CCNA Security Chapter 7 Exam Answers (CCNAS v1.2 and v1.1)
1. Which symmetrical encryption algorithm is the most difficult to crack?
2. What is the basic method used by 3DES to encrypt plaintext?
- The data is encrypted three times with three different keys.
- The data is encrypted, decrypted, and encrypted using three different keys.
- The data is divided into three blocks of equal length for encryption.
- The data is encrypted using a key length that is three times longer than the key used for DES.
3. What does it mean when a hashing algorithm is collision resistant?
- Exclusive ORs are performed on input data and produce a digest.
- It is not feasible to compute the hash given the input data.
- It uses a two-way function that computes a hash from the input and output data.
- Two messages with the same hash are unlikely to occur.
4. Which three primary functions are required to secure communication across network links? (Choose three.)
- accounting
- anti-replay protection
- authentication
- authorization
- confidentiality
- integrity
5. Which two encryption algorithms are commonly used to encrypt the contents of a message? (Choose two.)
6. Which statement describes asymmetric encryption algorithms?
- They include DES, 3DES, and AES.
- They have key lengths ranging from 80 to 256 bits.
- They are also called shared-secret key algorithms.
- They are relatively slow because they are based on difficult computational algorithms.
Explanation: DES, 3DES, and AES are examples of symmetric encryption algorithms (also known as shared secret key algorithms). The usual key length for symmetric algorithms is 80-256 bits. Asymmetric algorithms are relatively slow because they are based on difficult computational algorithms.
7. Which statement describes the use of keys for encryption?
- The sender and receiver must use the same key when using symmetric encryption.
- The sender and receiver must use the same key when using asymmetric encryption.
- The sender and receiver must use the same keys for both symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
- The sender and receiver must use two keys: one for symmetric encryption and another for asymmetric encryption.
8. How do modern cryptographers defend against brute-force attacks?
- Use statistical analysis to eliminate the most common encryption keys.
- Use an algorithm that requires the attacker to have both ciphertext and plaintext to conduct a successful attack.
- Use a keyspace large enough that it takes too much money and too much time to conduct a successful attack.
- Use frequency analysis to ensure that the most popular letters used in the language are not used in the cipher message.
Explanation: In a brute-force attack, an attacker tries every possible key with the decryption algorithm knowing that eventually one of them will work. To defend against the brute-force attacks, modern cryptographers have as an objective to have a keyspace (a set of all possible keys) large enough so that it takes too much money and too much time to accomplish a brute-force attack. A security policy requiring passwords to be changed in a predefined interval further defend against the brute-force attacks. The idea is that passwords will have been changed before an attacker exhausts the keyspace.
9. Refer to the exhibit. Which type of cipher method is depicted?
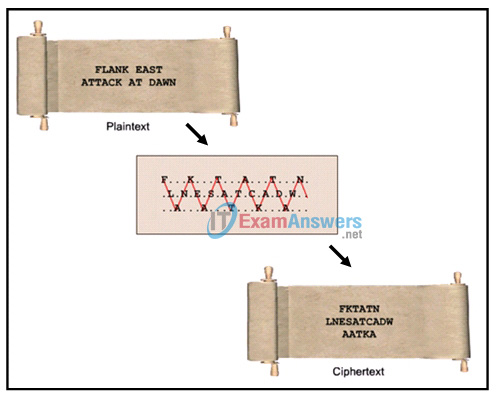
- Caesar cipher
- stream cipher
- substitution cipher
- transposition cipher
Explanation: There are many cipher methods developed for message encryptions. In transposition ciphers, no letters are replaced; they are simply rearranged. An example of this type of cipher is known as the rail fence cipher. In this transposition, the words are spelled out as if they were a rail fence, meaning some are in front and some in back across several parallel lines.
10. Which statement describes a cryptographic hash function?
- A one-way cryptographic hash function is hard to invert.
- The output of a cryptographic hash function can be any length.
- The input of a cryptographic hash function has a fixed length.
- A cryptographic hash function is used to provide confidentiality.
11. A customer purchases an item from an e-commerce site. The e-commerce site must maintain proof that the data exchange took place between the site and the customer. Which feature of digital signatures is required?
- authenticity of digitally signed data
- integrity of digitally signed data
- nonrepudiation of the transaction
- confidentiality of the public key
Explanation: Digital signatures provide three basic security services:
Authenticity of digitally signed data – Digital signatures authenticate a source, proving that a certain party has seen and signed the data in question.
