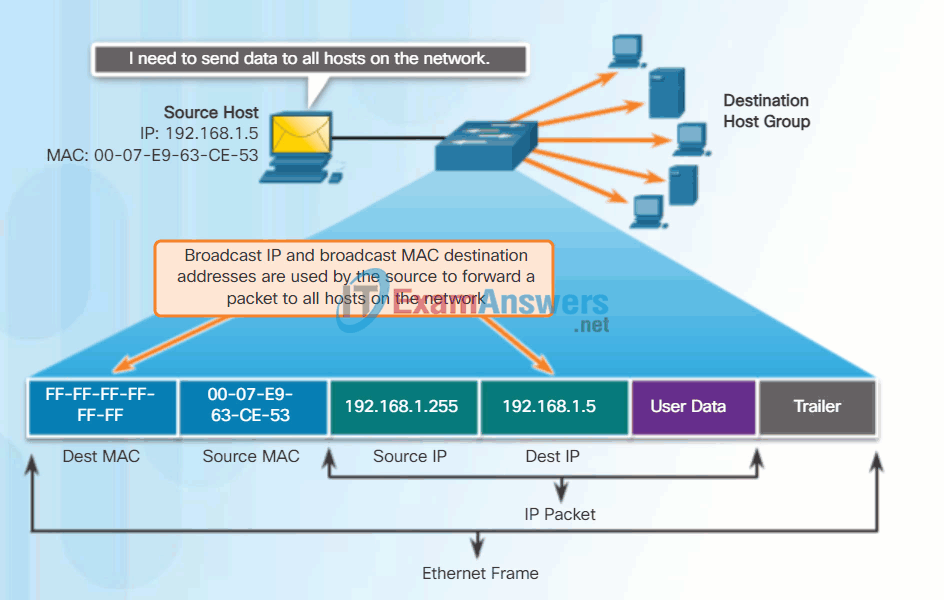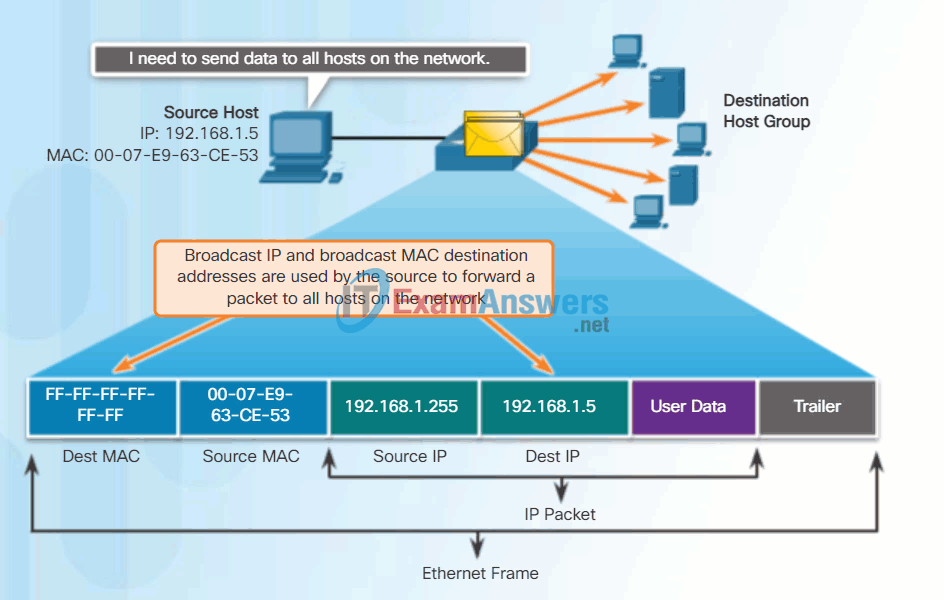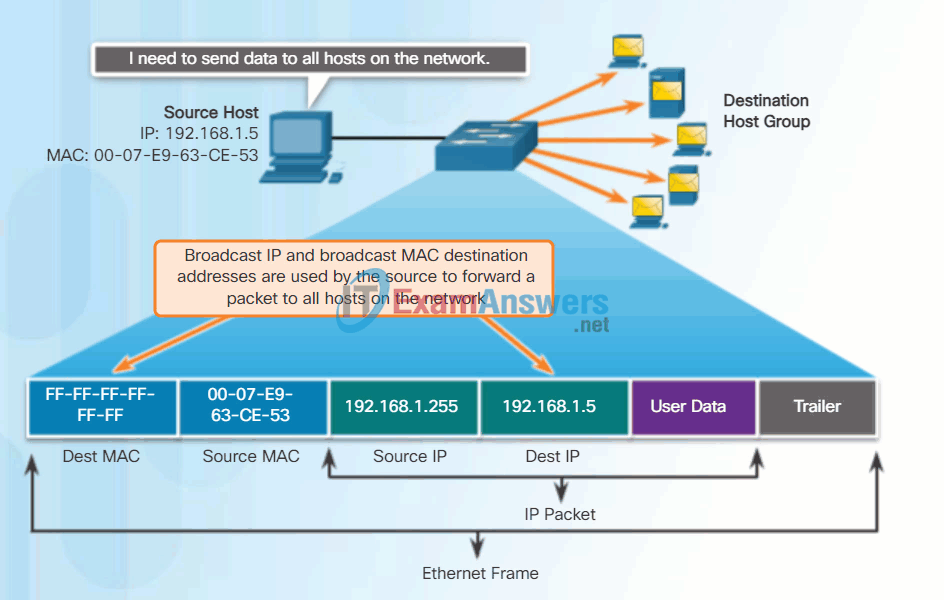
Broadcast
5.1.2.7 Modes of Deployment
Multicast MAC Address
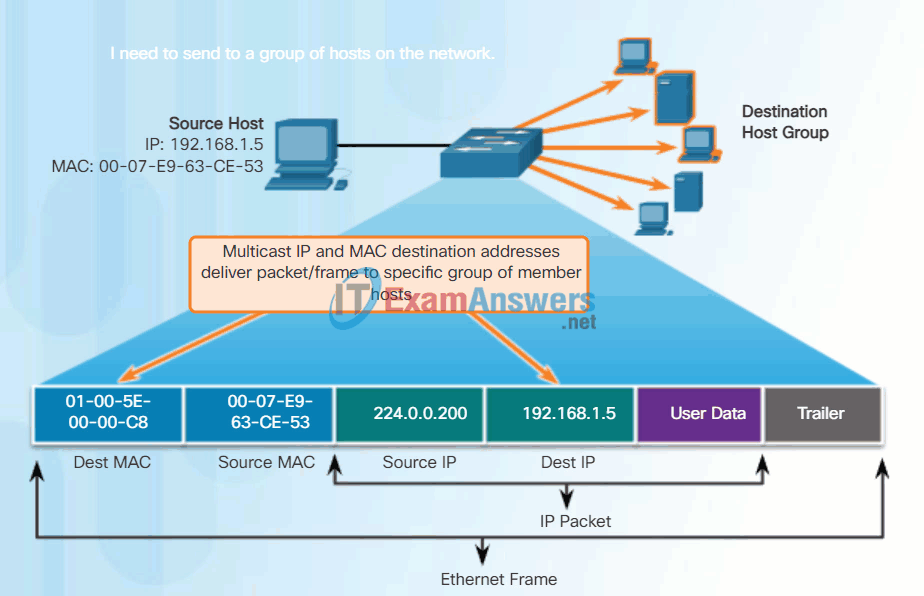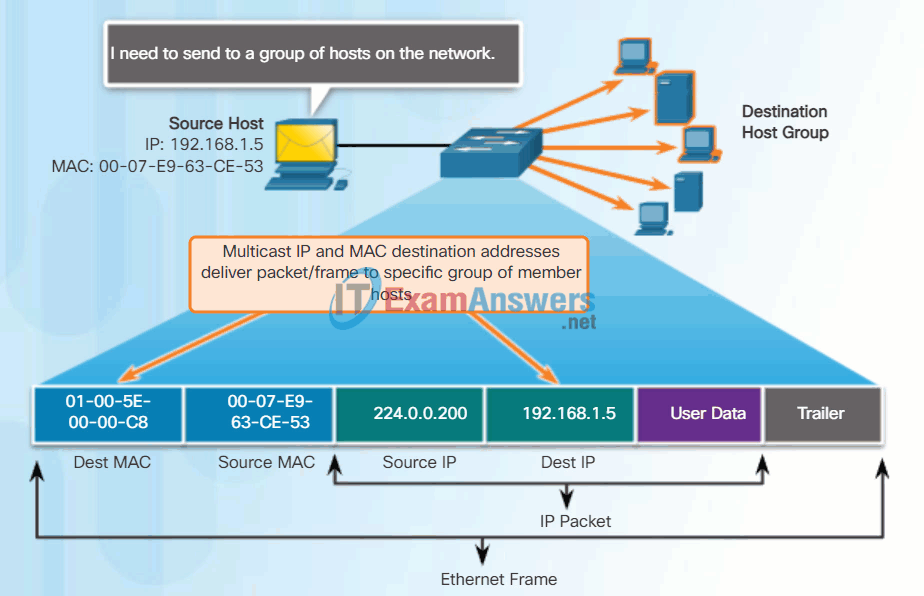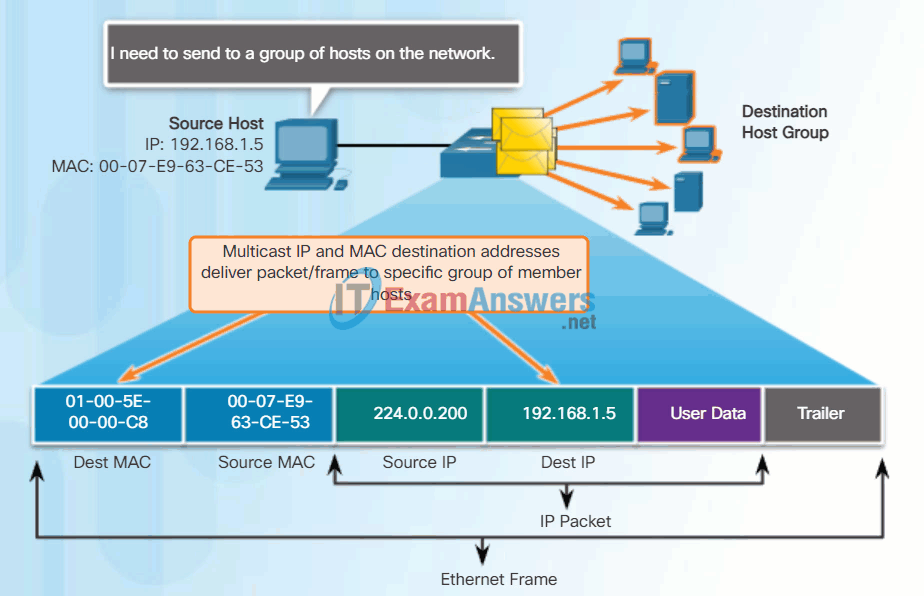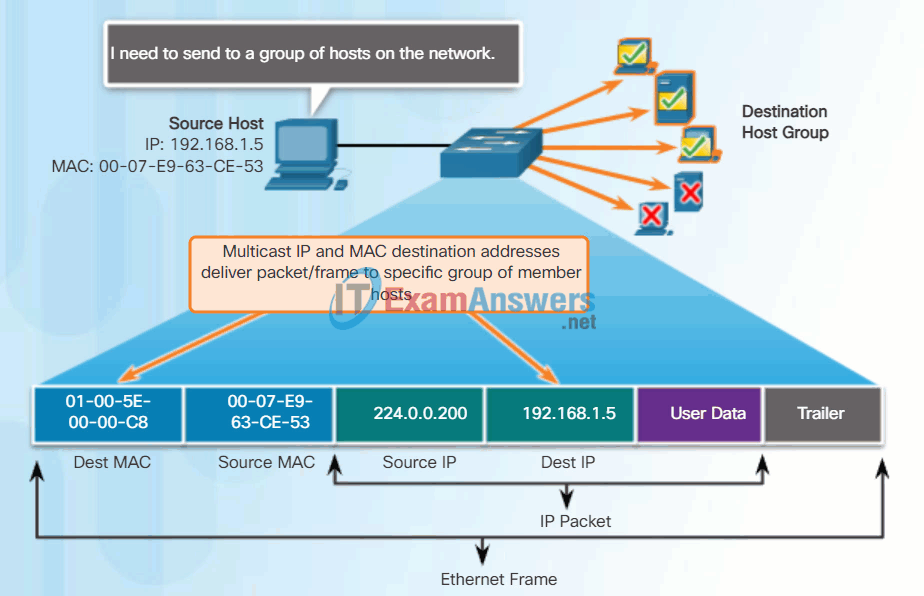
Multicast addresses allow a source device to send a packet to a group of devices. Devices that belong to a multicast group are assigned a multicast group IP address. The range of IPv4 multicast addresses is 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The range of IPv6 multicast addresses begin with FF00::/8. Because multicast addresses represent a group of addresses (sometimes called a host group), they can only be used as the destination of a packet. The source will always be a unicast address.
