Sections & Objectives
2.1 Safe Lab procedures
- Explain the purpose of safe working conditions and safe lab procedures.
2.2 Proper Use of Tools
- Explain how to use tools and software with personal computer components.
2.1 Safe Lab Procedures
2.2.1 Procedures to Protect People
General Safety
- Make sure a first-aid kit is available.
- Unsecured cables create tripping hazards.
- Food and drinks should not be in the workspace.
- Remove jewelry.
Electrical Safety
- Computer power supplies are dangerous when disassembled.
- Watch for printer areas that are hot or that use high voltage.
- Check the voltage output of AC adapters and chargers before connecting them to devices.
Fire Safety
- Turn off the power and unplug equipment before performing service.
- Different types of fires require different types of fire extinguishers; make sure to use to correct one.
- Be alert for odors emitting from computers and electronic devices.
2.1.2 Procedures to Protect Equipment and Data
ESD and EMI
- ESD can cause damage to computer equipment if not discharged properly.
- ESD can build up on you as you walk on a carpeted floor.
- EMI distorts the signals, degrading computer communication.
- EMI can be generated by large motors, power lines, electrical storms, or any other source of electromagnetic energy.
- Wireless networks are affected by RFI.
- RFI is caused by radio transmitters transmitting in the same frequency.

Environmental temperature and humidity levels also affect computers.
Power Fluctuation Types
- Power fluctuations may impact the operation of computer components.
- Blackouts, brownouts, noise, spike and power surge are types of power fluctuations that can cause data loss or hardware failure.
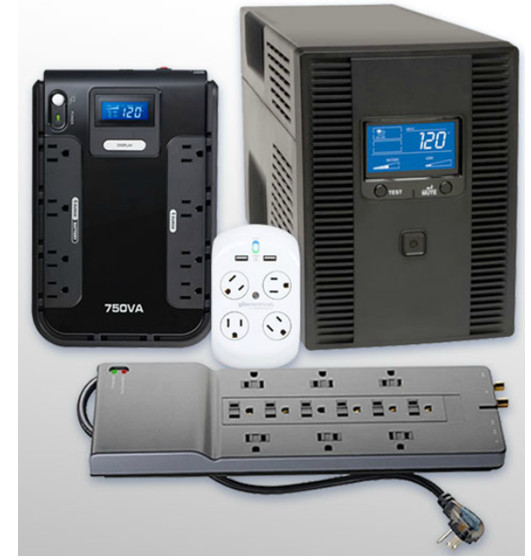

Power Protection Devices
- Surge suppressors, UPSs, SPSs are devices designed to protect computer systems from power fluctuations.
- Laser printers should not be plugged to UPSs
2.2.3 Procedures to Protect the Environment

Safety Data Sheet
- Use an SDS to obtain information about a material, including procedures for proper disposal.
- The SDS contains information on the material’s composition, how it can affect personal health, fire hazards, and first-aid requirements.
- It also includes protective measures for the safe handling and storage of materials and spill, leak, and disposal procedures.
Equipment Disposal
- Computer equipment contains hazardous materials and should be properly disposed.
- Follow regulations to protect the environment and avoid fines.
- Batteries, monitors, toner kits, cartridges, developers, chemical solvents and aerosol cans are examples of equipment that must be properly disposed.
2.2 Proper Use of Tools
2.2.1 Hardware Tools
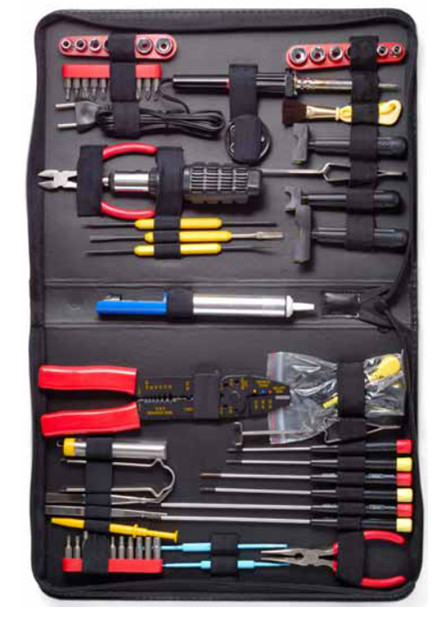