Integrity of digitally signed data – Digital signatures guarantee that the data has not changed from the time it was signed.
Nonrepudiation of the transaction – The recipient can take the data to a third party, and the third party accepts the digital signature as a proof that this data exchange did take place. The signing party cannot repudiate that it has signed the data.
12. Which encryption protocol provides network layer confidentiality?
- IPsec protocol suite
- Keyed MD5
- Message Digest 5
- Secure Sockets Layer
- Secure Hash Algorithm 1
- Transport Layer Security
Explanation: Cryptographic encryption can provide confidentiality at several layers of the OSI model. For example, network layer protocols, such as the IPsec protocol suite, provide network layer confidentiality. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS), provide session layer confidentiality. MD5, Keyed MD5, and Secure Hash Algorithm 1 are examples of hash functions. They provide data integrity but not data confidentiality.
13. Which statement is a feature of HMAC?
- HMAC is based on the RSA hash function.
- HMAC uses a secret key that is only known to the sender and defeats man-in-the-middle attacks.
- HMAC uses a secret key as input to the hash function, adding authentication to integrity assurance.
- HMAC uses protocols such as SSL or TLS to provide session layer confidentiality.
Explanation: A keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC or KHMAC) is a type of message authentication code (MAC). HMACs use an additional secret key as input to the hash function, adding authentication to data integrity assurance.
14. The network administrator for an e-commerce website requires a service that prevents customers from claiming that legitimate orders are fake. What service provides this type of guarantee?
- authentication
- confidentiality
- integrity
- nonrepudiation
15. What is a characteristic of the RSA algorithm?
- RSA is much faster than DES.
- RSA is a common symmetric algorithm.
- RSA is used to protect corporate data in high-throughput, low-latency environments.
- RSA keys of 512 bits can be used for faster processing, while keys of 2048 bits can be used for increased securit
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which encryption algorithm is described in the exhibit?
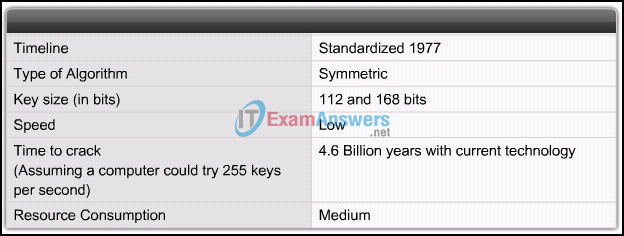
Explanation: 3DES is a good choice to protect data because it has an algorithm that is very trusted and has security strength.
17. An administrator requires a PKI that supports a longer lifetime for keys used for digital signing operations than for keys used for encrypting data. Which feature should the PKI support?
- certificate keys
- nonrepudiation keys
- usage keys
- variable keys
18. Which two statements correctly describe certificate classes used in the PKI? (Choose two.)
- A class 0 certificate is for testing purposes.
- A class 0 certificate is more trusted than a class 1 certificate.
- The lower the class number, the more trusted the certificate.
- A class 5 certificate is for users with a focus on verification of email.
- A class 4 certificate is for online business transactions between companies.
Explanation: A digital certificate class is identified by a number. The higher the number, the more trusted the certificate. The classes include the following:
Class 0 is for testing purposes in which no checks have been performed.
Class 1 is for individuals with a focus on verification of email.
Class 2 is for organizations for which proof of identity is required.
Class 3 is for servers and software signing for which independent verification and checking of identity and authority is done by the issuing certificate authority.
Class 4 is for online business transactions between companies.
Class 5 is for private organizations or governmental security.
19. Two users must authenticate each other using digital certificates and a CA. Which option describes the CA authentication procedure?
- The CA is always required, even after user verification is complete.
- The users must obtain the certificate of the CA and then their own certificate.
- After user verification is complete, the CA is no longer required, even if one of the involved certificates expires.
- CA certificates are retrieved out-of-band using the PSTN, and the authentication is done in-band over a network.
Explanation: When two users must authenticate each other using digital certificates and CA, both users must obtain their own digital certificate from a CA. They submit a certificate request to a CA, and the CA will perform a technical verification by calling the end user (out-of-band). Once the request is approved, the end user retrieves the certificate over the network (in-band) and installs the certificate on the system. After both users have installed their certificate, they can perform authentication by sending their certificate to each other. Each site will use the public key of the CA to verify the validity of the certificate; no CA is involved at this point. If both certificates are verified, both users can now authenticate each other.