Multicast addresses would be used in remote gaming, where many players are connected remotely but playing the same game. Another use of multicast addresses is in distance learning through video conferencing, where many students are connected to the same class.
As with the unicast and broadcast addresses, the multicast IP address requires a corresponding multicast MAC address to actually deliver frames on a local network. The multicast MAC address associated with an IPv4 multicast address is a special value that begins with 01-00-5E in hexadecimal. The remaining portion of the multicast MAC address is created by converting the lower 23 bits of the IP multicast group address into 6 hexadecimal characters. For an IPv6 address, the multicast MAC address begins with 33-33.
An example, as shown in the animation, is the multicast hexadecimal address 01-00-5E-00-00-C8. The last byte, or eight bits, of the IPv4 address 224.0.0.200, is the decimal value 200. The easiest way to see the hexadecimal equivalent is to first convert it to binary with a space between each four bits, 200 (decimal) = 1100 1000 (binary). Using the binary to hexadecimal conversion chart shown earlier, 1100 1000 (binary) = 0xC8.
5.1.2.8 Activity – Compare Network-Based and Host-Based IPS Devices
Lab – Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
In this lab, you will complete the following objectives:
- Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
- Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
- Part 3: Display, Describe, and Analyze Ethernet MAC Addresses
5.1.3 Cisco Switched Port Analyzer
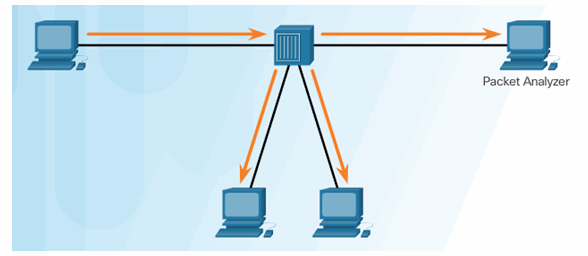
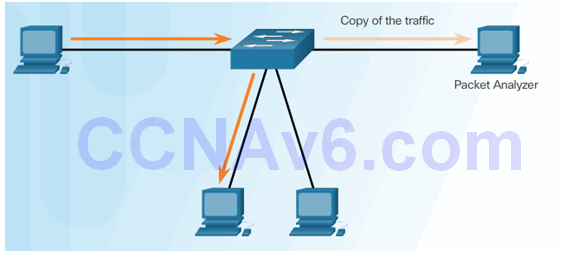
5.1.3.1 Port Mirroring
Traffic Sniffing Using a Hub
Traffic Sniffing Using a Switch
5.1.3.2 Cisco SPAN
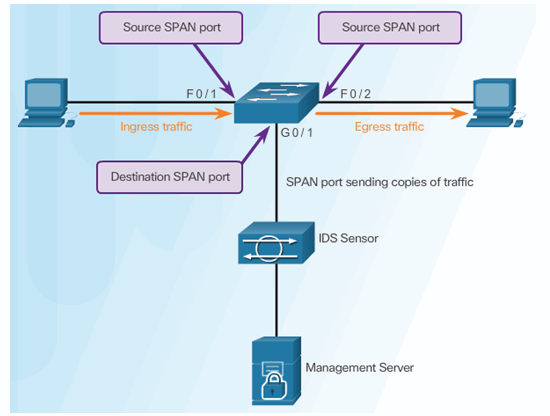
5.1.3.3 Configuring Cisco SPAN using Intrusion Detection
Cisco SPAN Commands:
- Monitor session command – used to associate a source port and a destination port with a SPAN session.
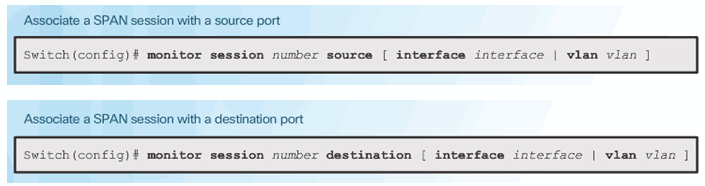
- Show monitor command – used to verify the SPAN session.
5.2 IPS Signatures
5.2.1 IPS Signature Characteristics
5.2.1.1 Signature Attributes
Switch Fundamentals
A Layer 2 Ethernet switch uses MAC addresses to make forwarding decisions. It is completely unaware of the protocol being carried in the data portion of the frame, such as an IPv4 packet. The switch makes its forwarding decisions based only on the Layer 2 Ethernet MAC addresses.
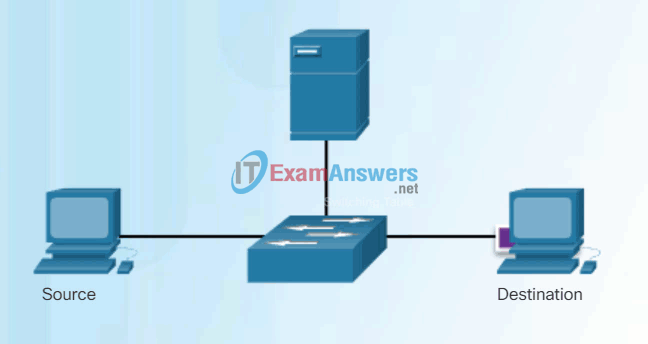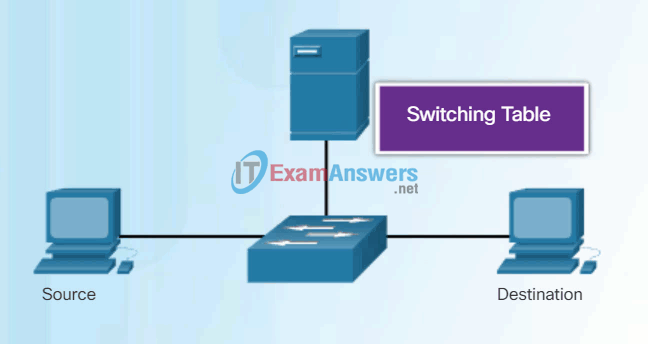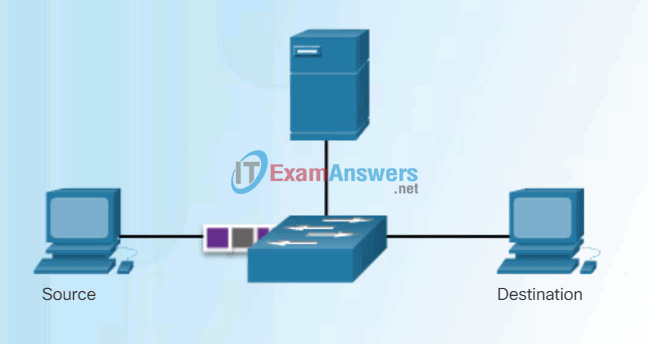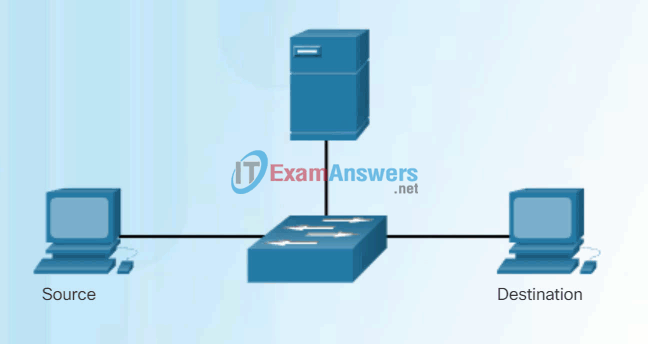
Unlike legacy Ethernet hubs that repeat bits out all ports except the incoming port, an Ethernet switch consults a MAC address table to make a forwarding decision for each frame. In the figure, the four-port switch was just powered on. It has not yet learned the MAC addresses for the four attached PCs.
Note: The MAC address table is sometimes referred to as a content addressable memory (CAM) table. While the term CAM table is fairly common, for the purposes of this course, we will refer to it as a MAC address table.
Learn: Examine Source MAC Address
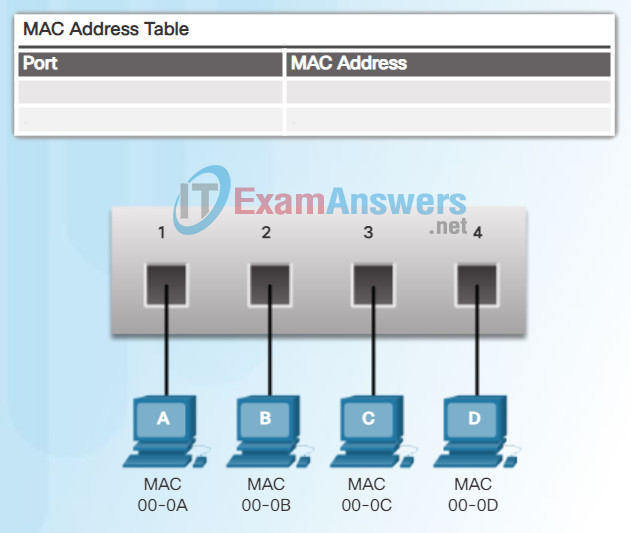
MAC addressess are shortened for demonstration purposes.
