1.3.2 Packet Tracer – Directly Connected Routes Answers
Topology
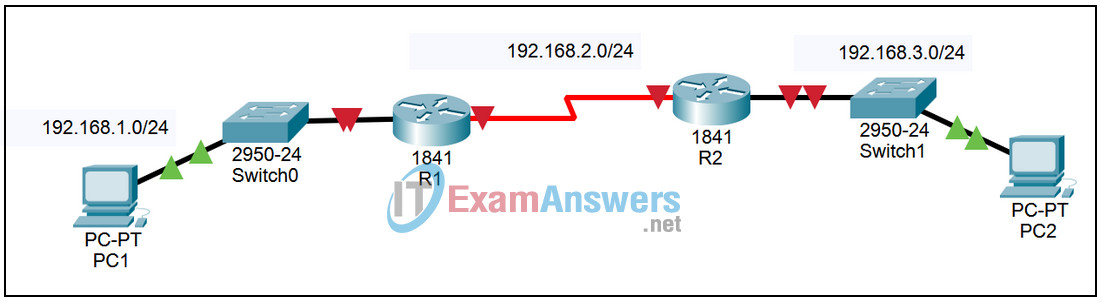
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 192.168.3.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 |
Introduction
This activity focuses on the routing table and how it is built. A router builds routing tables by first adding the networks for the IP addresses configured on each of the active interfaces for the router. (These networks are the directly connected networks for the router.) The focus of this activity is two routers, R1 and R2, and the networks supported through the configuration of the router interfaces. Initially, all interfaces have been configured with correct addressing but the interfaces are shutdown.
Learning Objectives:
- Describe the function of the routing table.
- Describe how a router manages directly connected routes in the routing table.
Task 1: Enable the Interfaces on Each Router.
All of the interfaces on the routers have been shutdown. With the interfaces down, no routing table exists for each router. Follow the steps below to view the addition of routes to the routing table:
Step 1 – Enable the FastEthernet interface on R1.
1. Click R1 in the logical workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI (command line interface) type the following commands:
Password:cisco R1>enable Password: class R1# show ip route
(Note: The routing table is completely empty of any routes.)
4. Activate the interface FastEthernet:
R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# end
Step 2 – Examine the routing table on R1.
1. From the CLI type the following commands:
R1# show ip route
2. Are there any routes in the routing table? If so, list the route(s) below:
_____________________________________________________
3. If there are no routes in the routing table, retrace your steps and troubleshoot the problem.
Step 3 – Enable the Serial interface on R1.
1. Click R1 in the logical workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
R1# configure terminal R1(config)# interface Serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# end
Step 4 – Repeat steps 1 through 3 on R2.
1. How many routes are in the routing table for R1?
2. How many routes are in the routing table for R2?
(Note: There should be two routes in the routing tables on each router.)
3. Now shut down the FastEthernet interface on R1.
4. How many routes are shown in the routing table for R1 now?
_____________________________________________________
5. Did the number of routes in R2 change? Explain: _____________________________________________________
6. Enter global configuration and use the no shutdown command to bring the FastEthernet 0/0 interface back up.
Task 2: Verify connectivity using ping
1. PC1 should be able to ping each interface on R1.
2. PC2 should be able to ping each interface on R2.
3. Can the PCs successfully ping each other? Explain.
_____________________________________________________