Hardware tools are grouped into:
ESD Tools
- Antistatic wrist strap and antistatic mat
Hand Tools
- Include screwdrivers, flashlights and pliers.
Cable Tools
- Include wire cutters and strippers, crimpers and punch down tool.
Cleaning Tools
- Include special cloths, chemicals and cable ties.
Diagnostic Tools
- Include digital multimeters, loopback adapters, WiFi analyzer, external HDD enclosure
2.2.2 Software Tools
Like hardware tools, software tools are task-specific.
Used to diagnose problems, maintain hardware, and protect the data stored on a computer.
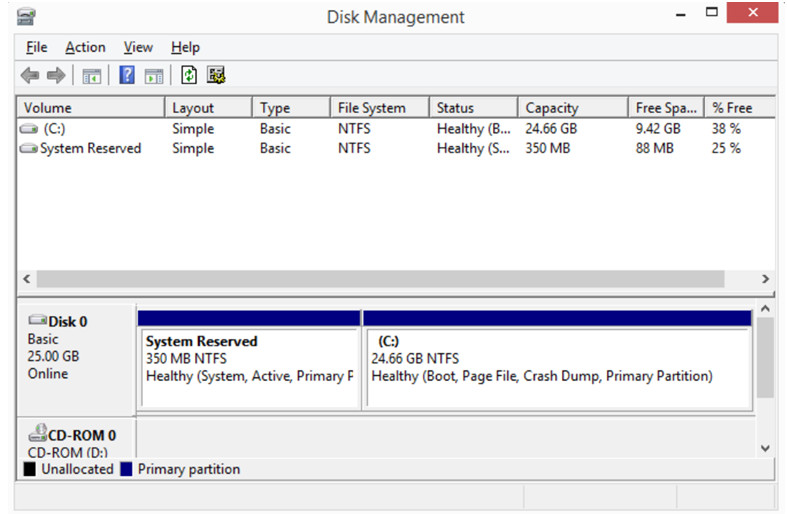
Disk Management Tools
- Used for disk management, formatting, error checking, drive optimization, disk cleanup and more.
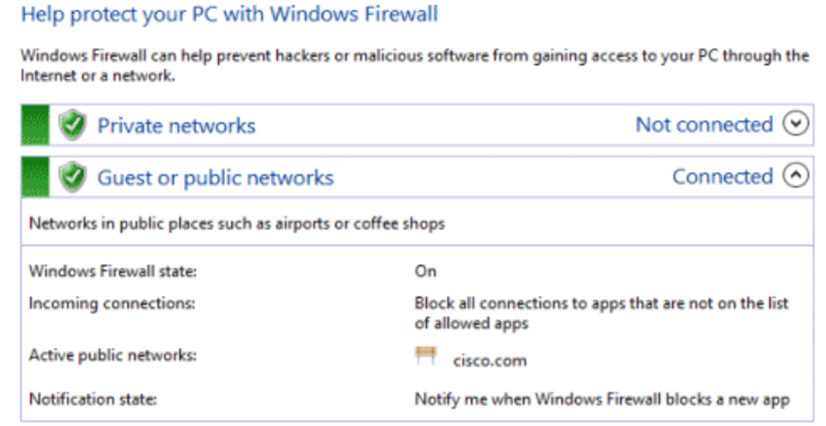
Protection Software Tools
- Malicious software can damage or compromise operating systems, applications, and data.
- Software protection tools include antivirus, antispyware, firewalls and update manager software.
2.2.3 Organizational Tools
It is important that a technician document all services and repairs for future reference.

Personal Reference Tools
- Include troubleshooting guides, manufacturer manuals, quick reference guides, and repair journals.
- History of repairs and a notepad can be extremely useful as a technician performs troubleshooting and repairs.
- The Internet can be a great reference tool by providing access to specialized forums, search engines, manufacturer’s FAQs, and more.
Miscellaneous Tools
- Additional secondary items can be added to the toolkit.
- Masking tape, a working computer and even pencil eraser can be very useful additions to a technician’s kit.
2.3 Chapter Summary
- This chapter discussed safe lab procedures, correct tool usage, and the proper disposal of computer components and supplies.
- Work in a safe manner to protect users and equipment.
- Follow all safety guidelines to prevent injuries to yourself and others.
- Know how to protect equipment from ESD damage.
- Know about and be able to prevent power issues that can cause equipment damage or data loss.
- Know which products and supplies require special disposal procedures.
- Familiarize yourself with the SDS for safety issues and disposal restrictions to help protect the environment.
- Be able to use the correct tools for the task.
- Know how to clean components safely.
- Use organizational tools during computer repairs.
