CCNA Security Chapter 4 Exam Answers (CCNAS v1.2 and v1.1)
1. Which statement accurately describes Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall operation?
- The pass action works in only one direction.
- A router interface can belong to multiple zones.
- Service policies are applied in interface configuration mode.
- Router management interfaces must be manually assigned to the self zone.
2. Which location is recommended for extended numbered or extended named ACLs?
- a location as close to the destination of traffic as possible
- a location as close to the source of traffic as possible
- a location centered between traffic destinations and sources to filter as much traffic as possible
- if using the established keyword, a location close to the destination to ensure that return traffic is allowed
3. When using Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall, where is the inspection policy applied?
- a global service policy
- an interface
- a zone
- a zone pair
4. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the SDM screen shown, which statement describes the zone-based firewall component being configured?
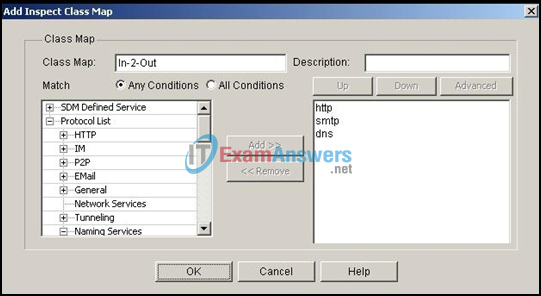
- a class map that inspects all traffic that uses the HTTP, IM, P2P, and email protocols
- a class map that prioritizes traffic that uses HTTP first, followed by SMTP, and then DNS
- a class map that denies all traffic that uses the HTTP, SMTP, and DNS protocols
- a class map that inspects all traffic that uses the HTTP, SMTP, and DNS protocols
- a class map that inspects all traffic, except traffic that uses the HTTP, SMTP, and DNS protocols
5. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the SDM screen shown, which two statements describe the effect this zone-based policy firewall has on traffic? (Choose two.)
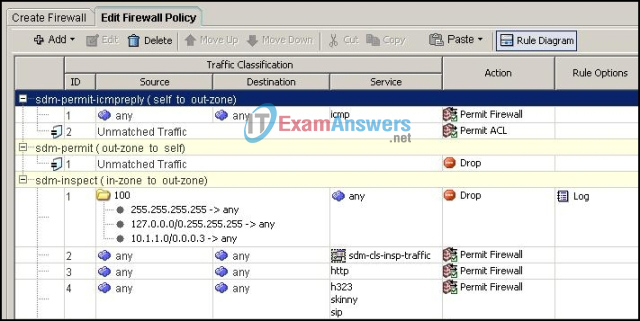
- HTTP traffic from the in-zone to the out-zone is inspected.
- Unmatched traffic to the router from the out-zone is permitted.
- ICMP replies from the router to the out-zone are denied.
- Traffic from the in-zone to the out-zone is denied if the source address is in the 127.0.0.0/8 range.
- Traffic from the in-zone to the out-zone is denied if the destination address is in the 10.1.1.0/29 range.
6. Which type of packet is unable to be filtered by an outbound ACL?
- ICMP packet
- broadcast packet
- multicast packet
- router-generated packet
7. Refer to the exhibit. If a hacker on the outside network sends an IP packet with source address 172.30.1.50, destination address 10.0.0.3, source port 23, and destination port 2447, what does the Cisco IOS firewall do with the packet?
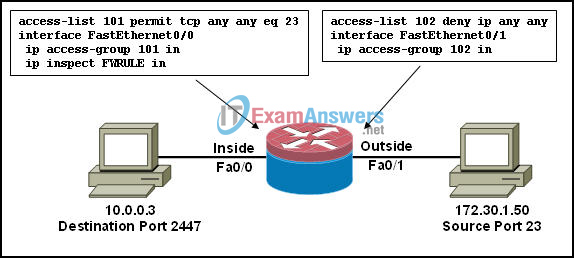
- The packet is forwarded, and an alert is generated.
- The packet is forwarded, and no alert is generated.
- The initial packet is dropped, but subsequent packets are forwarded.