5.2.1.2 Signature Types
Learning MAC Addresses
The switch dynamically builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of the frames received on a port. The switch forwards frames by searching for a match between the destination MAC address in the frame and an entry in the MAC address table.
The following process is performed on every Ethernet frame that enters a switch.
Learn – Examining the Source MAC Address
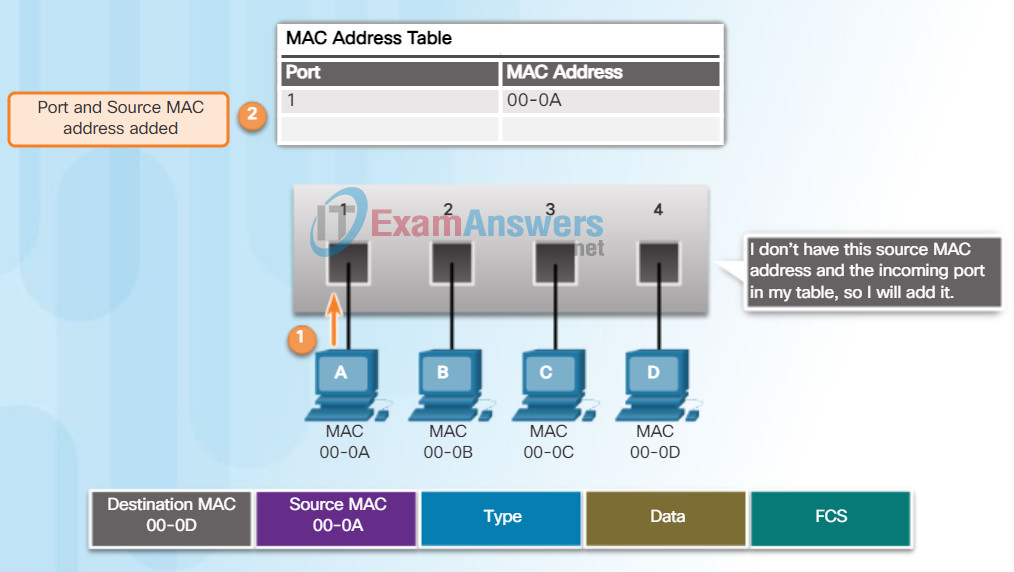
Every frame that enters a switch is checked for new information to learn. It does this by examining the frame’s source MAC address and port number where the frame entered the switch.
- If the source MAC address does not exist, it is added to the table along with the incoming port number. In Figure 1, PC-A is sending an Ethernet frame to PC-D. The switch adds the MAC address for PC-A to the table.
- If the source MAC address does exist, the switch updates the refresh timer for that entry. By default, most Ethernet switches keep an entry in the table for 5 minutes.
Note: If the source MAC address does exist in the table but on a different port, the switch treats this as a new entry. The entry is replaced using the same MAC address but with the more current port number.
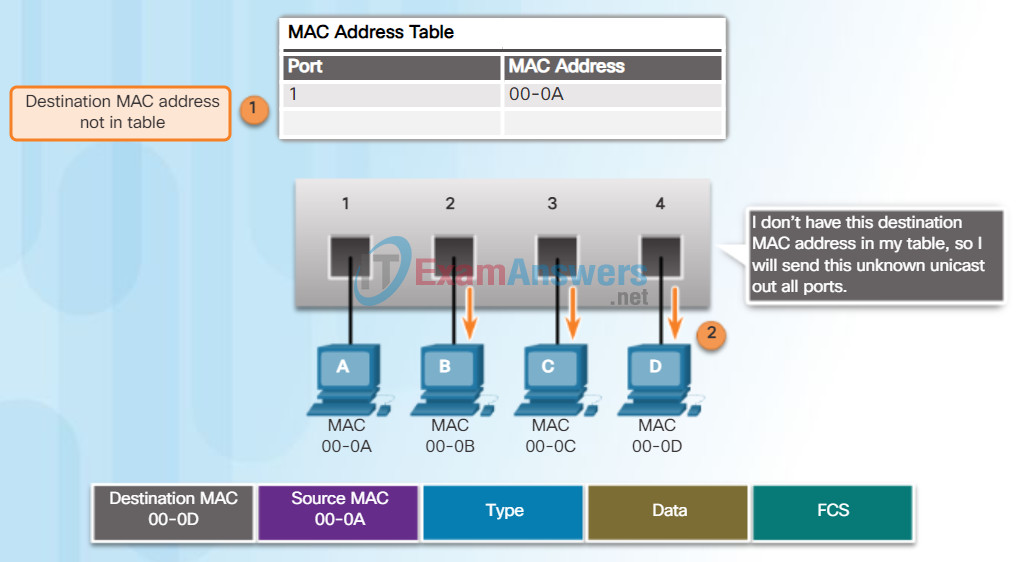
Forward – Examining the Destination MAC Address
Next, if the destination MAC address is a unicast address, the switch will look for a match between the destination MAC address of the frame and an entry in its MAC address table.
- If the destination MAC address is in the table, it will forward the frame out the specified port.
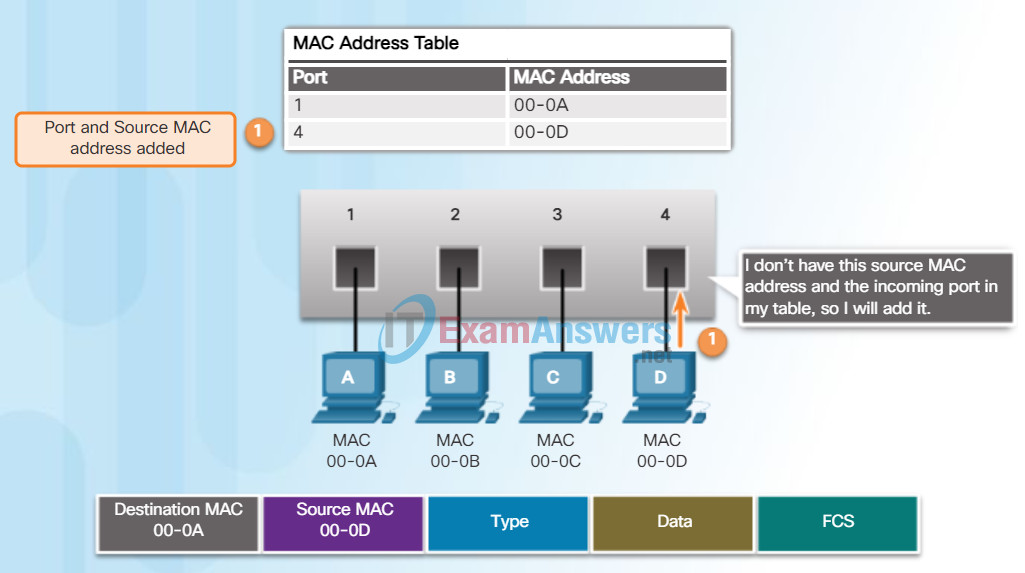
- If the destination MAC address is not in the table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the incoming port. This is known as an unknown unicast. As shown in Figure 2, the switch does not have the destination MAC address in its table for PC-D, so it sends the frame out all ports except port 1.
Note: If the destination MAC address is a broadcast or a multicast, the frame is also flooded out all ports except the incoming port.
5.2.1.3 Signature File
Filtering Frames
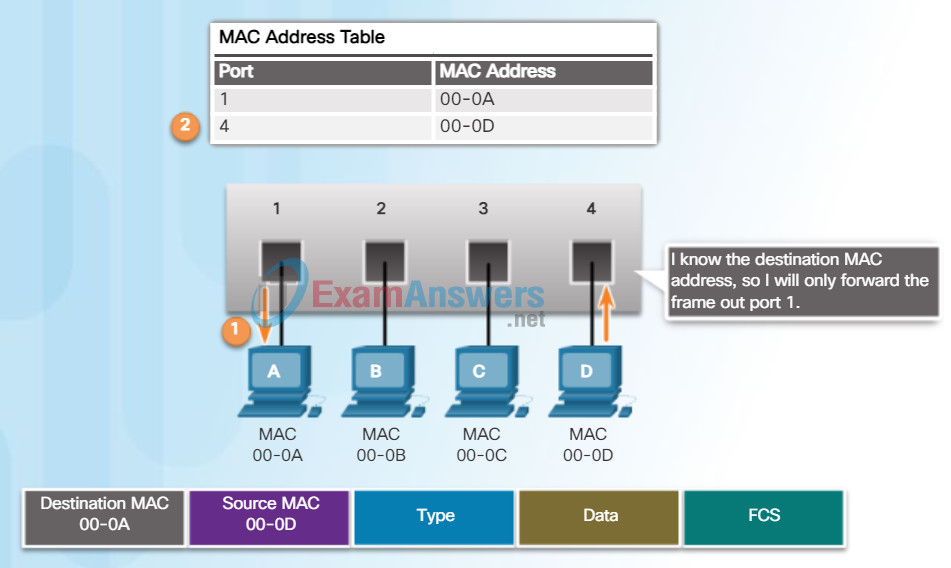
As a switch receives frames from different devices, it is able to populate its MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of every frame. When the switch’s MAC address table contains the destination MAC address, it is able to filter the frame and forward out a single port.
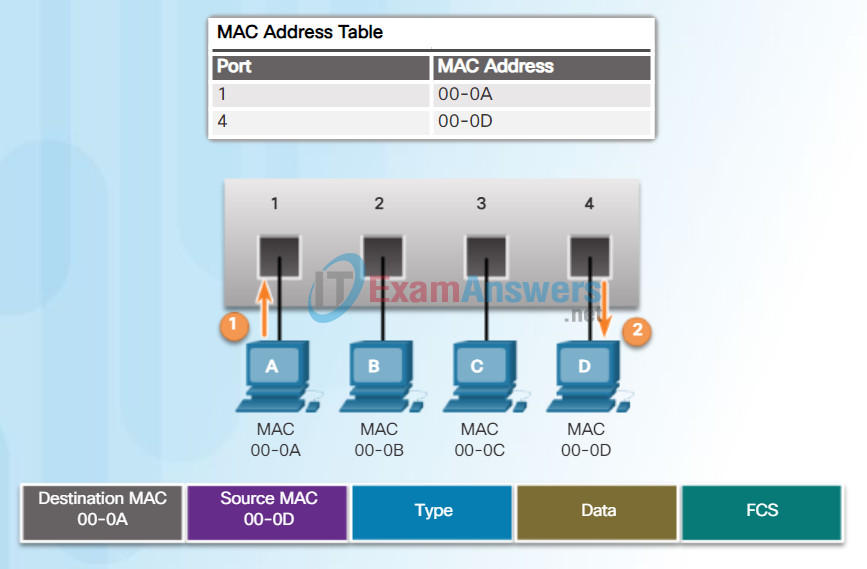
Figures 1 and 2 show PC-D sending a frame back to PC-A. The switch will first learn PC-D’s MAC address. Next, because the switch has PC-A’s MAC address in its table, it will send the frame only out port 1.
Figure 3 shows PC-A sending another frame to PC-D. The MAC address table already contains PC-A’s MAC address, so the five-minute refresh timer for that entry is reset. Next, because the switch’s table contains PC-D’s MAC address, it sends the frame only out port 4.