20. Why is RSA typically used to protect only small amounts of data?
- The keys must be a fixed length.
- The public keys must be kept secret.
- The algorithms used to encrypt data are slow.
- The signature keys must be changed frequently.
21. Which algorithm would provide the best integrity check for data that is sent over the Internet?
22. Which characteristic of security key management is responsible for making certain that weak cryptographic keys are not used?
- verification
- exchange
- generation
- revocation and destruction
Explanation:
To make a key strong, there are several essential characteristics of key management that should be considered:
- Generation – The use of good random number generators is needed to ensure that all keys are likely to be equally generated so that the attacker cannot predict which keys are more likely to be used.
- Verification – Almost all cryptographic algorithms have some weak keys that should not be used. With the help of key verification procedures, these keys can be regenerated if they occur.
- Exchange – Key management procedures should provide a secure key exchange mechanism that allows secure agreement on the keying material with the other party, probably over an untrusted medium.
- Revocation and Destruction – Revocation notifies all interested parties that a certain key has been compromised and should no longer be used. Destruction erases old keys in a manner that prevents malicious attackers from recovering them.
23. Which type of cryptographic key would be used when connecting to a secure website?
- DES key
- symmetric keys
- hash keys
- digital signatures
Explanation: Typical usage of cryptographic keys includes the following:
- Symmetric keys, which can be exchanged between two routers supporting a VPN.
- Digital signatures, which are used when connecting to a secure website.
- Hash keys, which are used in symmetric and asymmetric key generation, digital signatures, and other types of applications.
24. Which algorithm is used to automatically generate a shared secret for two systems to use in establishing an IPsec VPN?
Explanation: The Diffie-Helman (DH) algorithm is the basis of most modern automatic key exchange methods. It is a mathematical algorithm that allows two computers to generate an identical shared secret on both systems without having communicated before. DH is commonly used when data is exchanged using an IPsec VPN.
25. Which two non-secret numbers are initially agreed upon when the Diffie-Hellman algorithm is used? (Choose two.)
- elliptic curve invariant
- generator
- pseudorandom nome
- binomial coefficient
- prime modulus
- topological index
Explanation: DH is a mathematical algorithm that allows two hosts to generate an identical shared secret on both systems without having communicated before. To start a DH exchange, both hosts must agree on two nonsecret numbers. The first number is a base number, also called the generator. The second number is a prime number that is used as the modulus. These numbers are usually public and are chosen from a table of known values.
26. What are two properties of a cryptographic hash function? (Choose two.)
- The input for a particular hash algorithm has to have a fixed size.
- Complex inputs will produce complex hashes.
- The hash function is one way and irreversible.
- The output is a fixed length
- Hash functions can be duplicated for authentication purposes.
Explanation: A cryptographic hash function should have the following properties:The input can be any length.
The output has a fixed length.
The hash value is relatively easy to compute for any given input.
The hash is one way and not reversible.
The hash is collision free, meaning that two different input values will result in different hash values
27. Which cryptographic technique provides both data integrity and nonrepudiation?
Explanation: A Keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC and KHMAC) is a type of message authentication code that uses an additional secret key as input to the hash function. This adds authentication to integrity assurance. When two parties share a secret key and use HMAC functions for authentication, the received HMAC digest of a message indicates that the other party was the originator of the message (non-repudiation), because it is the only other entity possessing the secret key. 3DES is an encryption algorithm, and MD5 and SHA-1 are hashing algorithms.
28. Why is the 3DES algorithm often preferred over the AES algorithm?
- AES is more expensive to implement than 3DES.
- 3DES performs better in high-throughput, low-latency environments than AES.
- 3DES is more trusted because it has been proven secure for a longer period than AES.
- Major networking equipment vendors such as Cisco have not yet adopted AES.
Explanation: Despite its advantages, AES is a relatively young algorithm. An important rule of cryptography is that a mature algorithm is always more trusted. 3DES is therefore a more trusted choice in terms of strength, because it has been tested and analyzed for 35 years. AES can be used in high-throughput, low-latency environments, especially when 3DES cannot handle the throughput or latency requirements. AES is available in a number of Cisco VPN devices as an encryption transform.