- The packet is dropped.
8. Which zone-based policy firewall zone is system-defined and applies to traffic destined for the router or originating from the router?
- self zone
- system zone
- local zone
- inside zone
- outside zone
9. Which statement correctly describes a type of filtering firewall?
- A transparent firewall is typically implemented on a PC or server with firewall software running on it.
- A packet-filtering firewall expands the number of IP addresses available and hides network addressing design.
- An application gateway firewall (proxy firewall) is typically implemented on a router to filter Layer 3 and Layer 4 information.
- A stateful firewall monitors the state of connections, whether the connection is in an initiation, data transfer, or termination state.
10. In addition to the criteria used by extended ACLs, what conditions are used by CBAC to filter traffic?
- TCP/IP protocol numbers
- IP source and destination addresses
- application layer protocol session information
- TCP/UDP source and destination port numbers
11. Which statement describes the characteristics of packet-filtering and stateful firewalls as they relate to the OSI model?
- Both stateful and packet-filtering firewalls can filter at the application layer.
- A stateful firewall can filter application layer information, while a packet-filtering firewall cannot filter beyond the network layer.
- A packet-filtering firewall typically can filter up to the transport layer, while a stateful firewall can filter up to the session layer.
- A packet-filtering firewall uses session layer information to track the state of a connection, while a stateful firewall uses application layer information to track the state of a connection.
12. Refer to the exhibit. What is represented by the area marked as “A”?
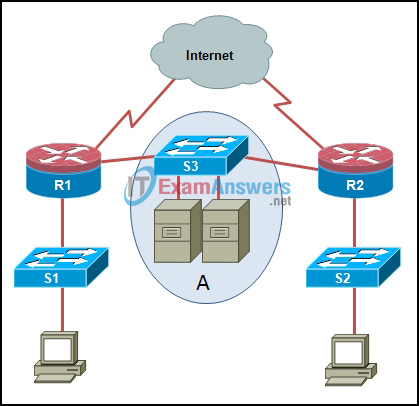
- DMZ
- internal network
- perimeter security boundary
- trusted network
- untrusted network
13. Which three actions can a Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall take if configured with Cisco SDM? (Choose three.)
- inspect
- evaluate
- drop
- analyze
- pass
- forward
14. A router has CBAC configured and an inbound ACL applied to the external interface. Which action does the router take after inbound-to-outbound traffic is inspected and a new entry is created in the state table?
- A dynamic ACL entry is added to the external interface in the inbound direction.
- The internal interface ACL is reconfigured to allow the host IP address access to the Internet.
- The entry remains in the state table after the session is terminated so that it can be reused by the host.
- When traffic returns from its destination, it is reinspected, and a new entry is added to the state table.
15. For a stateful firewall, which information is stored in the stateful session flow table?
- TCP control header and trailer information associated with a particular session
- TCP SYN packets and the associated return ACK packets
- inside private IP address and the translated inside global IP address
- outbound and inbound access rules (ACL entries)
- source and destination IP addresses, and port numbers and sequencing information associated with a particular session
16. Refer to the exhibit. The ACL statement is the only one explicitly configured on the router. Based on this information, which two conclusions can be drawn regarding remote access network connections? (Choose two.)
![]()
- SSH connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are allowed.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are allowed.
- SSH connections from the 192.168.2.0/24 network to the 192.168.1.0/24 network are allowed.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are blocked.
- SSH connections from the 192.168.1.0/24 network to the 192.168.2.0/24 network are blocked.
- Telnet connections from the 192.168.2.0/24 network to the 192.168.1.0/24 network are allowed.
17. When configuring a Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall, which three actions can be applied to a traffic class? (Choose three.)
- drop
- inspect
- pass
- reroute
- queue
- shape
18. Refer to the exhibit. In a two-interface CBAC implementation, where should ACLs be applied?
- inside interface
- outside interface
- inside and outside interfaces
- no interfaces
19. Which two parameters are tracked by CBAC for TCP traffic but not for UDP traffic? (Choose two.)
- source port
- protocol ID
- sequence number
- destination port
- SYN and ACK flags
20. What is the first step in configuring a Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall using the CLI?
- Create zones.