5.2.1.4 Signature Micro-Engines
Video Demonstration – MAC Address Tables on Connected Switches
A switch can have multiple MAC addresses associated with a single port. This is common when the switch is connected to another switch. The switch will have a separate MAC address table entry for each frame received with a different source MAC address.
5.2.1.5 Acquire the Signature File
Video Demonstration – Sending a Frame to the Default Gateway
When a device has an IP address that is on a remote network, the Ethernet frame cannot be sent directly to the destination device. Instead, the Ethernet frame is sent to the MAC address of the default gateway, the router.
Click Play in the figure to view a demonstration of how PC-A communicates with its default gateway.
Note: In the video, the IP packet that is sent from PC-A to a destination on a remote network has a source IP address of PC-A and a destination IP address of the remote host. The returning IP packet will have the source IP address of remote host and the destination IP address will be that of PC-A.
5.2.2 IPS Signature Alarms
5.2.2.1 Signature Alarm
Frame Forwarding Methods on Cisco Switches
Switches use one of the following forwarding methods for switching data between network ports:
- Store-and-forward switching
- Cut-through switching
Figure 1 highlights differences between these two methods.
Switch Packet Forwarding Methods

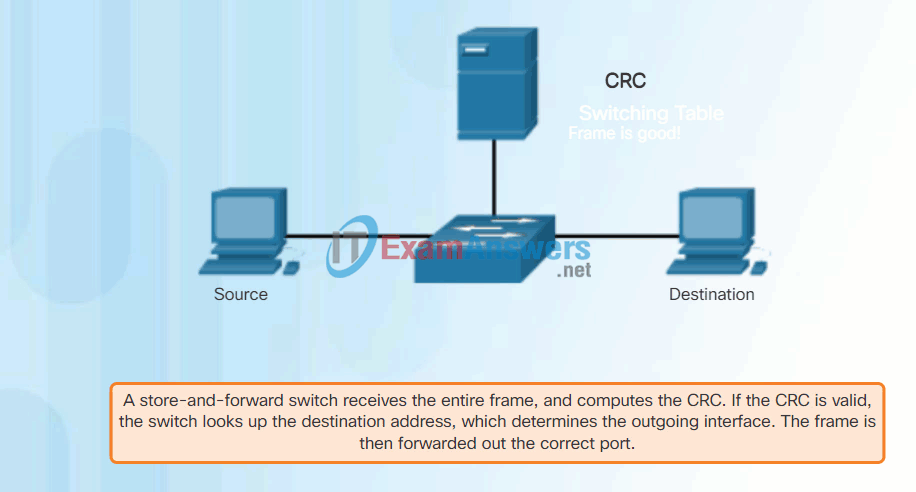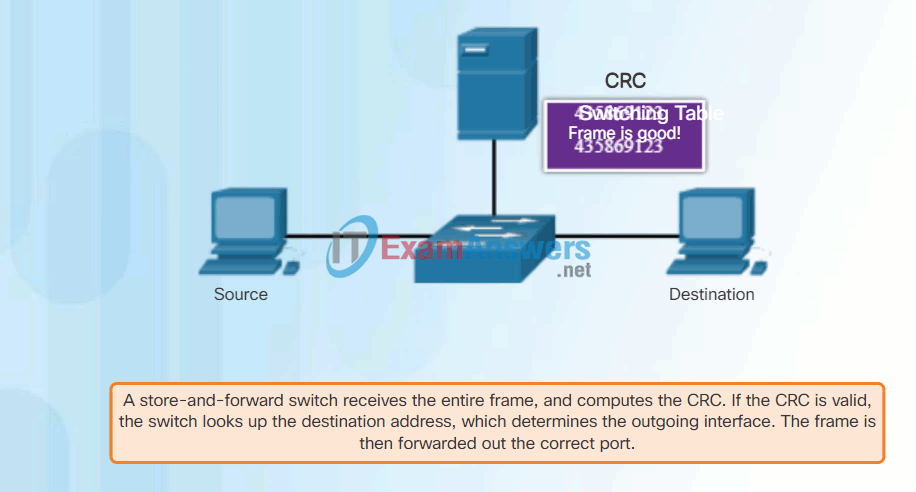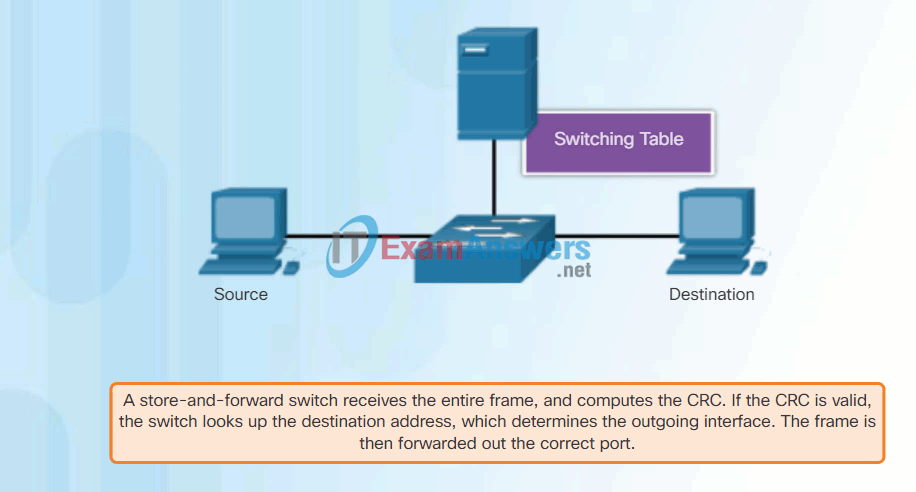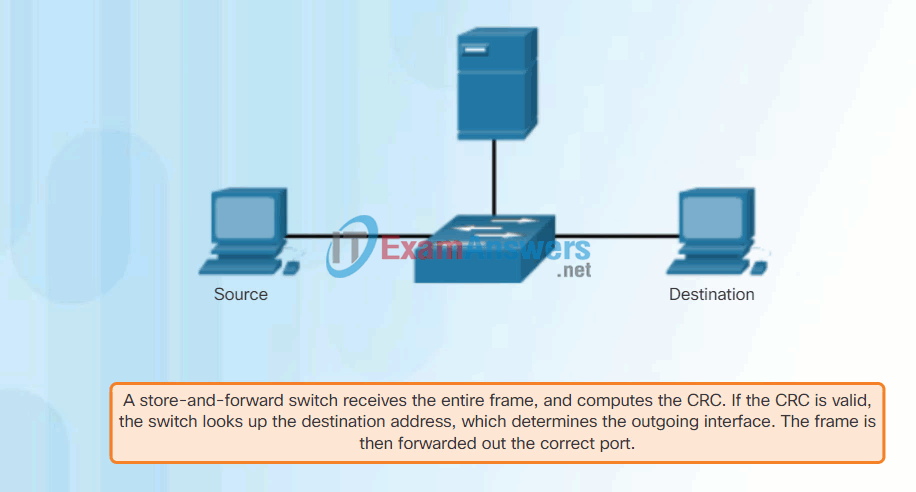
- A store-and-forward switch receives the entire frame, and computes the CRC. If the CRC is valid, the switch looks up the destination address, which determines the outgoing interface. The frame is then forwarded out the correct port.

- A cut-through switch forwards the frame before it is entirely received. At a minimum, the destination address of the frame must be read before the frame can be forwarded.
In store-and-forward switching, when the switch receives the frame, it stores the data in buffers until the complete frame has been received. During the storage process, the switch analyzes the frame for information about its destination. In this process, the switch also performs an error check using the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) trailer portion of the Ethernet frame.
CRC uses a mathematical formula, based on the number of bits (1s) in the frame, to determine whether the received frame has an error. After confirming the integrity of the frame, the frame is forwarded out the appropriate port, toward its destination. When an error is detected in a frame, the switch discards the frame. Discarding frames with errors reduces the amount of bandwidth consumed by corrupt data. Store-and-forward switching is required for Quality of Service (QoS) analysis on converged networks where frame classification for traffic prioritization is necessary. For example, voice over IP data streams need to have priority over web-browsing traffic.
In Figure 2, play the animation for a demonstration of the store-and-forward process.
Store-and-Forward Switching
Click here to learn more about store-and-forward and cut-through switching.
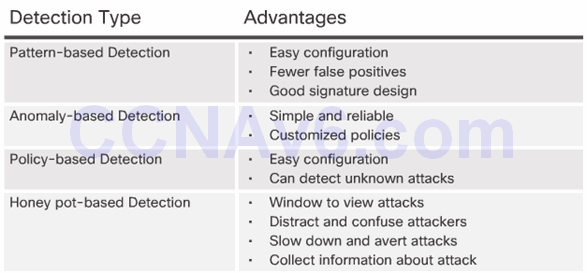
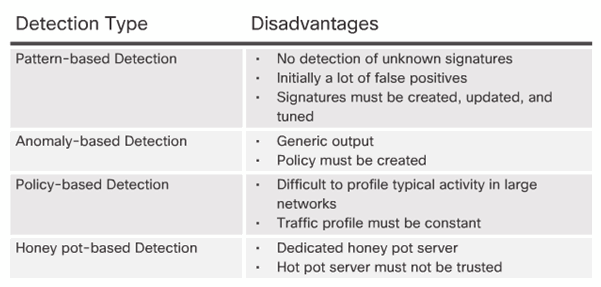
5.2.2.2 Pattern-Based Detection
Cut-Through Switching
In cut-through switching, the switch acts upon the data as soon as it is received, even if the transmission is not complete. The switch buffers just enough of the frame to read the destination MAC address so that it can determine to which port to forward the data. The destination MAC address is located in the first 6 bytes of the frame following the preamble. The switch looks up the destination MAC address in its switching table, determines the outgoing interface port, and forwards the frame onto its destination through the designated switch port. The switch does not perform any error checking on the frame.
Play the animation for a demonstration of the cut-through switching process.
There are two variants of cut-through switching:
- Fast-forward switching – Fast-forward switching offers the lowest level of latency. Fast-forward switching immediately forwards a packet after reading the destination address. Because fast-forward switching starts forwarding before the entire packet has been received, there may be times when packets are relayed with errors. This occurs infrequently, and the destination network adapter discards the faulty packet upon receipt. In fast-forward mode, latency is measured from the first bit received to the first bit transmitted. Fast-forward switching is the typical cut-through method of switching.
- Fragment-free switching – In fragment-free switching, the switch stores the first 64 bytes of the frame before forwarding. Fragment-free switching can be viewed as a compromise between store-and-forward switching and fast-forward switching. The reason fragment-free switching stores only the first 64 bytes of the frame is that most network errors and collisions occur during the first 64 bytes. Fragment-free switching tries to enhance fast-forward switching by performing a small error check on the first 64 bytes of the frame to ensure that a collision has not occurred before forwarding the frame. Fragment-free switching is a compromise between the high latency and high integrity of store-and-forward switching, and the low latency and reduced integrity of fast-forward switching.