29. In which situation is an asymmetric key algorithm used?
- An office manager encrypts confidential files before saving them to a removable device.
- User data is transmitted across the network after a VPN is established.
- A network administrator connects to a Cisco router with SSH.
- Two Cisco routers authenticate each other with CHAP.
Explanation: The SSH protocol uses an asymmetric key algorithm to authenticate users and encrypt data transmitted. The SSH server generates a pair of public/private keys for the connections. Encrypting files before saving them to a storage device uses a symmetric key algorithm because the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt files. The router authentication with CHAP uses a symmetric key algorithm. The key is pre-configured by the network administrator. A VPN may use both an asymmetric key and a symmetric encryption algorithm. For example in an IPSec VPN implementation, the data transmission uses a shared secret (generated with an asymmetric key algorithm) with a symmetric encryption algorithm used for performance.
30. What is the purpose of a nonrepudiation service in secure communications?
- to confirm the identity of the recipient of the communications
- to ensure that the source of the communications is confirmed
- to provide the highest encryption level possible
- to ensure that encrypted secure communications cannot be decoded
Explanation: Nonrepudiation uses the unique characteristics of the sender of a message to confirm that the reputed sender is in fact the actual sender.
31. In a hierarchical CA topology, where can a subordinate CA obtain a certificate for itself?
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at a higher level
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA anywhere in the tree
- from the root CA only
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at the same level
- from the root CA or from self-generation
Explanation: In a hierarchical CA topology, CAs can issue certificates to end users and to subordinate CAs, which in turn issue their certificates to end users, other lower level CAs, or both. In this way, a tree of CAs and end users is built in which every CA can issue certificates to lower level CAs and end users. Only the root CA can issue a self-signing certificate in a hierarchical CA topology.
32. Which encryption algorithm is an asymmetric algorithm?
Explanation: DH is an asymmetric algorithm. AES, 3DES, and SEAL are all symmetric algorithms.
33. How many bits does the Data Encryption Standard (DES) use for data encryption?
- 40 bits
- 56 bits
- 64 bits
- 72 bits
Explanation: DES uses a fixed length key. The key is 64-bits long, but only 56 bits are used for encryption. The remaining 8 bits are used for parity. A DES encryption key is always 56 bits long. When DES is used with a weaker encryption of a 40-bit key, the encryption key is 40 secret bits and 16 known bits, which make the key length 56 bits.
34. What feature of the AES encryption algorithm makes it more desirable to use than 3DES?
- It runs faster and more efficiently.
- AES uses the block cipher.
- It is a symmetric algorithm.
- It uses a longer key.
35. Which statement describes the Software-Optimized Encryption Algorithm (SEAL)?
- It requires more CPU resources than software-based AES does.
- It is an example of an asymmetric algorithm.
- It uses a 112-bit encryption key.
- SEAL is a stream cipher.
Explanation: SEAL is a stream cipher that uses a 160-bit encryption key. It is a symmetric encryption algorithm that has a lower impact on the CPU resources compared to other software-based algorithms, such as software-based DES, 3DES, and AES.
36. What is the most common use of the Diffie-Helman algorithm in communications security?
- to create password hashes for secure authentication
- to encrypt data for secure e-commerce communications
- to secure the exchange of keys used to encrypt data
- to provide routing protocol authentication between routers
Explanation: Diffie-Helman is not an encryption mechanism and is not typically used to encrypt data. Instead, it is a method to securely exchange the keys used to encrypt the data.
37. Which type of encryption algorithm uses public and private keys to provide authentication, integrity, and confidentiality?
- symmetric
- IPsec
- asymmetric
- shared secret
Explanation: An asymmetric encryption algorithm uses two keys, namely a public key and a private key. A symmetric encryption algorithm uses an identical key for both encryption and decryption. A shared secret is an example of using symmetric algorithm.
38. An online retailer needs a service to support the nonrepudiation of the transaction. Which component is used for this service?
- the unique shared secret known only by the retailer and the customer
- the public key of the retailer
- the private key of the retailer
- the digital signatures
Explanation: Digital signatures, generated by hash function, can provide the service for nonrepudiation of the transaction. Both public and private keys are used to encrypt data during the transaction. Shared secrets between the retailer and customers are not used.