- Define traffic classes.
- Define firewall policies.
- Assign policy maps to zone pairs.
- Assign router interfaces to zones.
21. What are two characteristics of ACLs? (Choose two.)
- Standard ACLs can filter on source and destination IP addresses.
- Standard ACLs can filter on source TCP and UDP ports.
- Standard ACLs can filter on source and destination TCP and UDP ports
- Extended ACLs can filter on source and destination IP addresses.
- Extended ACLs can filter on destination TCP and UDP ports.
22. Which type of packets exiting the network of an organization should be blocked by an ACL?
- packets that are not encrypted
- packets that are not translated with NAT
- packets with source IP addresses outside of the organization’s network address space
- packets with destination IP addresses outside of the organization’s network address space
23. When logging is enabled for an ACL entry, how does the router switch packets filtered by the ACL?
- topology-based switching
- autonomous switching
- process switching
- optimum switching
24. Class maps identify traffic and traffic parameters for policy application based on which three criteria? (Choose three.)
- access group
- access class
- policy map
- protocol
- interface pairs
- subordinate class map
25. What is a limitation of using object groups within an access control entry?
- It is not possible to append additional objects to a preexisting object group.
- It is not possible to delete an object group or make an object group empty if the object group is already applied to an ACE.
- To append additional objects to a preexisting object group that is applied to an ACE, the original object group must be removed using the no object group command, and then recreated and reapplied to the ACE.
- To append additional objects to a preexisting object group that is applied to an ACE, the access control list must be removed using the no access-list command, and then reapplied.
26. When using CCP to apply an ACL, the administrator received an informational message indicating that a rule was already associated with the designated interface in the designated direction. The administrator continued with the association by selecting the merge option. Which statement describes the effect of the option that was selected?
- Two separate access rules were applied to the interface.
- A new combined access rule was created using the new access rule number. Duplicate ACEs were removed.
- A new combined access rule was created using the new access rule number. Duplicate ACEs and overriding ACEs were highlighted to allow the administrator to make adjustments
- The existing rule was placed in a preview pane to allow the administrator to select specific ACEs to move to the new access rule.
27. Which statement correctly describes how an ACL can be used with the access-class command to filter vty access to a router?
- It is only possible to apply a standard ACL to the vty lines.
- An extended ACL can be used to restrict vty access based on specific source addresses, destination addresses, and protocol.
- An extended ACL can be used to restrict vty access based on specific source and destination addresses but not on protocol.
- An extended ACL can be used to restrict vty access based on specific source addresses and protocol but the destination can only specify the keyword any.
28. To facilitate the troubleshooting process, which inbound ICMP message should be permitted on an outside interface?
- echo request
- echo reply
- time-stamp request
- time-stamp reply
- router advertisement
29. Which command is used to activate an IPv6 ACL named ENG_ACL on an interface so that the router filters traffic prior to accessing the routing table?
- access-group ipv6_ENG_ACL in
- access-group ipv6_ENG_ACL out
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL in
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL out
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL in
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL out
30. Which statement describes a typical security policy for a DMZ firewall configuration?
- Traffic that originates from the outside interface is permitted to traverse the firewall to the inside interface with little or no restrictions.
- Traffic that originates from the DMZ interface is permitted to traverse the firewall to the outside interface with little or no restrictions.
- Traffic that originates from the DMZ interface is selectively permitted to the outside interface. (Similar Question warning! Use this answer if this answer available. Otherwise use the other one)
- Traffic that originates from the inside interface is generally blocked entirely or very selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Return traffic from the outside that is associated with traffic originating from the inside is permitted to traverse from the outside interface to the DMZ interface.
- Return traffic from the inside that is associated with traffic originating from the outside is permitted to traverse from the inside interface to the outside interface.
31. When configuring a Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall, which two actions can be applied to a traffic class? (Choose two.)
- log
- hold
- drop
- inspect
- copy
- forward
32. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the function of the ACEs?