Some switches are configured to perform cut-through switching on a per-port basis until a user-defined error threshold is reached, and then they automatically change to store-and-forward. When the error rate falls below the threshold, the port automatically changes back to cut-through switching.
A cut-through switch forwards the frame before it is entirely received. At a minimum, the destination address of the frame must be read before the frame can be forwarded.
5.2.2.3 Anomaly-Based Detection
Memory Buffering on Switches
An Ethernet switch may use a buffering technique to store frames before forwarding them. Buffering may also be used when the destination port is busy due to congestion and the switch stores the frame until it can be transmitted.
As shown in the figure, there are two methods of memory buffering: port-based and shared memory.
Port-based Memory Buffering
In port-based memory buffering, frames are stored in queues that are linked to specific incoming and outgoing ports. A frame is transmitted to the outgoing port only when all the frames ahead of it in the queue have been successfully transmitted. It is possible for a single frame to delay the transmission of all the frames in memory because of a busy destination port. This delay occurs even if the other frames could be transmitted to open destination ports.
Shared Memory Buffering
Shared memory buffering deposits all frames into a common memory buffer that all the ports on the switch share. The amount of buffer memory required by a port is dynamically allocated. The frames in the buffer are linked dynamically to the destination port. This allows the packet to be received on one port and then transmitted on another port, without moving it to a different queue.
The switch keeps a map of frame to port links showing where a packet needs to be transmitted. The map link is cleared after the frame has been successfully transmitted. The number of frames stored in the buffer is restricted by the size of the entire memory buffer and not limited to a single port buffer. This permits larger frames to be transmitted with fewer dropped frames. This is especially important to asymmetric switching. Asymmetric switching allows for different data rates on different ports. This allows more bandwidth to be dedicated to certain ports, such as a port connected to a server.
Port-Based and Shared Memory Buffering

5.2.2.4 Policy-Based and Honey Pot-Based Detection

Activity – Frame Forwarding Methods
5.2.2.5 Benefits of the Cisco IOS IPS Solution
Benefits:
- It uses underlying routing infrastructure to provide an additional layer of security.
- It is inline and is supported on a broad range of routing platforms.
- It provides threat protection at all entry points to the network when used in combination with Cisco IDS, Cisco IOS Firewall, VPN, and NAC solutions
- The size of the signature database used by the devices can be adapted to the amount of available memory in the router.

5.2.2.6 Alarm Triggering Mechanisms
Understanding Alarm Types:
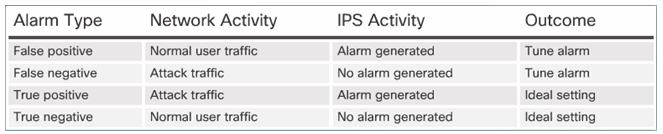
5.2.2.7 Activity – IPS Signature Alarms
5.2.3 IPS Signature Actions
5.2.3.1 Signature Actions
Duplex and Speed Settings
Two of the most basic settings on a switch are the bandwidth and duplex settings for each individual switch port. It is critical that the duplex and bandwidth settings match between the switch port and the connected devices, such as a computer or another switch.
There are two types of duplex settings used for communications on an Ethernet network: half duplex and full duplex.
- Full-duplex – Both ends of the connection can send and receive simultaneously.
- Half-duplex – Only one end of the connection can send at a time.
Autonegotiation is an optional function found on most Ethernet switches and NICs. Autonegotiation enables two devices to automatically exchange information about speed and duplex capabilities. The switch and the connected device will choose the highest performance mode. Full-duplex is chosen if both devices have the capability along with their highest common bandwidth.
For example, in Figure 1 PC-A’s Ethernet NIC can operate in full-duplex or half-duplex, and in 10 Mb/s or 100 Mb/s. PC-A is connected to switch S1 on port 1, which can operate in full-duplex or half-duplex, and in 10 Mb/s, 100 Mb/s or 1000 Mb/s (1 Gb/s). If both devices are using autonegotiation, the operating mode will be full-duplex and 100 Mb/s.
Note: Most Cisco switches and Ethernet NICs default to autonegotiation for speed and duplex. Gigabit Ethernet ports only operate in full-duplex.
Duplex Mismatch
One of the most common causes of performance issues on 10/100 Mb/s Ethernet links occurs when one port on the link operates at half-duplex while the other port operates at full-duplex, as shown in Figure 2. This occurs when one or both ports on a link are reset, and the autonegotiation process does not result in both link partners having the same configuration. It also can occur when users reconfigure one side of a link and forget to reconfigure the other. Both sides of a link should have autonegotiation on, or both sides should have it off.
Duplex and Speed Settings
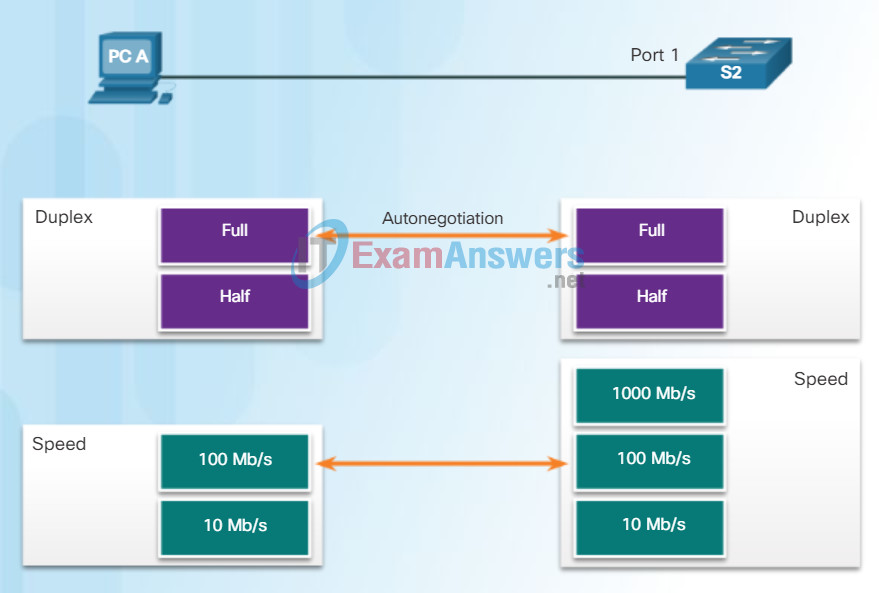
Duplex Mismatch

S2 will continually experience collisions because S1 keeps sending frames any time it has something to send.
5.2.3.2 Manage Generated Alerts
Auto-MDIX
In addition to having the correct duplex setting, it is also necessary to have the correct cable type defined for each port. Connections between specific devices, such as switch-to-switch, switch-to-router, switch-to-host, and router-to-host devices, once required the use of specific cable types (crossover or straight-through). Most switch devices now support the mdix auto interface configuration command in the CLI to enable the automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature.
When the auto-MDIX feature is enabled, the switch detects the type of cable attached to the port, and configures the interfaces accordingly. Therefore, you can use either a crossover or a straight-through cable for connections to a copper 10/100/1000 port on the switch, regardless of the type of device on the other end of the connection.
Note: The auto-MDIX feature is enabled by default on switches running Cisco IOS Release 12.2(18)SE or later.
MDIX auto detects the type of connection required and configures the interface accordingly.
5.2.3.3 Log Activities for Later Analysis
Logging the Activity:
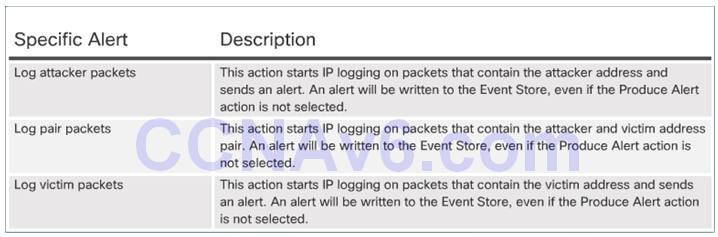
5.2.3.4 Deny the Activity
Dropping or Preventing the Activity:

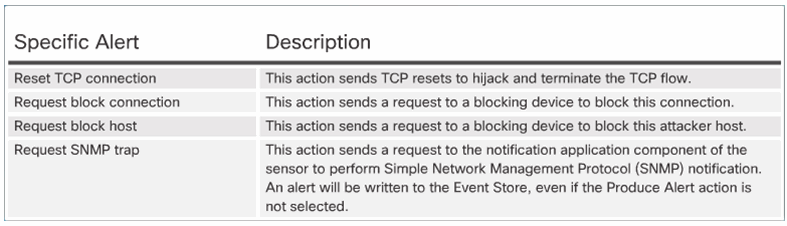
5.2.3.5 Reset, Block, and Allow Traffic
Resetting the Connection and Blocking the Activity:
5.2.3.6 Activity – Identify the IPS Signature Action
5.2.4 Manage and Monitor IPS
5.2.4.1 Monitor Activity
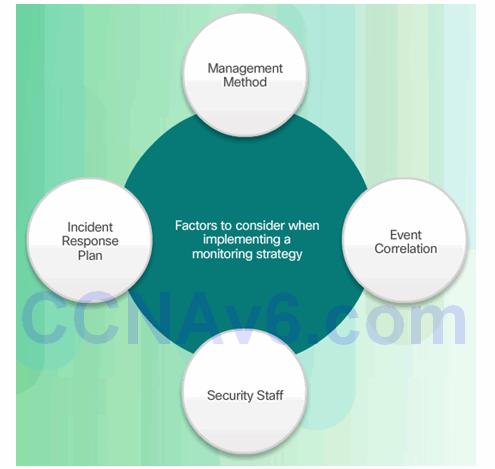
IPS Planning and Monitoring Considerations:
- Management method
- Event correlation
- Security staff
- Incident response plan
5.2.4.2 Monitoring Considerations
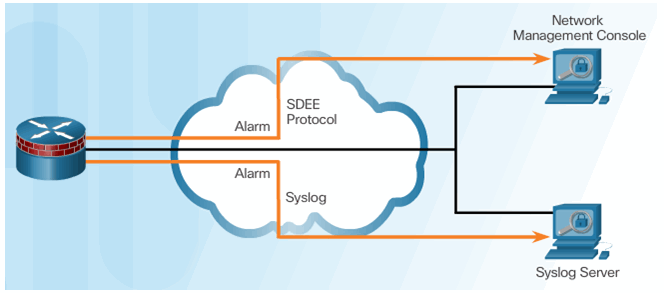
5.2.4.3 Secure Device Event Exchange
5.2.4.4 IPS Configuration Best Practices
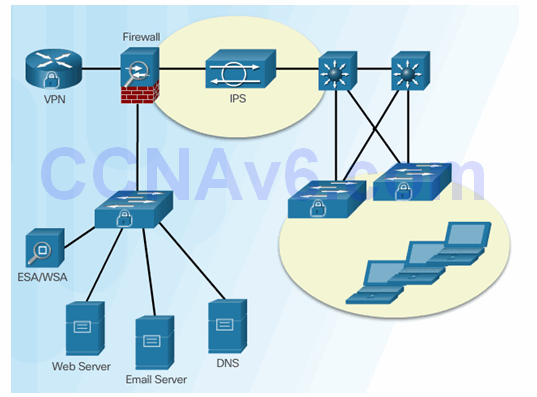
5.2.5 IPS Global Correlation
5.2.5.1 Cisco Global Correlation
Goals of global correlation:
- Dealing intelligently with alerts to improve effectiveness
- Improving protection against known malicious sites
- Sharing telemetry data with the SensorBase Network to improve visibility of alerts and sensor actions on a global scale
- Simplifying configuration settings
- Automatic handling of security information uploads and downloads
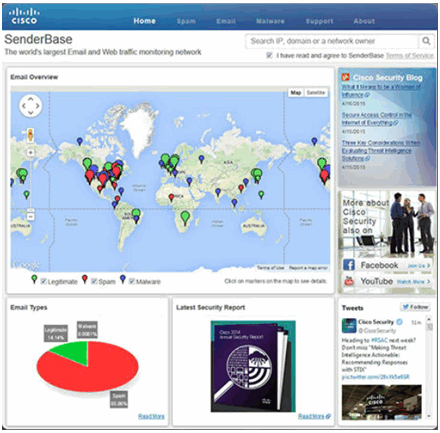
5.2.5.2 Cisco SensorBase Networ
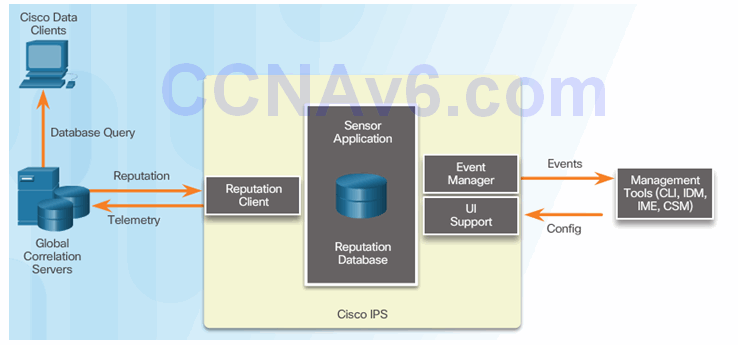
5.2.5.3 Cisco Security Intelligence Operation
Cisco Security Intelligence Operation
Network participation gathers the following data:
