13. Which table is used by EIGRP to store all routes that are learned from EIGRP neighbors?
- the routing table
- the neighbor table
- the topology table
- the adjacency table
14. Which multicast address does an EIGRP-enabled router use to send query packets?
- 224.0.0.10
- 224.0.0.9
- 224.0.0.12
- 224.0.0.5
15. Which three metric weights are set to zero by default when costs in EIGRP are being calculated? (Choose three.)
- k1
- k2
- k3
- k4
- k5
- k6
16. Where should EIGRP summarization be applied?
- on the router interface that connects to the internet
- on the area border router
- on any interface where end-user devices attach
- on any router interface participating in the EIGRP process
17. When are EIGRP update packets sent?
- only when necessary
- when learned routes age out
- every 5 seconds via multicast
- every 30 seconds via broadcast
18. How is bandwidth to a destination network calculated by EIGRP?
- the lowest configured bandwidth of any interface along the route
- the sum of the configured bandwidths of all interfaces along the path
- the highest configured bandwidth of any interface along the path
- the bandwidth of the ingress interface of the last hop router
19. Refer to the exhibit. What does the value 2816 represent in the output display?
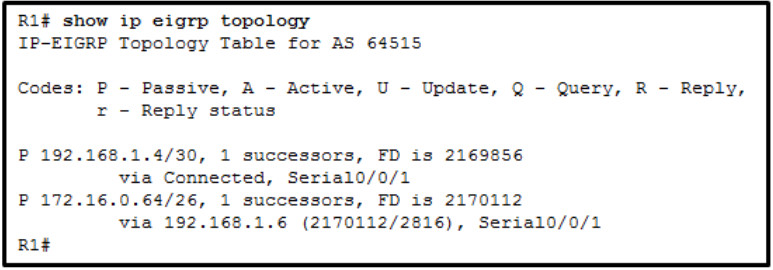
- feasible distance
- shortest distance
- reported distance
- administrative distance
20. Which algorithm does the EIGRP routing protocol use?
- Bellman-Ford
- RSA
- Dijkstra
- DUAL
21. Which two factors does an EIGRP router use to determine that a route to a remote network meets the feasible condition and is therefore loop-free? (Choose two.)
- the successor route on a neighbor router
- the feasible successor route on the remote router
- the reported distance on a neighbor router
- the administrative distance on the remote router
- the feasible distance on the local router
22. When will a router that is running EIGRP put a destination network in the active state?
- when the EIGRP domain is converged
- when there is outgoing traffic toward the destination network
- when there is an EIGRP message from the successor of the destination network
- when the connection to the successor of the destination network fails and there is no feasible successor available
23. Refer to the exhibit. R2 has two possible paths to the 192.168.10.4 network. What would make the alternate route meet the feasibility condition?
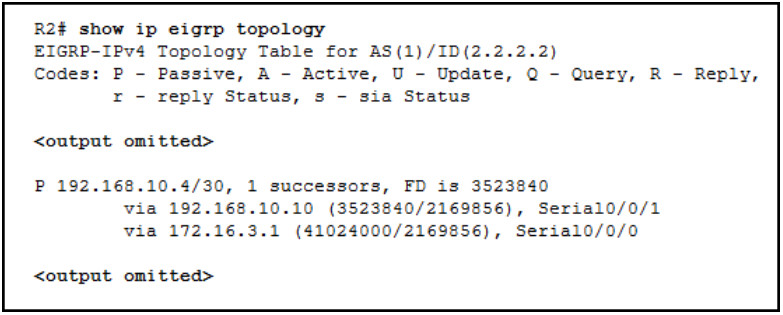
- a reported distance less than 3523840
- a reported distance greater than 41024000
- a feasible distance greater than 41024000
- an administrative distance less than 170
24. What is a characteristic of manual route summarization?
- requires high bandwidth utilization for the routing updates
- reduces total number of routes in routing tables
- cannot include supernet routes
- has to be configured globally on the router
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. EIGRP uses the protocol number _______ to identify its packets.
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
2. EIGRP uses _______ packet types for inter-router communication.
- three
- four
- five
- six
- seven
3. What is an EIGRP successor?
- The next-hop router for the path with the lowest path metric for a destination prefix
- The path with the lowest metric for a destination prefix
- The router selected to maintain the EIGRP adjacencies for a broadcast network
- A route that satisfies the feasibility condition where the reported distance is less than the feasible distance
4. Which of the following attributes does the EIGRP topology table contain? (Choose all that apply.)
- destination network prefix
- hop count
- total path delay
- maximum path bandwidth
- list of EIGRP neighbors
5. Which of the following destination addresses does EIGRP use when feasible? (Choose two.)
- IP address 224.0.0.9
- IP address 224.0.0.10
- IP address 224.0.0.8
- MAC address 01:00:5E:00:00:0A
- MAC address 0C:15:C0:00:00:01
6. Which value can be modified on a router to manipulate the path taken by EIGRP but avoid having impacts on other routing protocols, such as OSPF?
- interface bandwidth
- interface MTU
- interface delay
- interface priority
7. EIGRP uses a reference bandwidth of ________ with the default metrics.
- 100 Mbps
- 1 Gbps
- 10 Gbps
- 40 Gbps
8. The default EIGRP hello timer for a high-speed interfaces is ______.
- 1 second
- 5 seconds
- 10 seconds
- 20 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 60 seconds
9. When a path has been identified using EIGRP and in a stable fashion, the route is considered ______.
- passive
- dead
- active
- alive
10. How does an EIGRP router indicate that a path computation is required for a specific route?
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with the topology change notification flag set.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP update packet with a metric value of zero.
- EIGRP sends out an EIGRP query with the delay set to infinity.
- EIGRP sends a route withdrawal, notifying other neighbors to remove the route from the topology table.
11. True or false: EIGRP summarization occurs for network prefixes as it crosses all network interfaces.
- True
- False
