6.4.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting a VLSM Addressing Design Answers
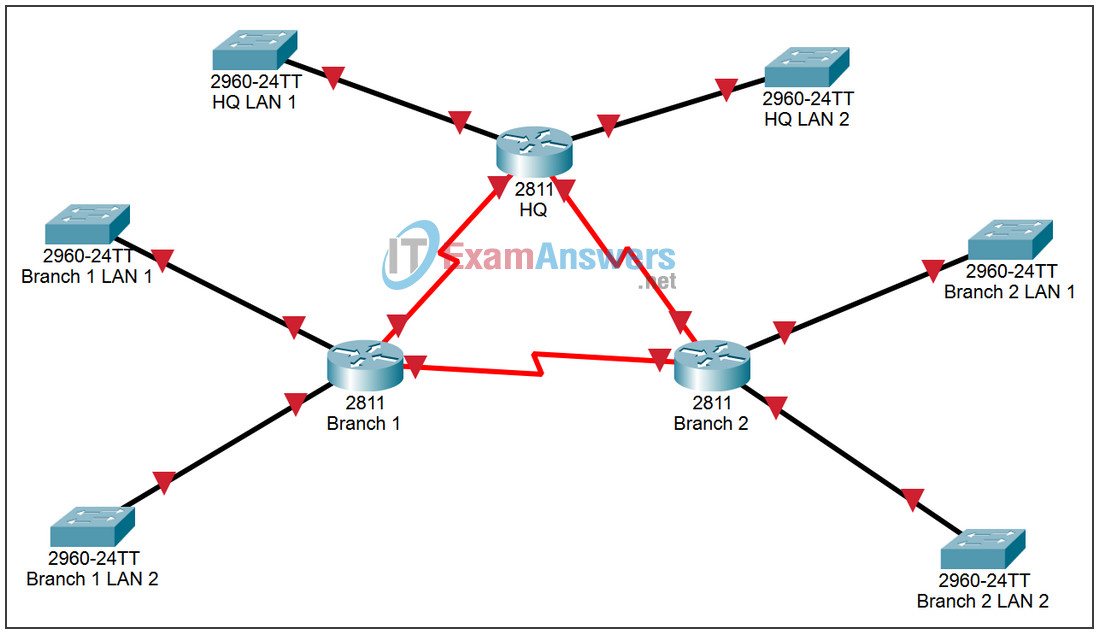
Topology
| Subnet | Number of IP Addresses Needed | Network Address |
|---|---|---|
| HQ LAN1 | 16,000 | 172.16.128.0/19 |
| HQ LAN2 | 8,000 | 172.16.192.0/18 |
| Branch1 LAN1 | 4,000 | 172.16.224.0/20 |
| Branch1 LAN2 | 2,000 | 172.16.240.0/21 |
| Branch2 LAN1 | 1,000 | 172.16.244.0/24 |
| Branch2 LAN2 | 500 | 172.16.252.0/23 |
| Link from HQ to Branch1 | 2 | 172.16.254.0/28 |
| Link from HQ to Branch2 | 2 | 172.16.154.6/30 |
| Link from Branch1 to Branch2 | 2 | 172.16.254.8/30 |
Learning Objectives:
Upon completion of this activity, you will be able to:
- Discover errors in a VLSM design.
- Propose solutions for VLSM design errors.
- Document the corrected VLSM assignments.
Scenario
In this activity, the network address 172.16.128.0/17 has been used to provide the IP addressing for the network shown in the topology diagram. VLSM has been used to subnet the address space incorrectly. You need to troubleshoot the addressing that has been assigned for each subnet to determine where errors exist and then determine the correct addressing assignments, where needed. Configure the devices with the correct addressing.
Task 1: Examine addressing for HQ LANs.
Step 1: Examine the addressing assignment for the HQ LAN1 subnet and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the HQ LAN1 subnet? _16,000_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _8,190_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for the HQ LAN1 subnet? _No_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. _/18 or 255.255.192.0_
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
Step 2: Examine the addressing assignment for the HQ LAN2 subnet and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the HQ LAN2 subnet? _8,000_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _16,382_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for the HQ LAN2 subnet? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. ___
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _Yes_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
_/19 or 255.255.224.0_
Task 2: Examine addressing for Branch1 LANs.
Step 1: Examine the addressing assignment for the LAN1 subnet of Branch1 and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the LAN1 subnet of Branch1? _4,000_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _4,094_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for Branch1’s LAN1 subnet? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. __
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
Step 2: Examine the addressing assignment for the LAN2 subnet of Branch1 and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for Branch1’s LAN2 subnet? _2,000_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _2,046_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for Branch1’s LAN2 subnet? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. __
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new network address that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
Task 3: Examine addressing for Branch2 LANs.
Step 1: Examine the addressing assignment for the LAN1 subnet of Branch2 and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the LAN1 subnet of Branch2? _1,000_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _254_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for Branch2’s LAN1 subnet? _No_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. _/22 or 255.255.252.0_
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
Step 2: Examine the addressing assignment for the Branch2 LAN2 subnet and answer the following questions:
1. How many IP addresses are needed for Branch2’s LAN2 subnet? _500_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _510_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for Branch2’s LAN2 subnet? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. ___
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new network address that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
______
Task 4: Examine the addressing for links between routers.
Step 1: Examine the addressing assignment for the link between the HQ and Branch1 routers and answer the following questions.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the link between the HQ and Branch1 routers?
_2_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _14_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for the link between the HQ and Branch1 routers? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. ___
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _ Yes_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
_/30 or 255.255.255.252_
Step 2: Examine the addressing assignment for the link between the HQ and Branch2 routers and answer the following questions.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the link between the HQ and Branch2 routers?
_2_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _2_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for the link between the HQ and Branch2 routers? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. ____
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _Yes_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new network address that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
_172.16.154.4_
Step 3: Examine the addressing assignment for the link between routers on Branch1 and Branch2 and answer the following questions.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for the link between the routers on Branch1 and Branch2? _2_
2. How many IP addresses are available on the currently assigned subnet? _2_
3. Will the currently assigned subnet meet the size requirement for the link between the Branch1 and Branch2 routers? _Yes_
4. If the answer to the previous question is no, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses. _______
5. Does the subnet overlap with any of the other currently assigned subnets? _No_
6. If the answer to the previous question is yes, propose a new subnet mask that allows the correct number of IP addresses without overlapping the other subnets.
_____
Task 5: Document the corrected addressing information.
Record the corrected addressing information in the Addressing Table below.
| Subnet | Number of IP addresses required | network address |
|---|---|---|
| HQ LAN1 | 16.000 | 172.16.128.0/18 |
| HQ LAN2 | 8.000 | 172.16.192.0/19 |
| Branch1 LAN1 | 4.000 | 172.16.224.0/20 |
| Branch1 LAN2 | 2.000 | 172.16.240.0/21 |
| Branch2 LAN1 | 1.000 | 172.16.248.0/22 |
| Branch2 LAN2 | 500 | 172.16.252.0/23 |
| Link from HQ to Branch1 | 2 | 172.16.254.0/30 |
| Link from HQ to Branch2 | 2 | 172.16.254.4/30 |
| Link from Branch1 to Branch2 | 2 | 172.16.254.8/30 |