- These ACEs allow for IPv6 neighbor discovery traffic.
- These ACEs must be manually added to the end of every IPv6 ACL to allow IPv6 routing to occur.
- These ACEs automatically appear at the end of every IPv6 ACL to allow IPv6 routing to occur.
- These are optional ACEs that can be added to the end of an IPv6 ACL to allow ICMP messages that are defined in object groups named nd-na and nd-ns.
33. When implementing an inbound Internet traffic ACL, what should be included to prevent the spoofing of internal networks?
- ACEs to prevent HTTP traffic
- ACEs to prevent ICMP traffic
- ACEs to prevent SNMP traffic
- ACEs to prevent broadcast address traffic
- ACEs to prevent traffic from private address spaces
34. Which statement describes one of the rules governing interface behavior in the context of implementing a zone-based policy firewall configuration?
- An administrator can assign an interface to multiple security zones.
- An administrator can assign interfaces to zones, regardless of whether the zone has been configured.
- By default, traffic is allowed to flow among interfaces that are members of the same zone.
- By default, traffic is allowed to flow between a zone member interface and any interface that is not a zone member.
35. Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the effect of this Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall configuration?
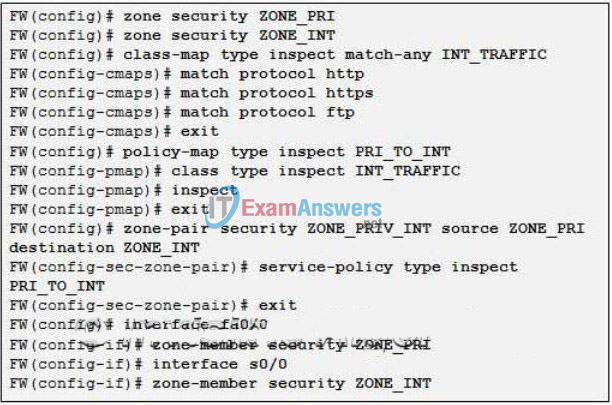
- The firewall will automatically drop all HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP traffic.
- The firewall will automatically allow HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP traffic from s0/0 to fa0/0 and will track the connections. Tracking the connection allows only return traffic to be permitted through the firewall in the opposite direction.
- The firewall will automatically allow HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP traffic from fa0/0 to s0/0 and will track the connections. Tracking the connection allows only return traffic to be permitted through the firewall in the opposite direction.
- The firewall will automatically allow HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP traffic from fa0/0 to s0/0, but will not track the state of connections. A corresponding policy must be applied to allow return traffic to be permitted through the firewall in the opposite direction.
- The firewall will automatically allow HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP traffic from s0/0 to fa0/0, but will not track the state of connections. A corresponding policy must be applied to allow return traffic to be permitted through the firewall in the opposite direction.
36. In addition to the criteria used by extended ACLs, what conditions are used by a classic firewall to filter traffic?
- TCP/UPD source and destination port numbers
- TCP/IP protocol numbers
- IP source and destination addresses
- Application layer protocol session information
37. Refer to the exhibit. Which Cisco IOS security feature is implemented on router FW?
- classic firewall
- reflexive ACL firewall
- zone-based policy firewall
- AAA access control firewall
38. Which three statements describe zone-based policy firewall rules that govern interface behavior and the traffic moving between zone member interfaces? (Choose three.)
- An interface can be assigned to multiple security zones.
- Interfaces can be assigned to a zone before the zone is created.
- Pass, inspect, and drop options can only be applied between two zones.
- If traffic is to flow between all interfaces in a router, each interface must be a member of a zone.
- Traffic is implicitly prevented from flowing by default among interfaces that are members of the same zone.
- To permit traffic to and from a zone member interface, a policy allowing or inspecting traffic must be configured between that zone and any other zone.
39. Which two parameters are tracked by a classic firewall for TCP traffic but not for UDP traffic? (Choose two.)
- destination port
- sequence number
- source port
- protocol ID
- SYN and ACK flags