- Signature ID
- Attacker IP address
- Attacker port
- Maximum segment size
- Victim IP address
- Victim port
- Signature version
- TCP options string
- Reputation score
- Risk rating
5.2.5.4 Reputations, Blacklists, and Traffic Filters
5.2.5.5 Reputations, Blacklists, and Traffic Filters (Cont.)
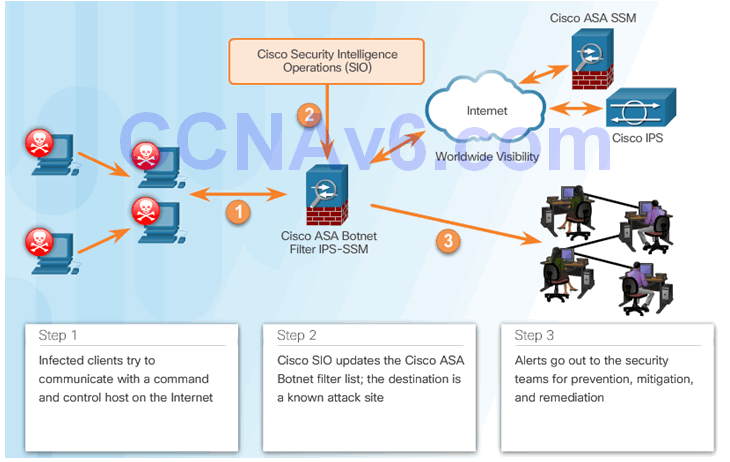
5.3 Implement IPS
5.3.1 Configure Cisco IOS IPS with CLI
5.3.1.1 Implement IOS IPS
Destination on Same Network
There are two primary addresses assigned to a device on an Ethernet LAN:
- Physical address (the MAC address) – Used for Ethernet NIC to Ethernet NIC communications on the same network.
- Logical address (the IP address) – Used to send the packet from the original source to the final destination.
IP addresses are used to identify the address of the original source and the final destination. The destination IP address may be on the same IP network as the source or may be on a remote network.
Note: Most applications use DNS (Domain Name System) to determine the IP address when given a domain name such as www.cisco.com. DNS is discussed in a later chapter.
Layer 2 or physical addresses, like Ethernet MAC addresses, have a different purpose. These addresses are used to deliver the data link frame with the encapsulated IP packet from one NIC to another NIC on the same network. If the destination IP address is on the same network, the destination MAC address will be that of the destination device.
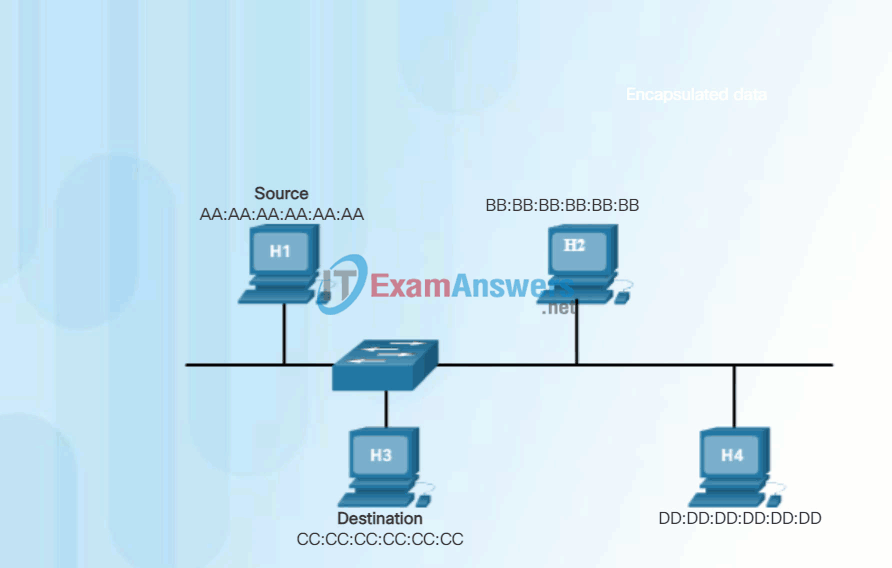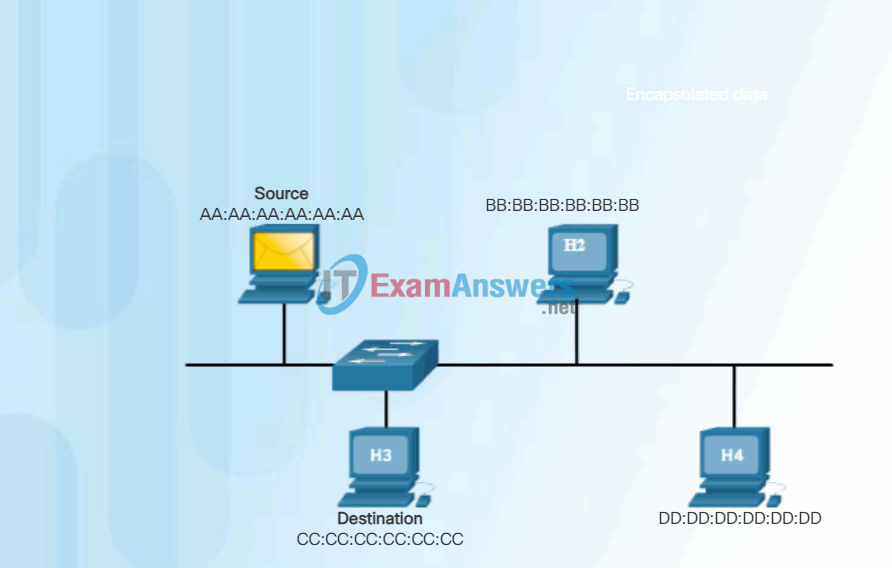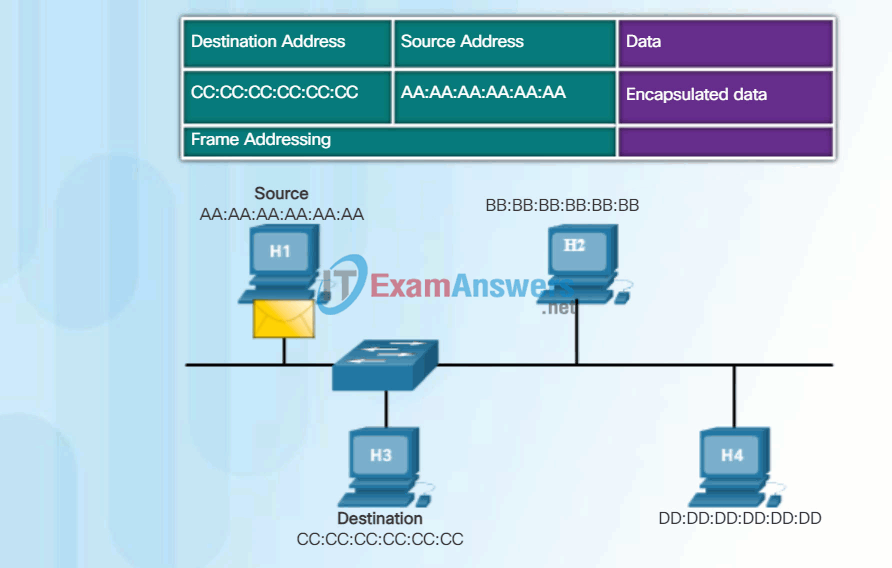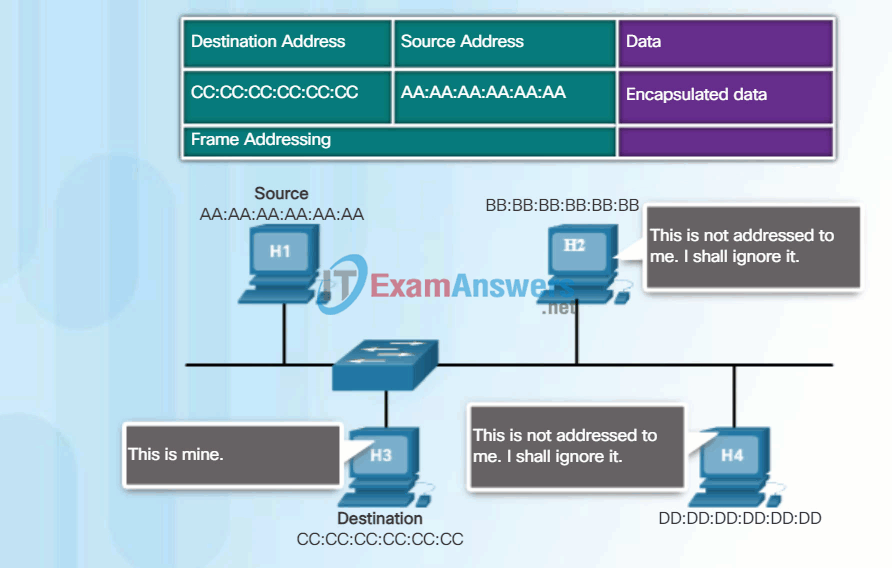
The figure shows the Ethernet MAC addresses and IP address for PC-A sending an IP packet to the file server on the same network.
The Layer 2 Ethernet frame contains:
- Destination MAC address – This is the MAC address of the file server’s Ethernet NIC.
- Source MAC address – This is the MAC address of PC-A’s Ethernet NIC.
The Layer 3 IP packet contains:
- Source IP address – This is the IP address of the original source, PC-A.
- Destination IP address – This is the IP address of the final destination, the file server.
Communicating on a Local Network
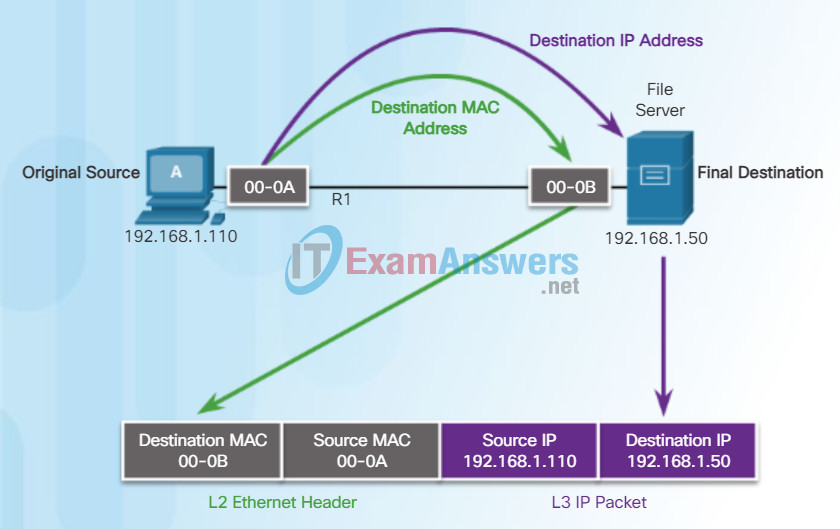
MAC addresses are shortened for demonstration purposes.
5.3.1.3 IPS Crypto Key
Packet Tracer – Identify MAC and IP Addresses
This activity is optimized for viewing PDUs. The devices are already configured. You will gather PDU information in simulation mode and answer a series of questions about the data you collect.

5.3.1.4 Enable IOS IPS
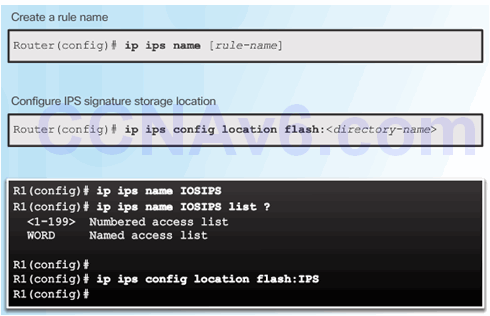
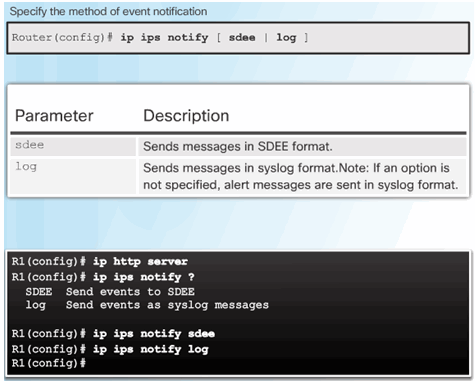
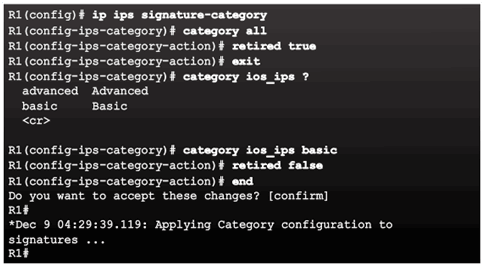
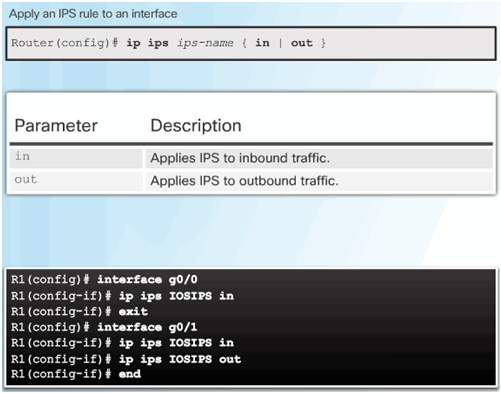
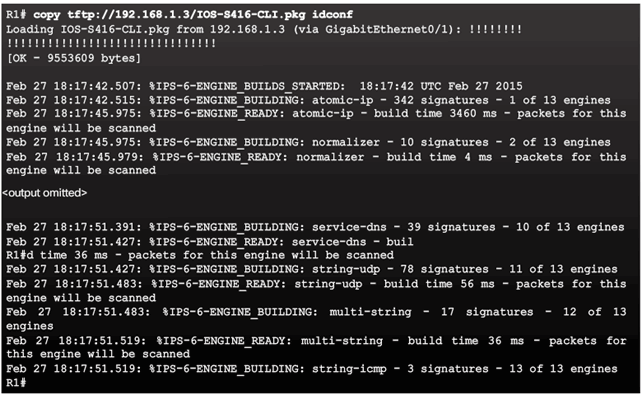
5.3.1.5 Load the IPS Signature Package in RAM
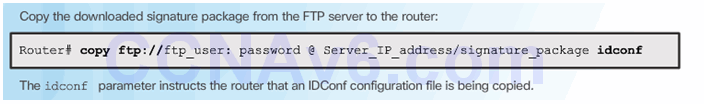
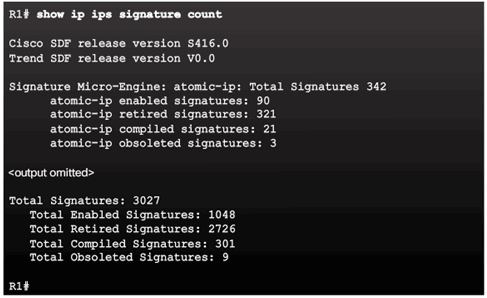
5.3.1.6 Activity – Implementing IPS
5.3.2 Modifying Cisco IOS IPS Signatures
5.3.2.1 Retire and Unretire Signatures
Introduction to ARP
Recall that every device with an IP address on an Ethernet network also has an Ethernet MAC address. When a device sends an Ethernet frame, it contains these two addresses:
- Destination MAC address – The MAC address of the Ethernet NIC, which will be either the MAC address of the final destination device or the router.
- Source MAC address – The MAC address of the sender’s Ethernet NIC.
To determine the destination MAC address, the device uses ARP. ARP provides two basic functions:
- Resolving IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
- Maintaining a table of mappings
5.3.2.2 Change Signature Actions
ARP Functions
Resolving IPv4 Addresses to MAC Addresses
When a packet is sent to the data link layer to be encapsulated into an Ethernet frame, the device refers to a table in its memory to find the MAC address that is mapped to the IPv4 address. This table is called the ARP table or the ARP cache. The ARP table is stored in the RAM of the device.
The sending device will search its ARP table for a destination IPv4 address and a corresponding MAC address.
- If the packet’s destination IPv4 address is on the same network as the source IPv4 address, the device will search the ARP table for the destination IPv4 address.
- If the destination IPv4 address is on a different network than the source IPv4 address, the device will search the ARP table for the IPv4 address of the default gateway.
In both cases, the search is for an IPv4 address and a corresponding MAC address for the device.
Each entry, or row, of the ARP table binds an IPv4 address with a MAC address. We call the relationship between the two values a map – it simply means that you can locate an IPv4 address in the table and discover the corresponding MAC address. The ARP table temporarily saves (caches) the mapping for the devices on the LAN.
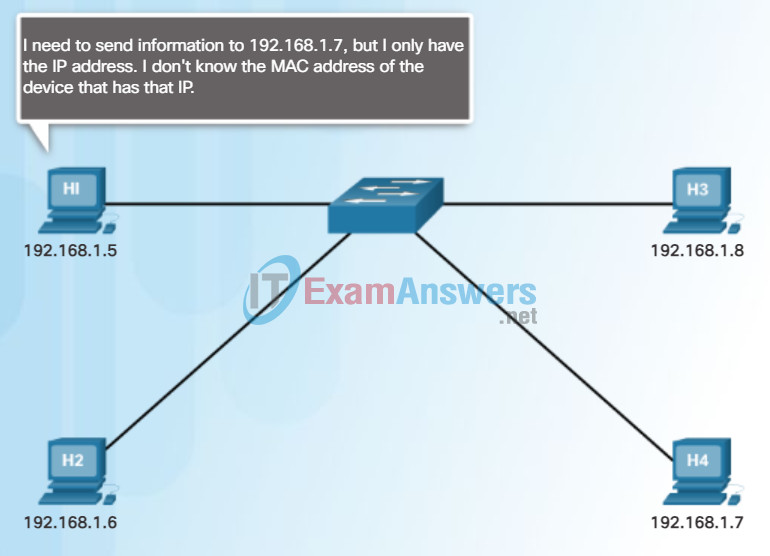
If the device locates the IPv4 address, its corresponding MAC address is used as the destination MAC address in the frame. If there is no entry is found, then the device sends an ARP request.
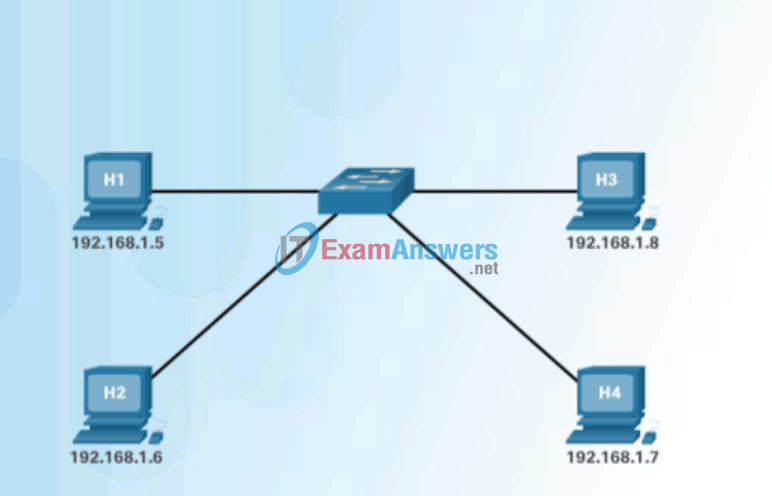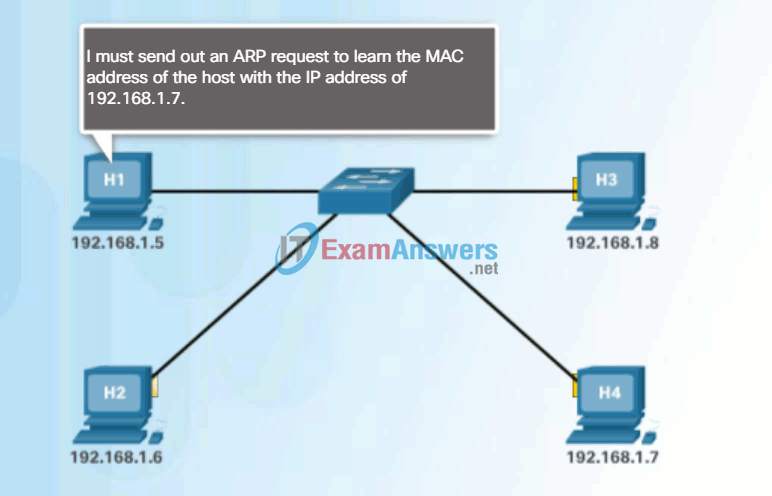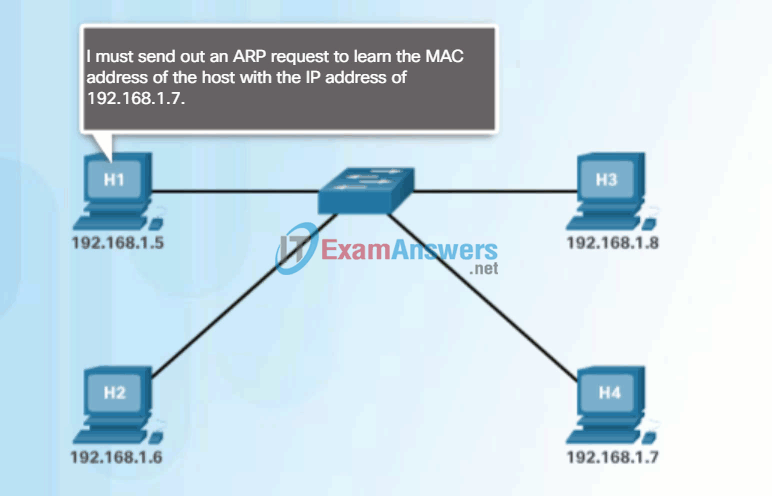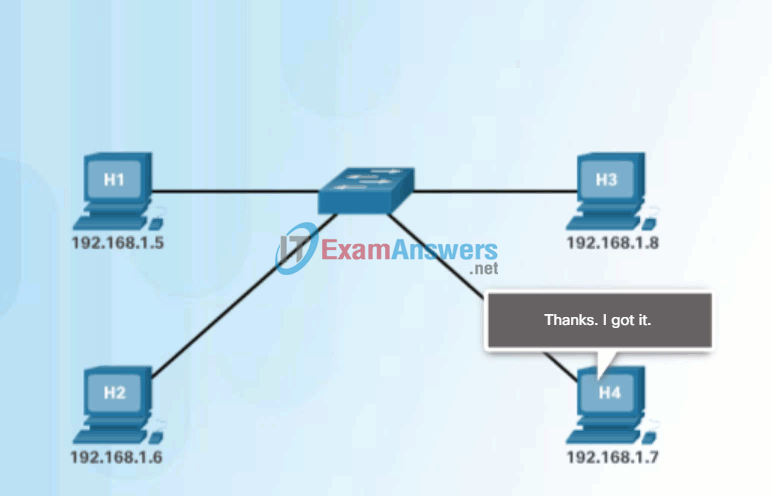
The ARP Process
5.3.3 Verify and Monitor IPS
5.3.3.1 Verify IOS IPS
ARP Broadcasts
As a broadcast frame, an ARP request is received and processed by every device on the local network. On a typical business network, these broadcasts would probably have minimal impact on network performance. However, if a large number of devices were to be powered up and all start accessing network services at the same time, there could be some reduction in performance for a short period of time, as shown in the figure. After the devices send out the initial ARP broadcasts and have learned the necessary MAC addresses, any impact on the network will be minimized.
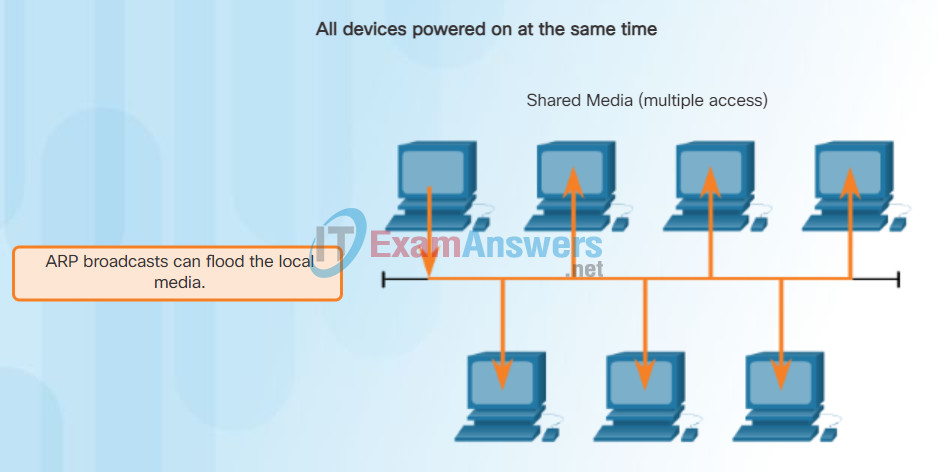
ARP Broadcasts and Security
5.3.3.2 Report IPS Alerts
ARP Spoofing
In some cases, the use of ARP can lead to a potential security risk known as ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning. This is a technique used by an attacker to reply to an ARP request for an IPv4 address belonging to another device, such as the default gateway, as shown in the figure. The attacker sends an ARP reply with its own MAC address. The receiver of the ARP reply will add the wrong MAC address to its ARP table and send these packets to the attacker.
Enterprise level switches include mitigation techniques known as dynamic ARP inspection (DAI). DAI is beyond the scope of this course.
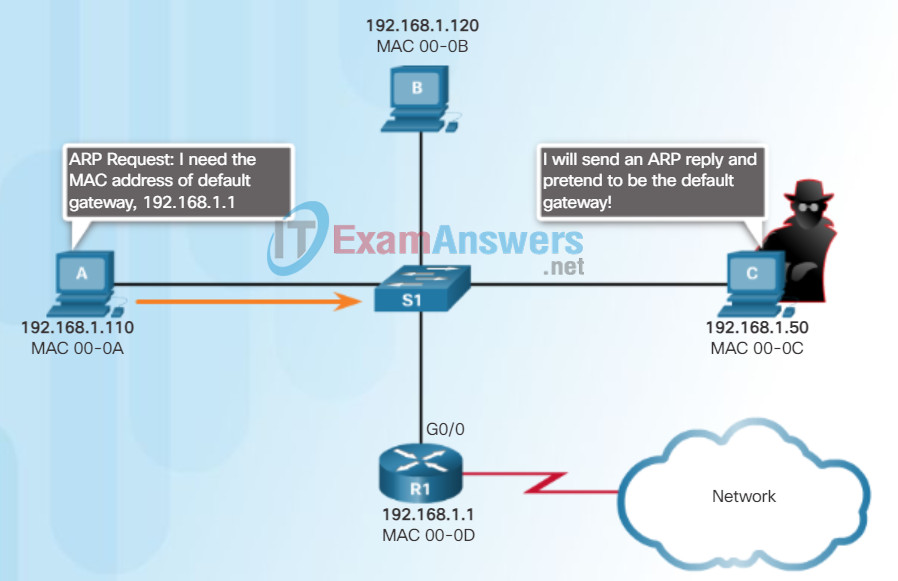
All Devices Powered On at the Same Time
Note: MAC addresses are shortened for demonstration purposes.
5.3.3.3 Enable SDEE
5.4 Summary
5.4.1 Conclusion
5.4.1.1 Lab – Configure an IOS IPS Using CLI
5.4.1.1 Lab – Configure an IOS IPS Using CLI
Class Activity – MAC and Choose…
MAC and Choose…
Note: This activity can be completed individually, in small groups, or in a full-classroom learning environment.
Please view the video located at the following link:
http://www.netevents.tv/video/bob-metcalfe-the-history-of-ethernet
Topics discussed include not only where we have come from in Ethernet development, but where we are going with Ethernet technology (a futuristic approach).
After viewing the video and comparing its contents to Chapter 5, go to the web and search for information about Ethernet. Use a constructivist approach:
What did Ethernet look like when it was first developed?
How has Ethernet stayed the same over the past 25 years or so, and what changes are being made to make it more useful/applicable to today’s data transmission methods?
Collect three pictures of old, current, and future Ethernet physical media and devices (focus on switches) – share these pictures with the class and discuss:
How have Ethernet physical media and intermediary devices changed?
How have Ethernet physical media and intermediary devices stayed the same?
How will Ethernet change in the future?

Ethernet uses end and intermediary devices to identify and deliver frames through networks.
5.4.1.2 Packet Tracer – Configure an IOS IPS Using the CLI
5.4.1.2 Packet Tracer – Configure an IOS IPS Using the CLI
Ethernet is the most widely used LAN technology today. It is a family of networking technologies that are defined in the IEEE 802.2 and 802.3 standards. Ethernet standards define both the Layer 2 protocols and the Layer 1 technologies. For the Layer 2 protocols, as with all 802 IEEE standards, Ethernet relies on the two separate sublayers of the data link layer to operate, the Logical Link Control (LLC) and the MAC sublayers.
At the data link layer, the frame structure is nearly identical for all bandwidths of Ethernet. The Ethernet frame structure adds headers and trailers around the Layer 3 PDU to encapsulate the message being sent.
There are two styles of Ethernet framing: IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard and the DIX Ethernet standard which is now referred to Ethernet II. The most significant difference between the two standards is the addition of a Start Frame Delimiter (SFD) and the change of the Type field to a Length field in the 802.3. Ethernet II is the Ethernet frame format used in TCP/IP networks. As an implementation of the IEEE 802.2/3 standards, the Ethernet frame provides MAC addressing and error checking.
The Layer 2 addressing provided by Ethernet supports unicast, multicast, and broadcast communications. Ethernet uses the Address Resolution Protocol to determine the MAC addresses of destinations and map them against known IPv4 addresses.
Each node on an IPv4 network has both a MAC address and an IPv4 address. The IP addresses are used to identify the original source and final destination of the packet. The Ethernet MAC addresses are used to send the packet from one Ethernet NIC to another Ethernet NIC on the same IP network. ARP is used to map a known IPv4 address to a MAC address, so the packet can be encapsulated in an Ethernet frame with the correct Layer 2 address.
ARP relies on certain types of Ethernet broadcast messages and Ethernet unicast messages, called ARP requests and ARP replies. The ARP protocol resolves IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses and maintains a table of mappings.
On most Ethernet networks, end devices are typically connected on a point-to-point basis to a Layer 2, full-duplex switch. A Layer 2 LAN switch performs switching and filtering based only on the OSI data link layer (Layer 2) MAC address. A Layer 2 switch builds a MAC address table that it uses to make forwarding decisions. Layer 2 switches depend on routers to pass data between independent IP subnetworks.
